Five Years of AB-PMJAY | 09 Aug 2023
This editorial is based on Five years of Ayushman Bharat which was published in The Indian Express on 09/08/2023. It talks about the achievements and challenges of Ayushman Bharat health scheme.
For Prelims: Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana, Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission, Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission , Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY Startup Grand Challenge, Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY Awards, Comptroller and Auditor General of India, Sustainable Development Goal 3.8.
For Mains: Challenges and Achievements of Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana
Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY) is a flagship health protection scheme launched by the Government of India in 2018. It aims to provide universal health coverage to the poor and vulnerable sections of society by ensuring access to quality healthcare services agnostic of economic status. It has the potential to transform the healthcare landscape of the country by reducing poverty, enhancing productivity, and promoting social justice.
What are the Main Objectives of AB-PMJAY?
- To reduce the financial burden of out-of-pocket expenditure (OOPE) on healthcare for the beneficiaries.
- To improve the access and affordability of healthcare services for the beneficiaries.
- To enhance the quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery systems in the country.
- To promote preventive, promotive, and curative health interventions for the beneficiaries.
What are the Key Features of AB-PMJAY?
- Health Cover:
- The scheme provides a health cover of Rs 5 lakh per family per year for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization to more than 12 crore families (bottom 40% of the population).
- Packages:
- The scheme covers medical and surgical procedures for almost all health conditions through a comprehensive list of 1,949 packages, including cancer care, cardiac care, neurosurgery, orthopedics, burns management, mental disorders, etc.
- Funding:
- The scheme is a centrally sponsored scheme, which means that it is funded by both the central and state governments.
- The funding ratio is 60:40 for most states, 90:10 for northeastern states and Himalayan states, and 100:0 for union territories without a legislature.
- The scheme is a centrally sponsored scheme, which means that it is funded by both the central and state governments.
- IT Platform:
- The scheme uses a robust IT platform to ensure seamless delivery of services and prevent fraud and abuse.
- The platform includes features such as beneficiary identification system, hospital empanelment module, transaction management system, claim management system, grievance redressal mechanism, etc.
- Hospitals:
- The scheme has a network of more than 27,000 empanelled hospitals across the country, out of which more than half are private hospitals.
- The scheme also encourages public-private partnership models such as trust-based models, insurance-based models, or hybrid models for effective implementation.
- The scheme has a network of more than 27,000 empanelled hospitals across the country, out of which more than half are private hospitals.
- Portability:
- The scheme has an interstate portability feature, which means that a beneficiary registered in one state can avail services in any other state that has an AB-PMJAY programme.
- This has proved helpful to migrants, especially in emergencies.
- The scheme has an interstate portability feature, which means that a beneficiary registered in one state can avail services in any other state that has an AB-PMJAY programme.
- Arogya Mitras:
- The scheme has a dedicated workforce of Pradhan Mantri Arogya Mitras (PMAMs) who guide and assist the beneficiaries at every step of their journey under the scheme.
- They are responsible for beneficiary verification, registration, pre-authorisation, claim submission, etc.
- The scheme has a dedicated workforce of Pradhan Mantri Arogya Mitras (PMAMs) who guide and assist the beneficiaries at every step of their journey under the scheme.
- Monitoring and Evaluation:
- The scheme has a monitoring and evaluation mechanism to ensure accountability and transparency.
- The scheme has a public dashboard where the implementation details can be tracked on a day-to-day basis.
- The scheme also publishes the details of beneficiaries who have availed treatment under the scheme without compromising their privacy.
- The claim processing is completely faceless.
- Anti-fraud:
- The scheme has a National Anti-Fraud Unit (NAFU) that designs, implements and oversees anti-fraud initiatives.
- There are also Anti-Fraud Units at the state level.
- The NAFU uses Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) technologies to detect suspicious transactions/potential frauds.
- The NAFU also conducts desk and field audits (including surprise ones) to check abuse.
- More than 210 hospitals have been de-empanelled for fraud or malpractice.
- The scheme has a National Anti-Fraud Unit (NAFU) that designs, implements and oversees anti-fraud initiatives.
- Call Centre:
- The scheme has a call center that makes calls to every beneficiary who has availed treatment within 48 hrs of discharge to verify the quantity and quality of the treatment.
- Another call is made after 15 days to know about the prognosis.
- The scheme has a call center that makes calls to every beneficiary who has availed treatment within 48 hrs of discharge to verify the quantity and quality of the treatment.
What are the Achievements of AB-PMJAY?
- Coverage:
- As AB-PMJAY completes its fifth year, it has covered more than 15.5 crore families (about 50 crore beneficiaries) with a health cover of Rs 5 lakh per family per year for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization.
- Eleven states/UTs have pushed for 100% coverage of their respective population.
- As AB-PMJAY completes its fifth year, it has covered more than 15.5 crore families (about 50 crore beneficiaries) with a health cover of Rs 5 lakh per family per year for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization.
- Savings:
- The scheme has catered to more than 5.39 crore admission events worth Rs 66,284 crore in the last five years.
- If the beneficiaries had availed the same care outside AB-PMJAY’s ambit, the total cost of treatment would have been nearly two times higher.
- This has resulted in savings of more than Rs 1 lakh crore for the beneficiaries.
- Impact:
- The scheme has reduced the Out of Pocket Expenditure(OOPE) of the beneficiaries by 60 % and increased their access to tertiary care by 65 %.
- The scheme has also improved the health-seeking behavior and satisfaction of the beneficiaries.
- The scheme has reduced the Out of Pocket Expenditure(OOPE) of the beneficiaries by 60 % and increased their access to tertiary care by 65 %.
