Social Issues
World Leprosy Day
- 02 Feb 2024
- 6 min read
For Prelims: World Leprosy Day, Leprosy, Mahatma Gandhi, National Strategic Plan (NSP) & Roadmap for Leprosy, National Leprosy Eradication Programme (NLEP)
For Mains: Initiatives Related to Health, Leprosy and Associated Social Stigma.
Why in News?
World Leprosy Day is observed every year on the last Sunday of January. In India, it is observed on 30th January every year, coinciding with the death anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi.
What is the Purpose of World Leprosy Day Observation?
- The theme for World Leprosy Day 2024 is “Beat Leprosy”. This theme encapsulates the dual objectives of the day: to eradicate the stigma associated with leprosy and to promote the dignity of people affected by the disease.
- The primary objective of the day is to raise awareness among the general public about the stigma associated with leprosy.
- Educating people that leprosy is caused by a specific bacteria and is easily treatable forms a crucial part of the awareness campaign.
What is Leprosy?
- About:
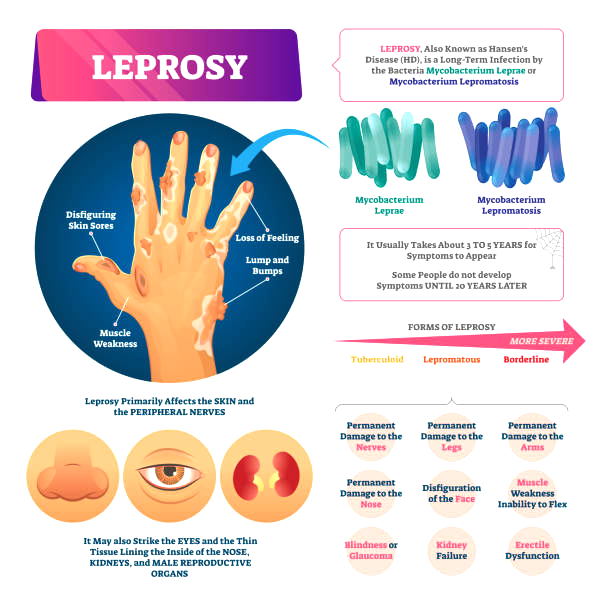
- Leprosy, also known as Hansen’s disease, is a chronic infectious disease caused by a type of bacteria called “Mycobacterium leprae”.
- The disease affects the skin, the peripheral nerves, mucosal surfaces of the upper respiratory tract and the eyes.
- Leprosy is known to occur at all ages ranging from early childhood to old age.
- Leprosy is not inherited, but it is transmitted via droplets, from the nose and mouth, during close and frequent contact with untreated cases.
- Classification:
- Paucibacillary (PB) and multibacillary (MB) are classifications of leprosy.
- PB leprosy includes all smear-negative cases (smaller bacterial load), while MB leprosy includes all smear-positive (more infectious compared to smear-negative PTB) cases.
- Paucibacillary (PB) and multibacillary (MB) are classifications of leprosy.
- Treatment:
- Leprosy is curable and treatment during early stages can prevent disability.
- The currently recommended treatment regimen consists of three drugs: dapsone, rifampicin and clofazimine. The combination is referred to as multi-drug therapy (MDT).
- MDT has been made available through the World Health Organization (WHO) free of cost to all patients worldwide since 1995.
- Leprosy is curable and treatment during early stages can prevent disability.
- Global Burden of Leprosy:
- Leprosy is a neglected tropical disease (NTD) that still occurs in more than 120 countries, with more than 200,000 new cases reported every year.
- In 2022, 182 countries reported over 1.65 lakh cases of leprosy, including 174,087 new cases.
- According to the WHO, most countries with high rates of new leprosy cases are in the WHO African and South-East Asia Regions.
- India and Leprosy:
- India has achieved the elimination of leprosy as a public health problem as per WHO criteria of less than 1 case per 10,000 population at the National level in 2005.
- Leprosy is endemic in several states and union territories of India.
- The prevalence rate of leprosy is 0.4 per 10,000 population in the country.
- India has achieved the elimination of leprosy as a public health problem as per WHO criteria of less than 1 case per 10,000 population at the National level in 2005.
- Initiatives Taken:
- Global:
- The Global Leprosy Strategy:
- In 2016 WHO launched the Global Leprosy Strategy 2016–2020, which aims to reinvigorate efforts to control leprosy and avert disabilities, especially among children still affected by the disease in endemic countries.
- Global Partnership for Zero Leprosy (GPZL):
- The Global Partnership for Zero Leprosy is a coalition of individuals and organizations committed to ending leprosy.
- World Leprosy Day.
- The Global Leprosy Strategy:
- India:
- National Strategic Plan (NSP) & Roadmap for Leprosy (2023-27):
- It is launched to achieve zero transmission of leprosy by 2027 i.e. three years before the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3.3.
- SDG 3.3 is by 2030, to end the epidemics of AIDS, tuberculosis, malaria and neglected tropical diseases and combat hepatitis, water-borne diseases and other communicable diseases.
- It is launched to achieve zero transmission of leprosy by 2027 i.e. three years before the Sustainable Development Goal (SDG) 3.3.
- National Leprosy Eradication Programme (NLEP):
- The NLEP is a Centrally Sponsored Health Scheme introduced in 1983 and it has been implemented with the major objective of reducing the disease burden, prevention of disability and improving awareness among the masses about Leprosy and its curability.
- National Strategic Plan (NSP) & Roadmap for Leprosy (2023-27):
- Global:
Neglected Tropical Diseases (NTDs)
- NTDs are a diverse group of conditions caused by a variety of pathogens (including viruses, bacteria, parasites, fungi and toxins) and associated with devastating health, social and economic consequences.
- NTDs are most common among marginalized communities in the developing regions of Africa, Asia and the Americas.
- It is estimated that NTDs affect more than 1 billion people, while the number of people requiring NTD interventions (both preventive and curative) is 1.6 billion.
- Few examples of NTDs include: Buruli ulcer; Chagas disease; dengue chikungunya; and lymphatic filariasis.
Mahatma Gandhi’s Death Anniversary 2024
- January 30th marks the death anniversary of Mahatma Gandhi who was assassinated on this day by Nathuram Godse in 1948.
- Gandhi's campaign for leprosy saved innumerable lives of lepers and improved their condition in India.
Read More: Martyrs' Day
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. Appropriate local community-level healthcare intervention is a prerequisite to achieving ‘Health for All’ in India. Explain. (2018)

.png)





-min.jpg)