Important Facts For Prelims
World Bank Enhances Lending Capacity
- 15 Nov 2024
- 7 min read
Why in News?
Recently, the World Bank has increased its lending capacity by 50% through balance sheet optimisation, aiming to provide USD 150 billion over the next decade.
- This expansion has a strong focus on green projects, supporting climate action and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- With current annual lending of USD 5 billion, India is one of the World Bank’s largest clients, and will receive a major share of the increased funding, focusing on climate resilience, rural development, energy, healthcare, and digital education.
What are Recent Financial Reforms in the World Bank?
- Reduced Borrowing Costs for Middle-Income Countries: The World Bank has waived commitment fees on loan balances for middle-income countries (like India) for four years, reducing borrowing costs by approximately 1% over this period.
- Commitment fees are charged by the World Bank on undisbursed loan amounts to ensure borrowers use the funds within a set period.
- Reducing commitment fees make financing more affordable for these countries.
- Commitment fees are charged by the World Bank on undisbursed loan amounts to ensure borrowers use the funds within a set period.
- Internal Reforms and Efficiency Gains: Recent World Bank meetings focused on internal reforms to improve efficiency, collaboration, and increase private sector financing.
- These reforms are guided by recommendations from the G20-backed International Expert Group (IEG).
- IEG Report and MDB Funding Goals: The IEG report recommended that Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs), including the World Bank, should increase annual funding by USD 3 trillion by 2030 to effectively support climate action and other SDGs.
- In September 2024, MDBs reported that their global climate finance reached a record high of USD 125 billion in 2023.
- New Lending Strategies: To expand its lending capacity, the World Bank is lowering its equity-to-loan ratio and using hybrid capital models. These strategies will allow the Bank to increase its loans without requiring additional capital.
What is the Role and Structure of the World Bank?
- About the World Bank:
- The World Bank is a global development cooperative comprising 189 member countries.
- These countries, or shareholders, are governed by a Board of Governors, typically made up of finance or development ministers.
- The Board meets annually to set policy and oversee the institution’s work in global development.
- Mission and Functions:
- The World Bank aims to reduce poverty and promote shared prosperity.
- It provides financial products, technical assistance, and policy advice to help countries address complex development challenges.
- The World Bank collaborates with multilateral institutions, civil society, private sector players, and foundations to maximise impact.
- The World Bank has funded over 15,000 projects in areas such as education, health, infrastructure, and environmental sustainability.
- Some of the Projects funded by the Word Bank in India are India Energy Efficiency Scale-up Program, SANKALP, Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP), Eastern Dedicated Freight Corridor, and Mumbai Urban Transport Projects etc.
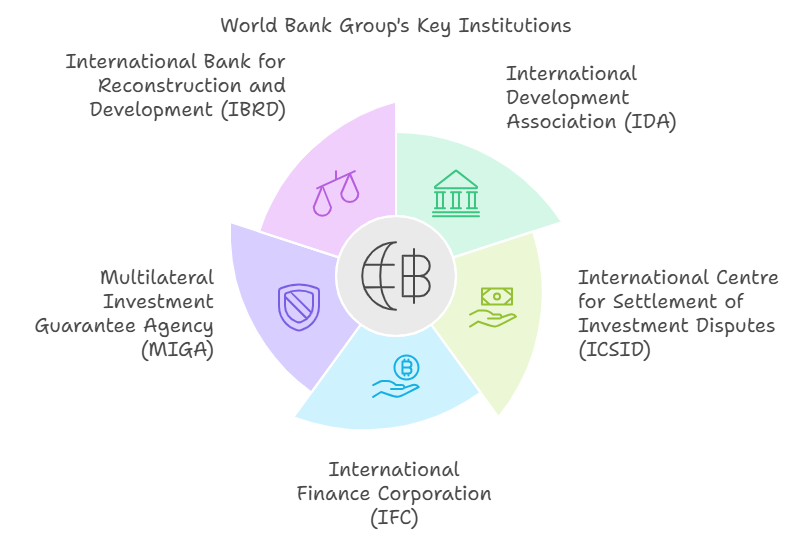
- Key Institutions within the World Bank Group:
- International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD): IBRD offers loans, guarantees, and policy advice to middle-income and creditworthy low-income countries with focus on poverty reduction, sustainable growth, and infrastructure development.
- Middle-income countries (MICs) account for over 60% of IBRD’s portfolio, serving as key drivers of global growth while housing the majority of the world’s poor.
- International Development Association (IDA): IDA provides concessional loans and grants to the world’s poorest countries, with terms that carry little or no interest.
- IDA supports projects in rural development, education, health, and post-conflict recovery.
- IDA’s financial products are allocated based on a country’s income level and its success in managing past projects.
- IDA financing is highly concessional, offering zero-to-low interest loans or grants to the poorest countries.
- International Finance Corporation (IFC): IFC promotes private sector investment in developing countries by providing financing, advisory services, and risk mitigation.
- Multilateral Investment Guarantee Agency (MIGA): MIGA provides political risk insurance and guarantees to encourage foreign investment in developing economies, reducing the risk of loss from political instability.
- Political risk insurance is a tool for businesses to mitigate and manage risks arising from the adverse actions, or inactions, of governments.
- International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID): ICSID helps resolve investment disputes between investors and states, providing a legal framework for the peaceful settlement of conflicts.
- International Bank for Reconstruction and Development (IBRD): IBRD offers loans, guarantees, and policy advice to middle-income and creditworthy low-income countries with focus on poverty reduction, sustainable growth, and infrastructure development.
Note
- India is a member of four of the five institutions in the World Bank Group but is not a member of the International Centre for Settlement of Investment Disputes (ICSID), an international arbitration institution.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Q. With reference to ‘IFC Masala Bonds’, sometimes seen in the news, which of the statements given below is/are correct? (2016)
- The International Finance Corporation, which offers these bonds, is an arm of the World Bank.
- They are the rupee-denominated bonds and are a source of debt financing for the public and private sector.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)