- Quality and efficiency:
- The scheme has enhanced the quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery systems in the country by introducing standard treatment protocols, quality certification, and performance-based incentives for the empanelled hospitals.
- The scheme has also increased the bed occupancy rate and revenue generation of the public hospitals.
- The scheme has enhanced the quality and efficiency of healthcare delivery systems in the country by introducing standard treatment protocols, quality certification, and performance-based incentives for the empanelled hospitals.
- Innovations and initiatives:
- The scheme has launched several innovations and initiatives to enhance the quality and accessibility of healthcare services.
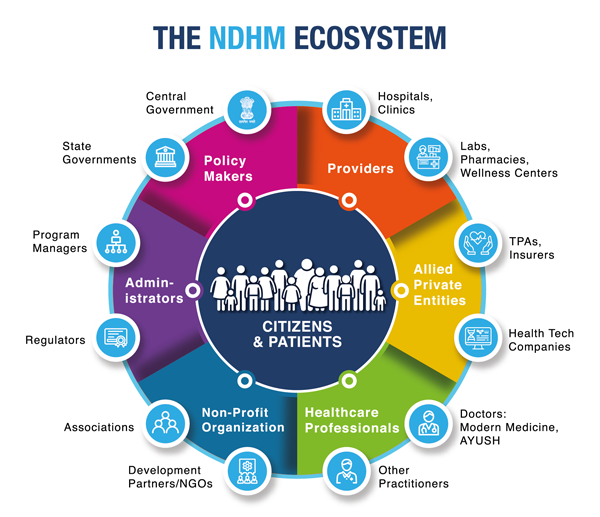
- Some of these are Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM), Ayushman Bharat Health Infrastructure Mission (ABHIM), Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY Startup Grand Challenge, Ayushman Bharat PM-JAY Awards, etc.
- Inclusivity:
- The scheme has stayed true to its promise of inclusivity by adding people from the transgender community to its list of beneficiaries.
- Around 50 packages were designed specifically for the community, including packages on Sex Reassignment Surgery (SRS).
What are the Challenges of AB-PMJAY?
- Lack of Awareness:
- The scheme faces a low awareness level among the potential beneficiaries, especially in rural areas.
- Many eligible beneficiaries are not aware of their entitlements or how to avail them.
- There is a need to increase the outreach and communication efforts of the scheme to create more awareness and demand.
- The scheme faces a low awareness level among the potential beneficiaries, especially in rural areas.
- Supply-Side Constraint:
- The scheme faces a supply-side constraint due to the uneven distribution and availability of healthcare infrastructure and human resources in the country.
- Many states have a shortage of empanelled hospitals, especially in remote and tribal areas.
- Reimbursement Issues:
- The scheme faces a challenge of ensuring timely and adequate reimbursement of claims to the empanelled hospitals, especially private ones.
- Many hospitals have complained of delayed payments, low package rates, high denial rates, and cumbersome processes.
- There is a need to streamline and expedite the claim settlement process and revise the package rates periodically to ensure sustainability and viability of the scheme.
- Fraud and Abuse:
- The scheme faces a challenge of preventing and detecting fraud and abuse by some unscrupulous elements who try to exploit the scheme for personal gain.
- Recently, the Comptroller and Auditor General of India has revealed that nearly 7.5 lakh beneficiaries were linked to a single cell phone number(9999999999).
- There is a need to strengthen the anti-fraud mechanisms and take strict action against those who indulge in fraud or malpractice under the scheme.
What are the Future Prospects of AB-PMJAY?
- Transformation:
- The scheme has a potential to transform the healthcare landscape of the country by providing universal health coverage to half of India’s population.
- The scheme can also contribute to achieving the Sustainable Development Goal 3.8, which envisions universal health coverage for all by 2030.
- Integration:
- The scheme can also act as a catalyst for strengthening the primary healthcare system in the country by linking it with the secondary and tertiary care system.
- The scheme can also leverage the potential of digital health technologies to improve access, affordability, and quality of healthcare services.
- Development:
- The scheme can also create a positive impact on the socio-economic development of the country by reducing poverty, enhancing productivity, and promoting social justice.
- The scheme can also generate employment opportunities and stimulate economic growth in the health sector.
What are Some Recommendations for Improving AB-PMJAY?
- Provision of Ayushman Card:
- The scheme should aim to provide every possible beneficiary with an Ayushman Card, which can act as a pre-paid card worth Rs 5 lakh that can be used to avail free treatment at any empanelled hospital.
- This can reduce the hassle and delay in beneficiary identification and verification.
- The scheme should aim to provide every possible beneficiary with an Ayushman Card, which can act as a pre-paid card worth Rs 5 lakh that can be used to avail free treatment at any empanelled hospital.
- Scope:
- The scheme should expand its scope and coverage by including more health conditions, procedures, and services under its ambit.
- The scheme should also consider covering outpatient care, diagnostics, medicines, etc., which constitute a major part of OOPE for many beneficiaries.
- The scheme should expand its scope and coverage by including more health conditions, procedures, and services under its ambit.
- Convergence:
- The scheme should enhance its coordination and convergence with other health schemes and programmes at the central and state levels to avoid duplication, fragmentation, and confusion.
- The scheme should also foster collaboration and partnership with various stakeholders such as civil society organizations, academic institutions, private sector entities, etc., to leverage their expertise and resources.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Critically analyze the achievements and challenges of Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY) in providing universal health coverage to the poor and vulnerable sections of society. Suggest some measures to improve the implementation and impact of the scheme. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year’s Question (PYQs)
Mains:
Q. Professor Amartya Sen has advocated important reforms in the realms of primary education and primary health care. What are your suggestions to improve their status and performance?