International Relations
NATO's 75th Anniversary
- 04 Apr 2024
- 17 min read
This editorial is based on “West Against the Rest” which was published in Indian Express on 04/04/2024. The article examines NATO's 75th anniversary and its role as a tool for maintaining Western hegemony through its military capabilities, along with other significant aspects related to the alliance.
For Prelims: Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe, NATO (North Atlantic Treaty Organization), Cold War, Warsaw Pact, World War II, The North Atlantic Treaty, Finland, Ukraine
For Mains: Challenges in the functioning of NATO, NATO’s significance for the West.
The North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) pompously celebrated the anniversary of its establishment on April 4, 75 years ago. On this day in 1949, western nations gathered in Washington, DC, to commit their nations to one another’s defence. With the scars of the Second World War still raw and new threats looming, they pledged to safeguard the freedom of their peoples. Key areas of focus for NATO's 75th anniversary are recommitting to the alliance's core values of democracy, freedom and rule of law, addressing evolving security challenges like Russia's invasion of Ukraine, and charting the course for NATO's future adaptation.
What is NATO?
- About:
- The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is an intergovernmental military alliance formed in 1949. It was established with the primary goal of providing collective defence against potential aggression, particularly from the Soviet Union during the Cold War era. Over the years, NATO has evolved to address a range of security challenges beyond its original mandate.
