World Heritage Day 2025 | 21 Apr 2025
Why in News?
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has declared free entry to its protected monuments on International Day for Monuments and Sites (World Heritage Day) on 18th April 2025.
What is World Heritage Day?
- It is a day observed globally to promote awareness about the importance of cultural heritage and the need to preserve it. It was declared by the International Council on Monuments and Sites (ICOMOS) in 1982 and later approved by UNESCO in 1983.
- The theme for 2025 is “Heritage under Threat from Disasters and Conflicts: Preparedness and Learning from 60 Years of ICOMOS Actions”.
What are World Heritage Sites?
- About: World Heritage Sites (WHS) are locations recognized for their outstanding universal value to humanity and are inscribed on the World Heritage List for protection and preservation for future generations.
- These sites may be cultural, natural, or mixed in nature. WHS are safeguarded under the World Heritage Convention, 1972, an international agreement adopted by UNESCO member countries.
- The Convention outlines the responsibilities of State Parties in identifying, protecting, and preserving such sites.
- The list of WHS are maintained by the international 'World Heritage Programme', administered by the UNESCO World Heritage Committee.
- India ratified the Convention in 1977.
- WHS Around the World: As of October 2024, there are around 1,223 sites in 196 countries comprising 952 cultural, 231 natural, and 40 mixed sites.
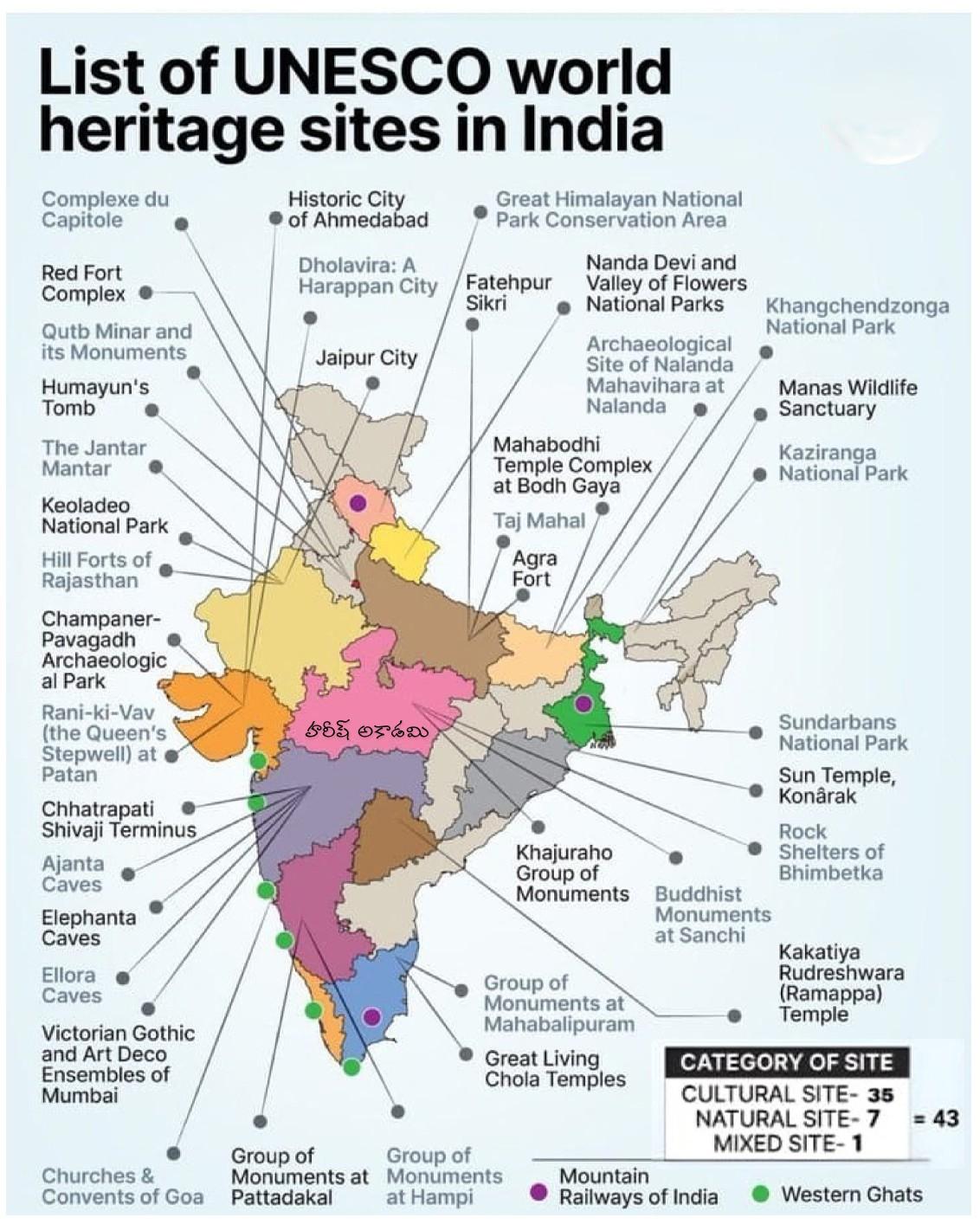
- WHS in India: As of April 2025, India has 43 World Heritage Sites (34 Cultural, 7 Natural, and 2 Mixed) and 62 sites on the Tentative List.
What are the Key Government Initiatives to Promote India’s Cultural Heritage?
- Restoration of Antiquities: India has intensified efforts to bring back cultural artifacts from foreign countries, retrieving 655 antiquities since 1976.
- In 2024, literary classics like the Ramcharitmanas, Panchatantra, and Sahrdayāloka-Locana were added to UNESCO’s 2024 Memory of the World Committee for Asia and the Pacific Regional Register.
- Heritage Scheme and Corridor Projects: Through the Adopt a Heritage Programme launched in 2017, public and private bodies can support heritage site upkeep via CSR funding.
- Digital Documentation: Over 12.3 lakh antiquities and 11,400 heritage sites have been digitized under the National Mission on Monuments and Antiquities (NMMA). The ‘Indian Heritage in Digital Space’ initiative uses technology to create immersive heritage experiences.
- The ASI’s ‘Must See’ portal showcases nearly 100 major monuments with detailed information and panoramic views.
- Global Cultural Leadership: India hosted the 46th Session of the UNESCO World Heritage Committee in Delhi (July 2024).
Archaeological Survey of India (ASI)
- About: ASI is the key government body responsible for archaeological research and protection of India’s cultural heritage.
- Establishment: It was established in 1861 by Alexander Cunningham, who is known as the “Father of Indian Archaeology” and served as its first Director-General.
- Functions: Its main functions include survey, exploration, excavation, conservation, and maintenance of ancient monuments.
- It also documents and protects antiquarian remains and archaeological heritage.
- Governing Framework: It works under the Ministry of Culture and operates under the Ancient Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains (AMASR) Act, 1958.
- It manages over 3,698 monuments and sites of national importance.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q1. Which one of the following statements is correct? (2021)
(a) Ajanta Caves lie in the gorge of Waghora river.
(b) Sanchi Stupa lies in the gorge of Chambal river.
(c) Pandu-lena Cave Shrines lie in the gorge of Narmada river.
(d) Amaravati Stupa lies in the gorge of Godavari river.
Ans: (a)