Ayushman Bharat | 21 Nov 2024
Key Points
|
About Ayushman Bharat
- Launched in 2018, Ayushman Bharat is a flagship program of the Government of India, in line with the recommendations of the National Health Policy 2017 to realize the vision of Universal Health Coverage (UHC).
- This initiative aligns with Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), aiming to improve healthcare access across primary, secondary, and tertiary levels through a comprehensive continuum-of-care approach.
- Ayushman Bharat comprises two interrelated components:
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs (formerly Health and Wellness Centres or AB-HWCs) and Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PM-JAY).
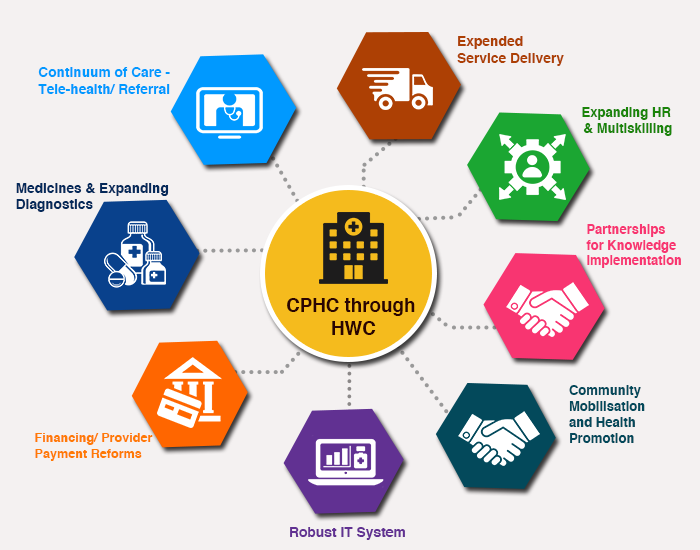
What is Ayushman Arogya Mandir (AAM)?
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs offer a wide range of healthcare services, including preventive, promotive, rehabilitative, and curative care.
- To enhance healthcare accessibility, existing Sub Health Centres (SHCs) and Primary Health Centres (PHCs), both rural and urban, are being upgraded to provide Comprehensive Primary Health Care (CPHC).
What is Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY)?
- About:
- AB PM-JAY is the world’s largest publicly funded health assurance scheme, offering up to Rs 5 lakh per family per year for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization.
- Under AB PM-JAY, there is no cap on family size, age, or gender, ensuring inclusivity for all beneficiaries.
- In addition, pre-existing diseases are covered from the very first day.
- Key Features:
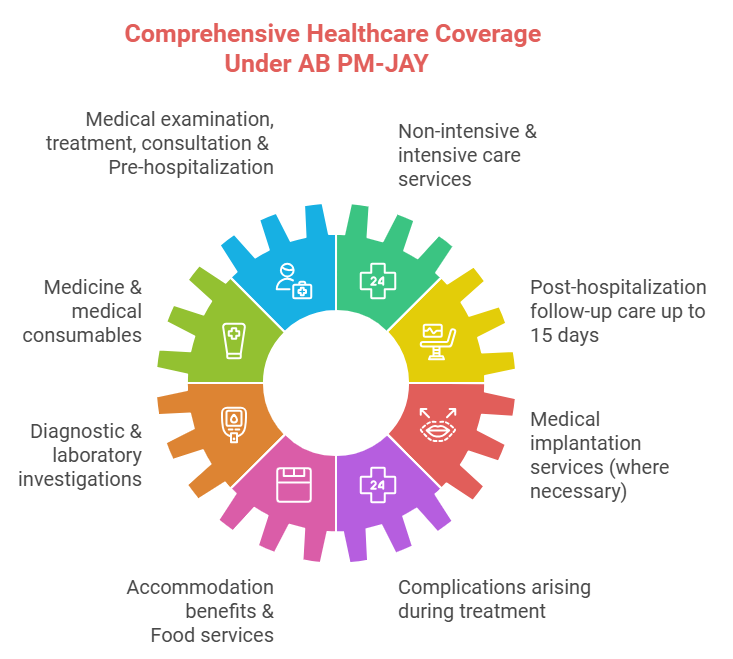
- Comprehensive Coverage: PM-JAY covers 1,949 medical procedures across 27 specialties, including free drugs, diagnostics, food, lodging, and 15 days of post-discharge medication.
