Important Facts For Prelims
Xenotransplantation
- 08 Nov 2022
- 2 min read
Why in News?
Genetically modified pig heart took longer than usual to beat for human receiver in the first-ever transplant of the gene-edited pig heart to human. The human recipient lived only for 61 days after the transplant.
- Prior attempts at such transplants have also failed.
What is Xenotransplantation?
- About:
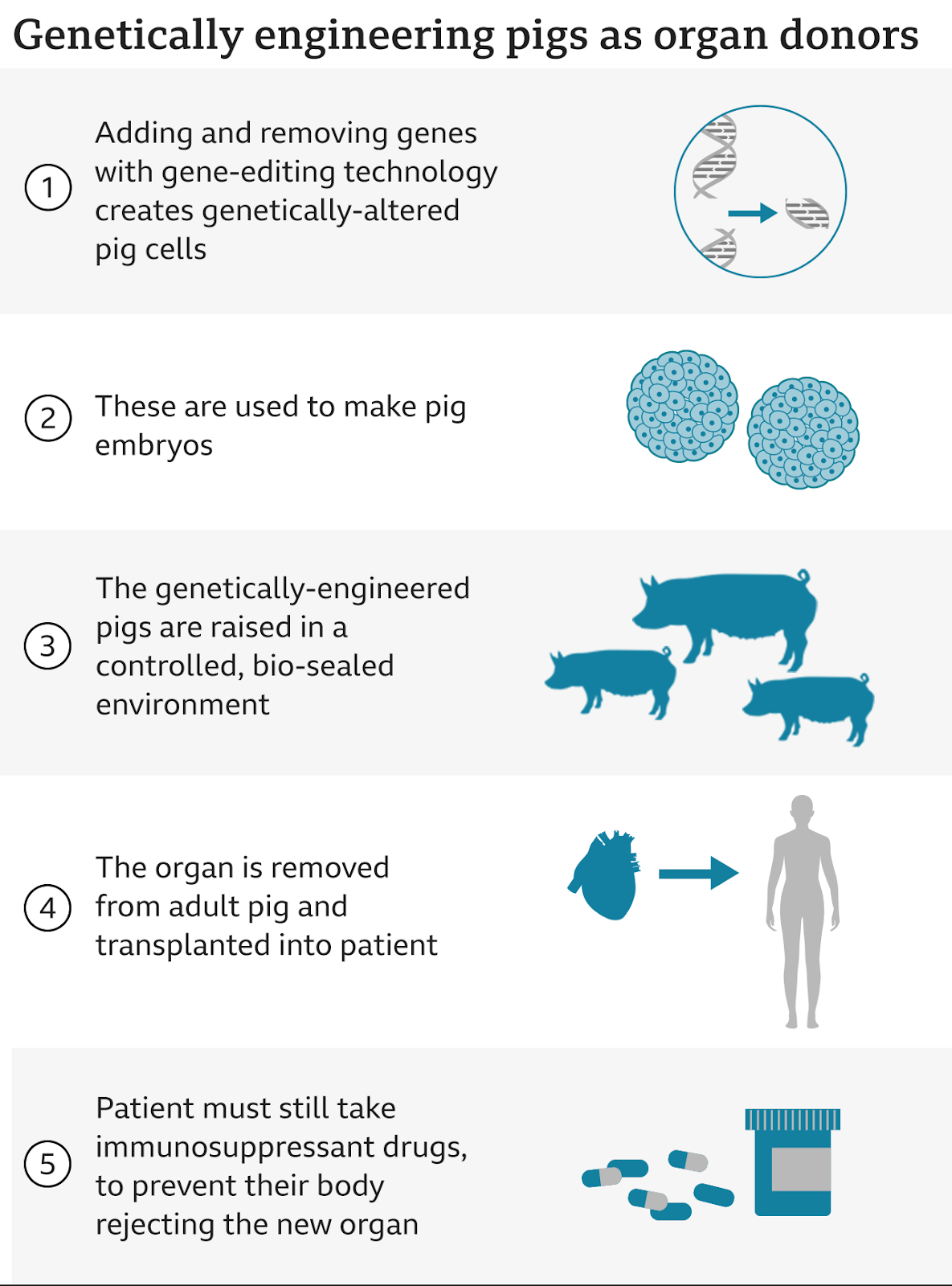
- Xenotransplantation involves the transplantation of nonhuman tissues or organs into human recipients.
- In the recent heart transplant from pig to human, gene-editing was adopted to remove a sugar in its cells that’s responsible for that hyper-fast organ rejection.
- Genome editing (also called gene editing) is a group of technologies that give scientists the ability to change an organism's Deoxy-Ribonucleic Acid (DNA).
- In the recent heart transplant from pig to human, gene-editing was adopted to remove a sugar in its cells that’s responsible for that hyper-fast organ rejection.
- One of the biggest obstacles to transplantation is organ rejection.
- Xenotransplantation involves the transplantation of nonhuman tissues or organs into human recipients.
- Significance:
- This development could bring us one step closer to solving the global organ shortage.
- In India, patients need 25,000-30,000 liver transplants annually. But only about 1,500 end up receiving them.
- Pigs are increasingly becoming popular candidates for organ transplantation.
- Pigs offer advantages over primates for organ procurements, because they are easier to raise and achieve adult human size in six months.
- The pig’s anatomical and physiological parameters are similar to that of humans, and the breeding of pigs in farms is widespread and cost-effective.
- Pigs offer advantages over primates for organ procurements, because they are easier to raise and achieve adult human size in six months.
- This development could bring us one step closer to solving the global organ shortage.