- History:
- Formation: NATO was established on April 4, 1949, with the signing of the North Atlantic Treaty in Washington, D.C. by 12 founding member countries from Europe and North America.
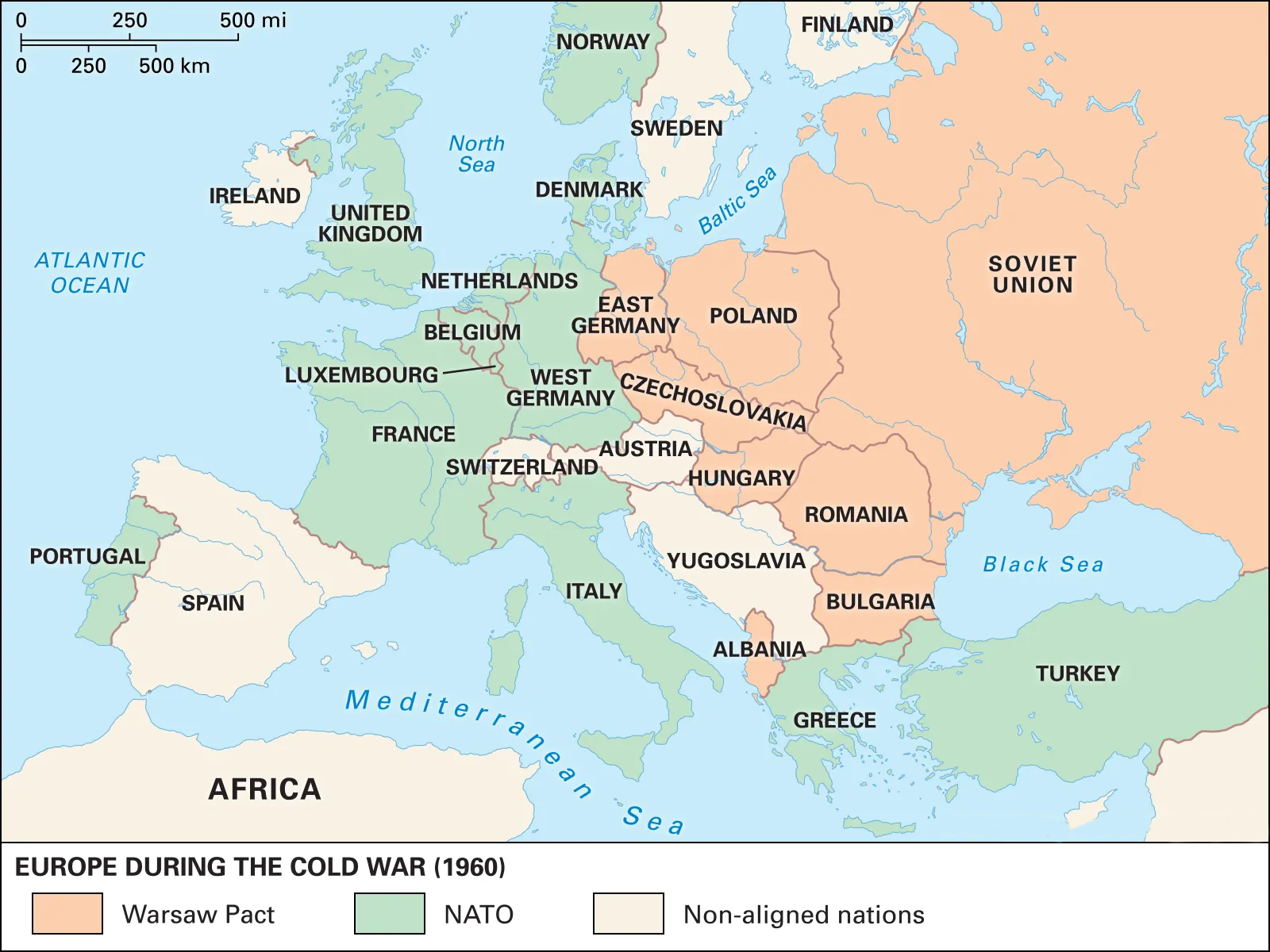
- Cold War Era: During the Cold War, NATO served as a deterrent against Soviet expansionism, with the US providing significant military support to its European allies.
- Post-Cold War: After the collapse of the Soviet Union, NATO expanded its focus to include crisis management, conflict prevention, and cooperative security efforts.
- Membership:
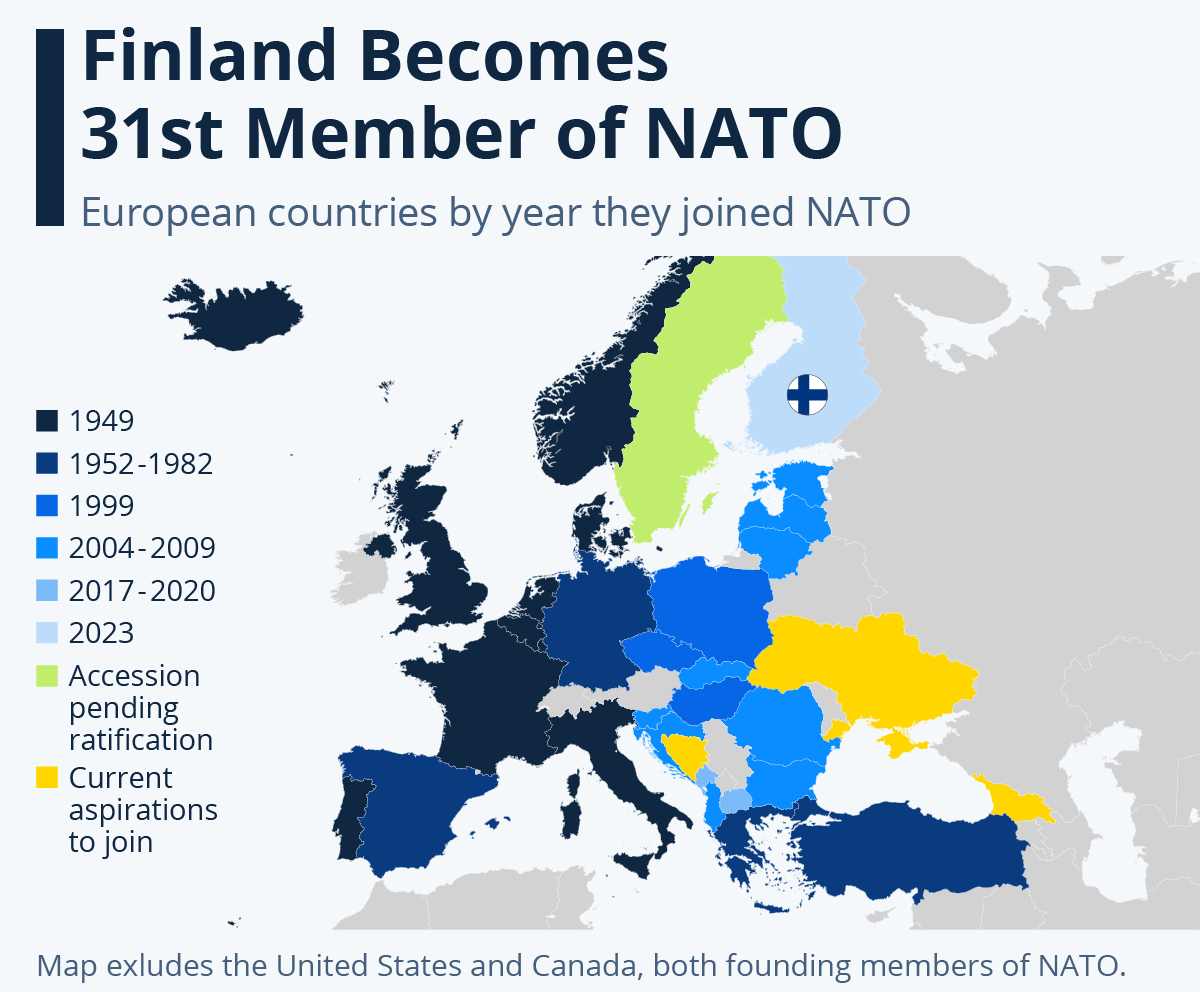
- Original Members: The original 12 founding members of NATO were Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
- Expansion: NATO has expanded since its founding, with new member countries joining in multiple rounds. The alliance currently consists of 32 member countries.
- Mission and Objectives:
- Collective Defence: NATO's primary mission is collective defence, as outlined in Article 5 of the North Atlantic Treaty. This article stipulates that an attack on one member country will be considered an attack on all, and the members will respond collectively.
- Crisis Management: In addition to collective defence, NATO engages in crisis management activities, including conflict prevention, peacekeeping, and stabilisation efforts in various regions around the world.
- Structure:
- Political Leadership: The North Atlantic Council (NAC) serves as NATO's principal political decision-making body, composed of ambassadors from all member countries.
