World Day of Social Justice 2025 | 22 Feb 2025
For Prelims: World Day of Social Justice, International Labour Organization (ILO), Denotified and Nomadic Tribes (DNTs), Fundamental Rights, Inequality, PM-AJAY, SRESHTA, NAMASTE, SMILE, PM-DAKSH Yojana.
For Mains: World day of social justice and its significance, Steps taken in India to ensure social justice in India.
Why in News?
The United Nations (UN) observed World Day of Social Justice (WDSJ) on 20th February 2025 advocating against poverty, exclusion, and unemployment while promoting equality and solidarity.
- The 2025 theme of WDSJ, “Empowering Inclusion: Bridging Gaps of Social Justice,” focuses on inclusive policies and social protection, while highlighting the importance of “Strengthening a Just Transition for a Sustainable Future.”
What is World Day of Social Justice?
- About: It is an initiative of the UN specifically led by the International Labour Organization (ILO) to promote social justice, equality, human rights, and fair opportunities for all.
- It was designated by the UN General Assembly on 26th November 2007.
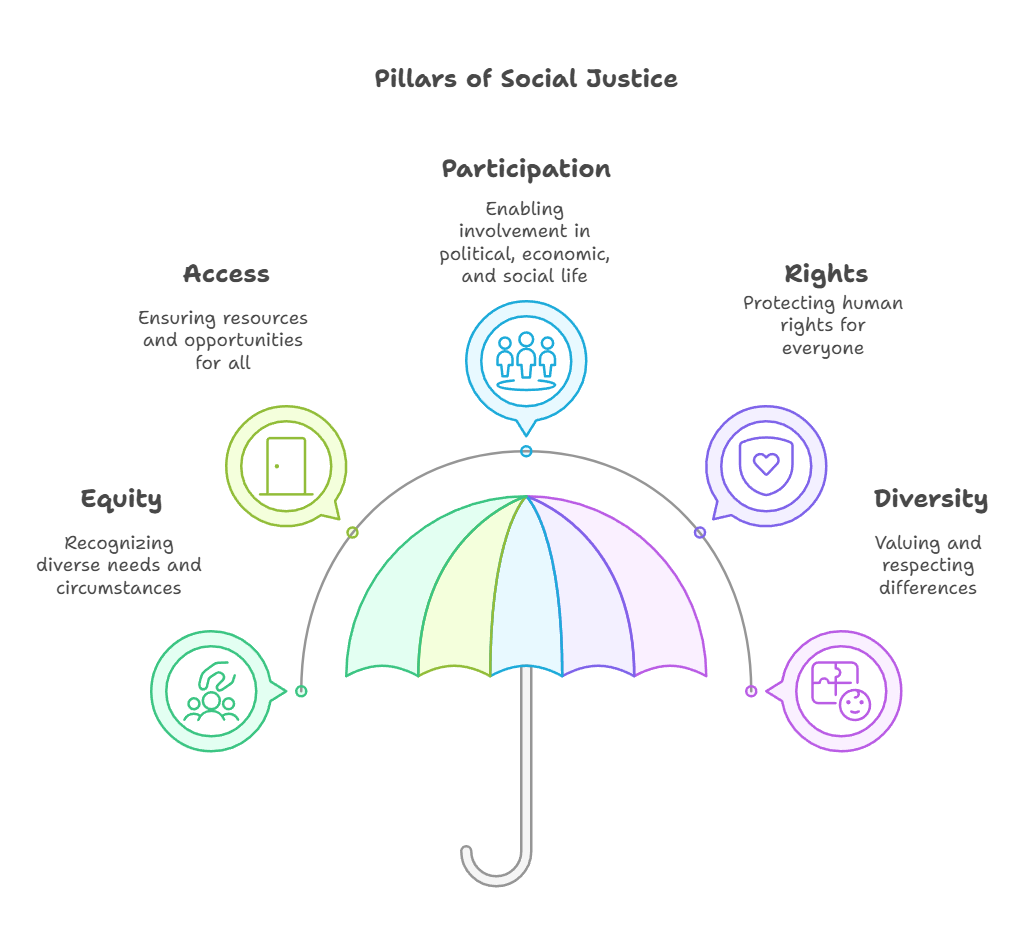
- Pillars of Social Justice:
- Role of ILO: ILO unanimously adopted the Declaration on Social Justice for a Fair Globalization on 10th June 2008 in response to the World Day of Social Justice.
- It expands upon the Philadelphia Declaration 1944 and the Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work 1998.
- In 2009, ILO launched Social Protection Floors that ensure basic social security to prevent or reduce poverty.
