Woody Encroachment in Grasslands | 06 Aug 2024
For Prelims: Carbon Sequestration, Climate Change.
For Mains: Significance of Forest Resources and Measures for Conservation of Resources.
Why in News?
Increasing tree cover is often seen as a positive outcome of biodiversity conservation, and a much-needed effort to combat climate change.
- However, a study published by the Universities of Witwatersrand, Cape Town, and Oxford reported that more trees in open ecosystems like savannahs and grasslands have substantially reduced the number of native grassland birds.
What has the Study Revealed?
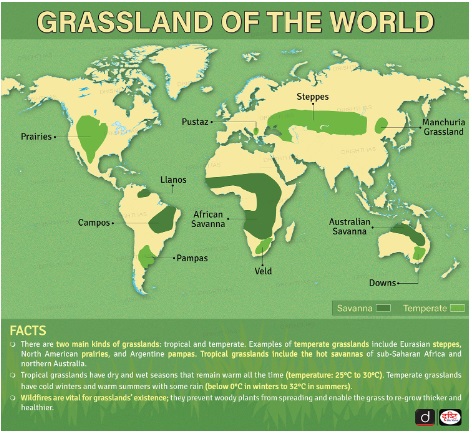
- Grasslands and Savannas:
- Grasslands and savannahs are diverse habitats found in tropical and temperate regions, covering nearly 40% of the Earth's landmass.
- These ecosystems are home to a variety of species, including large herbivores like elephants and rhinoceroses, and grassland birds such as bustards and floricans. Despite their importance, these habitats are rapidly declining due to various threats.
- Woody Encroachment:
- Woody encroachment refers to the gradual transformation of open habitats into areas with higher tree and shrub density.
- This process results in the homogenization of ecosystems, shifting from a diverse grassy understory to a uniform woody cover.
- Factors such as climate change, increased atmospheric CO2, and disruption of natural disturbance regimes like grazing and fire contribute to this phenomenon.
- Effects on Ecosystems:
- The increase in tree cover can have detrimental effects on grassland ecosystems.
- Higher CO2 levels promote the growth of deep-rooted woody plants, which can overshadow and suppress grasses.
- This shift in vegetation alters soil conditions and faunal associations, leading to declines in grassland species and disrupting ecological balance.
- Global and Local Impact:
- In South America, fire suppression is a major driver, while in Australia and Africa, increased CO2 and variations in rainfall play significant roles.
- In India, grasslands face threats from both natural encroachment and large-scale tree plantation programs.
- Studies have shown significant woody encroachment in national parks in India and Nepal, with grassland habitats shrinking by 34% and tree cover increasing by 8.7% over the past three decades.
- Human Influence:
- Human activities, including colonial-era conservation policies and modern tree plantation programs, have exacerbated woody encroachment.
- Historical policies viewed open ecosystems as "wastelands," leading to their conversion for timber and agricultural use. Today, the focus on carbon sequestration further pressures these habitats.
- Mitigation and Conservation:
- To address the issue of woody encroachment, it is crucial to gather more evidence on its impact, conduct long-term ecological monitoring, and challenge outdated colonial terminologies that misclassify open ecosystems.
- Effective conservation strategies must consider the ecological value of grasslands and promote practices that maintain their biodiversity and resilience.
What is the Impact of Declining Grasslands?
- Ecological Impacts:
- Loss of Biodiversity: Grasslands support diverse species of plants, insects, birds, and mammals. Their decline leads to habitat loss, threatening species that are specially adapted to these environments.
- Disruption of Ecosystem Services: Grasslands provide vital ecosystem services such as soil stabilisation, water filtration, and carbon sequestration.
- Their degradation can reduce these services, impacting soil health, water quality, and climate regulation.
- Their decline can lead to increased atmospheric CO2 levels, exacerbating climate change.
- Altered Fire Regimes: Grasslands help in maintaining natural disturbances like fire. When grasslands decline, the frequency and intensity of fires can change, which can further alter the ecosystem dynamics.
- Environmental Impacts:
- Increased Soil Erosion: Grasslands help bind soil with their root systems. Without them, soils are more prone to erosion, leading to loss of topsoil and degradation of land.
- Altered Water Cycles: Grasslands play a role in maintaining hydrological cycles by regulating water infiltration and runoff. Their loss can lead to changes in local and regional water cycles, potentially causing flooding or reduced water availability.
- Socio-Economic Impacts:
- Impact on Livelihoods: Many communities rely on grasslands for grazing livestock and other agricultural activities. The decline in grasslands can negatively affect these livelihoods, leading to economic hardship for pastoralists and farmers.
- Reduced Agricultural Productivity: The loss of grasslands can lead to a decrease in soil fertility and productivity, affecting crop yields and food security.
Way Forward
- Conservation and Restoration Efforts: Designate protected areas and conservation reserves to safeguard remaining grasslands from development and other threats.
- Restore Degraded Lands: Implement ecological restoration projects to rehabilitate degraded grasslands, including replanting native grasses and controlling invasive species.
- Promote Sustainable Agriculture: Encourage practices that reduce soil disturbance, such as no-till farming and rotational grazing, to maintain soil health and prevent erosion.
- Implement Controlled Grazing: Develop and enforce grazing management plans that prevent overgrazing and allow for natural recovery periods of grassland ecosystems.
- Control Invasive Plants: Monitor and manage invasive species that outcompete native grasses and disrupt the ecosystem balance.
- Enforce Land Use Regulations: Strengthen and enforce policies and regulations that prevent the conversion of grasslands to agricultural or urban uses.
- Support Incentives for Conservation: Provide financial incentives and support for landowners who engage in grassland conservation and sustainable land management practices.
- Involve Local Communities: Engage local communities in conservation efforts, including education about the value of grasslands and involving them in restoration projects.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Declining grasslands are a significant concern for global biodiversity and ecosystem health. Discuss the major impacts of declining grasslands on ecosystems and biodiversity. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. The vegetation of savannah consists of grassland with scattered small trees, but extensive areas have no trees. The forest development in such areas is generally kept in check by one or more or a combination of some conditions. Which of the following are such conditions? (2021)
1. Burrowing animals and termites
2. Fire
3. Grazing herbivores
4. Seasonal rainfall
5. Soil properties
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 4 and 5
(c) 2, 3 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 5
Ans: (c)