- Military Command Structure: NATO's military command structure includes Strategic Commands (e.g., Allied Command Operations) responsible for operational planning and execution, as well as Regional Commands and Force Headquarters.
- Integrated Military Forces: NATO maintains integrated military forces, allowing member countries to contribute personnel and assets to collective defence efforts under NATO command.
What are the Various Concerns Related to NATO’s Functioning?
- Unrestrained Offensive:
- NATO was created to defend its member states from aggression. As the facts go, it never suffered from one or the threat of one. On the contrary, in the name of defending its member states, NATO went on the offensive. Over the last seven decades, it initiated or participated in more than 200 military conflicts worldwide, including 20 major ones.
- Misadventures in Eastern European, Middle East and Asian Countries:
- The bombing of Yugoslavia, the invasion of Iraq, the ruined statehood of Libya, the unlawful military interference in Syria and the dubious results of combating terrorism in Afghanistan are the most prominent among numerous cases in point.
- Provoking Russia-Ukraine War:
- Five waves of the alliance’s expansion since 1991 despite assurances about the contrary and the transformation of Ukraine into the springboard against Russia have become the greatest provocation of all time.
- The alliance dismantled dialogue mechanisms with Russia and adopted the Strategic Concept at the 2022 NATO summit in Madrid by which Moscow is proclaimed to be the most significant and direct threat to allied security, peace and stability in the Euro-Atlantic, which Russia has never been.