- Social Justice in India: In India, MoSJE is the nodal agency for uplifting vulnerable communities, including:
- Scheduled Castes, Other Backward Classes, and Senior Citizens
- Victims of Alcoholism and Substance Abuse
- Transgender Persons, and Denotified and Nomadic Tribes (DNTs),
- Economically Backward Classes (EBCs), and the Economically Weaker Section (EWS).
- Significance:
- Globalization: The declaration redefined the ILO’s role in globalization, ensuring social justice remains central to economic policies.
- Alignment with UN Goals: It supports the UN’s vision of decent work, fair globalization, fundamental rights, social protections, and productive social dialogue.
- Global Stability: Social justice is essential for global peace and security which remains threatened by labor insecurity, inequality, and social contract breakdowns.
- Social Justice: Achieving social justice requires fundamental freedoms, human rights, and economic stability.
- Challenges: Persistent issues such as financial crises, insecurity, poverty, exclusion, and inequality continue to hinder social justice on a global scale.
What are India’s Constitutional Provisions on Social Justice?
- Preamble: It ensures social, economic, and political justice, guarantees equality of status and opportunity, and promotes fraternity to uphold individual dignity and national unity.
- Fundamental Rights:
- Article 23: It prohibits human trafficking and forced labour, making such practices punishable by law.
- Article 24: It bans child labour in hazardous occupations, protecting children’s rights to safety and education.
- Directive Principles of State Policy:
- Article 38: It directs the State to reduce social and economic inequalities.
- Article 39: It ensures equal livelihood, fair wages, and protection from exploitation.
- Article 39A: It guarantees free legal aid for disadvantaged people.
- Article 46: It mandates special educational and economic promotion for SCs, STs, and weaker sections to prevent discrimination.
What are Initiatives for Ensuring Social Justice in India?
- PM-AJAY: Pradhan Mantri Anusuchit Jaati Abhyuday Yojana (PM-AJAY) supports Scheduled Caste (SC) communities through skill development, income generation, and village infrastructure.
- It has three components i.e., Adarsh Gram development, Grants-in-Aid for socio-economic projects, and hostel construction in higher education institutions.
- SRESHTA: Scheme for Residential Education for Students in High Schools in Targeted Areas (SRESHTA) funds top CBSE/State Board schools for SC students in classes 9-12 and supports NGOs to run residential and non-residential schools and hostels.
- Purple Fests (Festival of Inclusion): It fosters inclusion, dignity, and equal opportunities for persons with disabilities (Divyangjan) promoting solidarity and mutual respect.
- NAMASTE: National Action for Mechanized Sanitation Ecosystem (NAMASTE) is a central sector scheme to ensure the safety, dignity, and sustainable livelihood of sanitation workers in urban India.
- It was expanded to include waste pickers as a target group from FY 2024-25.
- SMILE: Support for Marginalized Individuals for Livelihood and Enterprise (SMILE) scheme is aimed at the rehabilitation of transgender individuals and persons engaged in begging to create Begging-free India.
- It is currently implemented in 81 cities and as of November, 2024, 7,660 beggars were identified, and 970 rehabilitated.
- PM-DAKSH Yojana: Pradhan Mantri Dakshta Aur Kushalta Sampann Hitgrahi (PM-DAKSH) yojana provides free skill training to SCs, OBCs, EBCs, DNTs, and Safai Karamcharis for economic empowerment.
- Nasha Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (NMBA): It aims for a drug-free India by targeting 272 high-risk districts through supply control (Narcotics Control Bureau), awareness and demand reduction (MoSJE), and treatment (Ministry of Health).
- Since its launch (15th August 2020), NMBA has reached 13.57 crore people, including 4.42 crore youth, with 3.85 lakh educational institutions participating.
Conclusion
India’s efforts towards social justice are rooted in constitutional provisions and targeted schemes addressing socio-economic disparities. By promoting inclusive policies, skill development, and rehabilitation programs, the government aims to uplift marginalized communities, ensuring dignity, equity, and sustainable livelihoods, aligning with global commitments to social justice and empowerment.
|
Drishti Mains Question: How do constitutional provisions in India support social justice? Discuss with examples of key government initiatives. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Other than the Fundamental Rights, which of the following parts of the Constitution of India reflect/reflects the principles and provisions of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (1948)? (2020)
- Preamble
- Directive Principles of State Policy
- Fundamental Duties
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q.‘Economic Justice’ as one of the objectives of the Indian Constitution has been provided in (2013)
(a) the Preamble and the Fundamental Rights
(b) the Preamble and the Directive Principles of State Policy
(c) the Fundamental Rights and the Directive Principles of State Policy
(d) None of the above
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Does the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016 ensure effective mechanisms for empowerment and inclusion of the intended beneficiaries in the society? Discuss. (2017)