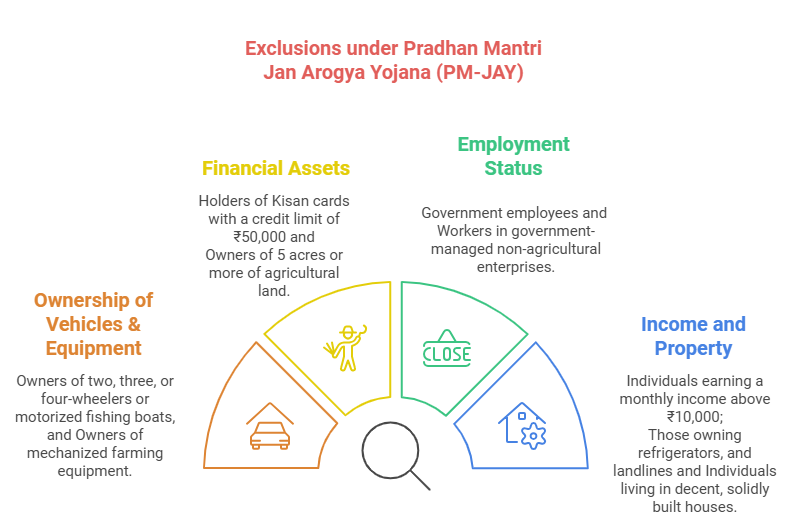
- Eligibility and Beneficiary Identification: The households included are based on the deprivation and occupational criteria of Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011 (SECC 2011) for rural and urban areas respectively.
- Eligibility for Rural Beneficiaries: PM-JAY covers families meeting at least one of six deprivation criteria, including destitute households, manual scavengers, primitive tribal groups, and legally released bonded laborers, as well as those with specific living conditions or lack of adult members.
- Eligibility for Urban Beneficiaries: PM-JAY covers beneficiaries from 11 occupational categories, including ragpickers, beggars, domestic workers, street vendors, cobblers, hawkers etc.
- Cashless and Paperless Process: Beneficiaries can receive free treatment without any out-of-pocket expenses, as the scheme employs a cashless and paperless model.
- The hospital's expenses are covered directly through the scheme, with funds transferred seamlessly to empaneled hospitals.
- Monitoring and Accountability: PM-JAY is implemented in partnership with states and Union Territories, managed by the National Health Authority (NHA).
- The National Health Authority oversees the program, setting up checks to prevent misuse, fraud, and overcharging.
- Regular audits and digital monitoring systems ensure transparency and accountability in fund utilization and service delivery.
- Comprehensive Coverage: PM-JAY covers 1,949 medical procedures across 27 specialties, including free drugs, diagnostics, food, lodging, and 15 days of post-discharge medication.
AB PM-JAY for Senior Citizens
- About:
- In 2024, the Union Cabinet approved a major expansion of the AB PM-JAY to provide all senior citizens aged 70 and above with free health insurance coverage of up to Rs 5 lakh, regardless of income.
- Key Development:
- New Distinct Card: Senior citizens aged 70 and above will receive free hospital treatment and a separate Ayushman Vaya Vandana Card under the AB PM-JAY scheme.
- Top-Up Coverage: Senior citizens within AB PM-JAY-covered families will get an additional top-up of up to Rs 5 lakh per year, exclusive to them, without sharing with other family members under 70.
- Family Coverage: Senior citizens not covered under an existing AB PM-JAY family plan will receive up to Rs 5 lakh per year on a family basis.
- Choice of Schemes: Senior citizens already enrolled in other public health schemes can choose to continue with their current scheme or switch to AB PM-JAY.
- Eligibility with Private Insurance: Senior citizens with private health insurance or coverage under the Employees' State Insurance scheme are also eligible for benefits under AB PM-JAY.
What are Other Initiatives to Support Ayushman Bharat?