- Maintaining Western Hegemony:
- The stark reality is that NATO, while proclaiming its peaceful aspirations, go in for war or threaten to attack any state that refuses to accept the decadent liberal “rules-based order”.
- In this sense, NATO’s military potential stands as an effective tool for maintaining the West’s hegemony over the nations that are not viewed as a military menace.
- This sets a notion of NATO being a continuation of colonial practices in a modern form under the slogans of democracy, human rights and freedom as prescribed by the Euro-Atlantic rulers.
- The stark reality is that NATO, while proclaiming its peaceful aspirations, go in for war or threaten to attack any state that refuses to accept the decadent liberal “rules-based order”.
- Unwarranted Expansion:
- The coalition’s capabilities are being built up in outer- and cyberspace. NATO’s “eastern flank” is pumped with new assets and forces to gear up for the adjusted regional military plans. NATO’s aggressive behaviour expands beyond Russia. The search is on for new partners in Africa, Asia and Latin America.
- NATO's radar has turned towards the post-Soviet space and Eurasia at large to create more alienation lines and damage the traditionally close ties between countries.
- Capitalising the Threat Posed in The Indo-Pacific:
- A new manifestation of the block’s expansionism can be seen in NATO’s attempts to extend its responsibility over the entire eastern hemisphere under the slogan of indivisibility of security in the Euro-Atlantic and Indo-Pacific regions.
- To this end, the US has been busy creating pocket minilateral formats, such as AUKUS, US-Japan-South Korea troika, and the Tokyo-Seoul-Canberra-Wellington quartet to drag them into practical cooperation with NATO.
What were the Successes And Failures of NATO Grouping?
- Successes:
- The Cold War:
- During the Cold War, NATO’s efforts were centred around three goals: controlling the Soviet Union, dissuading militant nationalism and communism across Europe, and establishing greater European political unity.
- The alliance played a major role in maintaining the tense peace of the Cold War and ensuring the war remained ‘cold’. With the end of the war, NATO worked to further maintain peace.
- They established the North Atlantic Cooperation Council and, in 1997, NATO encouraged bilateral discussion between the US and Russia through the Founding Act.
- Modern Day Protection:
- Today, NATO continues to provide a level of protection for its members. Since its founding, a NATO member has only been attacked and evoked Article 5 once (the US after 9/11).
- Member countries are afforded collective security, just as NATO originally sought to do. Additionally, NATO has created a global network of more than 40 countries and other partners around the globe - ranging from the African Union to the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe (OSCE).
- This network provides NATO support in its crisis management operations, ranging from aid operations such as its delivery of relief supplies after the 2005 Kashmir Earthquake to counter-terrorism operations in the Mediterranean and the coast of Somalia.
- Providing Humanitarian Aid to Ukraine:
- NATO has publicly denounced the Russian invasion of Ukraine and NATO member countries and allies have provided substantial aid to Ukraine. The US has contributed roughly USD 54 billion to Ukraine.
- Other countries have provided humanitarian aid and support for the more than 5 million refugees of the war. The Ukraine war has reaffirmed the importance of NATO, and even spurred Finland and Sweden to increase their efforts to join the alliance.
- These countries’ membership would strengthen the alliance militarily through increased air and submarine capabilities, allowing for NATO to further dissuade Russian aggression.
- The Cold War:
- Failures:
- Funding Issues:
- In 2006, NATO Defense Ministers agreed to a commitment that 2% of their countries’ GDP would be allocated towards defence spending. However, the majority of NATO members do not meet this goal. Currently, the US accounts for over 2/3rd of the alliance’s defence spending.
- Afghanistan:
- After 9/11, NATO was a considerable presence in Afghanistan, and their forces were crucial in their support of the Afghan government. When President Donald Trump signed an agreement with the Taliban in 2020, both NATO and American troops were withdrawn from Afghanistan.