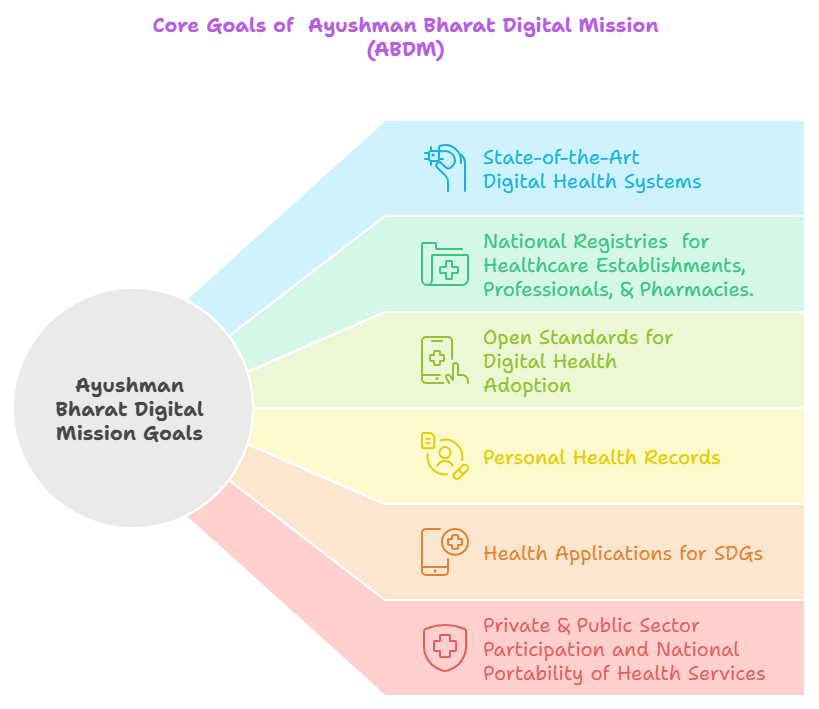
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM):
- About: Launched in 2021, the ABDM aims to create a digital health infrastructure for India, enabling a seamless exchange of health data and enhancing accessibility, equity, and the quality of healthcare services.
- Components of ABDM:
- ABHA Number (Unique Health ID): ABDM’s key initiative is the creation of Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA), which provides a unique 14-digit number to each citizen, simplifying the access and sharing of health records.
- It ensures secure and accurate health data, collecting demographic and contact details, with easy updates.
- ABHA Mobile App (Personal Health Record - PHR): The ABHA app enables users to create an ABHA address, link health records, and manage consent for data sharing.
- Other Components: The Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR) is a digital platform connecting healthcare professionals to India's healthcare ecosystem, while the Health Facility Registry (HFR) catalogs healthcare facilities to enhance service coordination and integration.
- ABHA Number (Unique Health ID): ABDM’s key initiative is the creation of Ayushman Bharat Health Accounts (ABHA), which provides a unique 14-digit number to each citizen, simplifying the access and sharing of health records.
- Technological Support: Leverages India’s existing digital infrastructure (Aadhaar, UPI, JAM trinity) for identity verification, electronic transactions, and secure storage of health data.
- Uses emerging technologies like AI, IoT, Blockchain, and cloud computing to enhance the digital health ecosystem.
- Significance:
- The strong digital infrastructure supports the streamlined management of health records and services, enabling paperless transactions and secure healthcare management.
- The integration with existing platforms like AB-PMJAY ensures a seamless health service experience.
- Ayushman Bhav Campaign
- About:
- The Ayushman Bhav campaign was launched in 2023 with the objective to provide comprehensive healthcare coverage across India, ensuring every individual in rural and urban areas has access to essential health services.
- This initiative, aligned with the Ayushman Bharat program, focuses on achieving UHC through a whole-of-nation approach, involving government sectors, civil society, and communities.
- Key Components of the Campaign Include:
- Ayushman Apke Dwar 3.0: Providing Ayushman cards to eligible beneficiaries under PM-JAY.
- Ayushman Melas: Held at Health and Wellness Centres (HWCs) and Community Health Centres (CHCs), offering health services, ABHA ID creation, and teleconsultation with specialists.
- Ayushman Sabhas: Community gatherings in villages and Panchayats to distribute Ayushman cards, generate ABHA IDs, and raise awareness about health schemes and diseases.
- About:
Achievements of Ayushman Bharat
- AB PM-JAY: As of September 2024, AB PM-JAY has significantly enhanced healthcare accessibility across India, with over 35.4 crore Ayushman cards issued.
- The scheme is operational in 33 States and Union Territories, excluding NCT Delhi, West Bengal, and Odisha.
- Key Achievements Include:
- Hospital Admissions: Rs 1,07,125 crores in financial coverage for 7.79 crore hospital admissions.
- Gender Equity: 49% of Ayushman cards have been issued to women, with 3.61 crore women utilizing hospital admissions.
- Portability: 11.9 lakh hospitalizations worth Rs 3,100 crores authorized under the portability feature, enabling beneficiaries to access treatment anywhere in India.
- Wide Network: 30,529 hospitals empanelled, including 17,063 public and 13,466 private hospitals, ensuring extensive healthcare coverage nationwide.
- Ayushman Arogya Mandirs: As of September 2024, there were a total of 1,74,453 Ayushman Arogya Mandirs operating across the country.
- Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM): As of September 2024, ABDM has achieved significant milestones, including the creation of 66.70 crore ABHA accounts and the linking of 42.01 crore health records to these accounts.