- What followed was an immediate fall in the Afghan government at the hands of the Taliban. Despite the two decades NATO spent in Afghanistan, no long term solution was reached, and without their presence, the nation’s former government could not survive.
- Right-Wing Nationalism:
- With the spread of right-wing nationalism across Europe, discontent with international institutions like NATO and the EU grows. If right-wing nationalist movements continue to increase in popularity across Europe, there could be increased calls for countries to leave institutions like NATO. The challenge NATO faces now is how to combat and address their criticism, and how to unify a divided Europe.
- Russian Aggression:
- Despite supposed verbal promises to Russia that it would not expand to the east, NATO has admitted several former Warsaw Pact members since the fall of the Soviet Union.
- Now, with NATO members bordering Russia and the promise of further expansion, Russia feels increasingly threatened. The possibility of Ukraine joining NATO has been cited as a significant reason for Russian actions in the Russia-Ukraine Conflict.
- Funding Issues:
Note:
- India maintains a nuanced stance between NATO and Russia, balancing strategic interests with both while emphasising non-alignment and bilateral cooperation in defence and economic spheres.
What are the Reforms Required to Make NATO More Effective and Efficient?
- The Quality, Coherence and Timelines of Advice:
- Enhance the importance and functions of the five main policy committees within NATO, including the Military Committee, Political Committee, Policy Coordination Group, Executive Working Group, and Senior Resource Board.
- Improve coordination among these committees, aligning their agendas with the Council's priorities. This will help translate the Council's guidance into effective and timely advice for both military and civilian NATO bodies.
- NATO’s Non-Military Dimension:
- Ensure that, when the allies decide to engage the Alliance operationally, it benefits from the civil expertise at the political level and capacity on the ground necessary to complete its mandate successfully, in concert with other international organisations and local actors; this may require the creation of a civil security committee or an analogous structure.
- Organisational Cohesion and Internal Synergy:
- Orient not only NATO headquarters but a streamlined set of NATO bodies in and outside of Brussels, to deliver against a rolling set of strategic-level priorities, to enhance transparency, visibility and commonality of purpose across the Alliance.
- An Inclusive and United Alliance:
- Institutional arrangements should mirror the inseparability of Alliance security, aiming to uphold and reinforce allied unity and cohesion, and foster a shared sense of purpose.
- Therefore, NATO structures and procedures must primarily unite the interests, concerns, political will, and military capabilities of all allies, enabling the consensus-building and collective actions.
- Wherever possible, structures and procedures should encourage and facilitate political dialogue, consultation, combined planning, training, exercising and operations between the allies and an increasing number of non-NATO nations.
- Institutional arrangements should mirror the inseparability of Alliance security, aiming to uphold and reinforce allied unity and cohesion, and foster a shared sense of purpose.
- The Alliance Must Remain Distinct:
- While NATO should actively integrate with other international organisations to address complex crises through a Comprehensive Approach, this should not diminish its core strength of combining robust military capabilities with nuanced strategies.
- Focus on Non-Traditional Threats:
- While territorial defence remains a core task, many argue NATO must further adapt to address non-traditional threats like terrorism, cyber attacks, disinformation campaigns, and threats to supply chain security.
Conclusion
As NATO celebrates its 75th anniversary in 2024, the alliance stands at a crucial juncture in its storied history. NATO has successfully upheld its core mission of safeguarding the freedom and security of its members through a rules-based international order. However, the past decades have borne witness to a rapidly evolving global security landscape characterised by the resurgence of great power rivalries, transnational threats, and complex modern challenges.
To remain an effective bulwark of peace and stability, NATO must continue to adapt and reform itself through greater investment in defence capabilities, streamlined decision-making processes, and a broadened focus on emerging arenas like cyber, space, and technological superiority.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Evaluate the impact of NATO expansion on global security dynamics and its implications for non-NATO countries. Also discuss the role of NATO in contemporary geopolitics and its significance for India's strategic interests. |