Wildfires in California | 13 Jan 2025
Why in News?
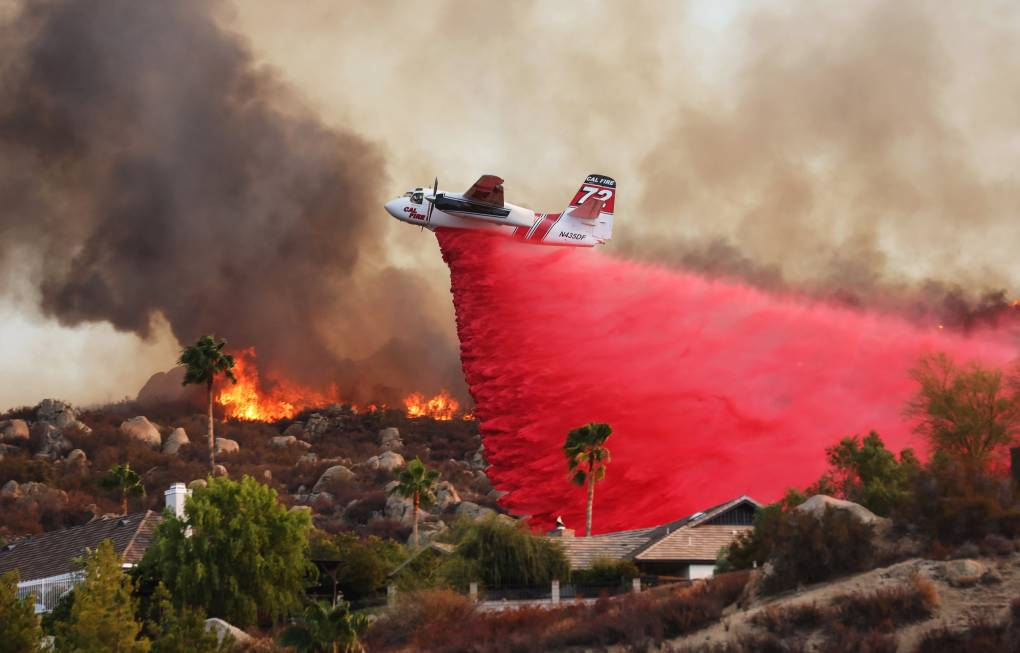
Los Angeles, California, is battling devastating wildfires, with fatalities and structural losses, as authorities deploy pink fire retardants to contain the flames.
- These wildfires have been occurring with increasing frequency and outside the usual wildfire season, prompting questions about their causes, the role of climate change, and potential solutions.
- Authorities are using pink fire retardants to control the wildfires.
Note: In India, as per the India State of Forest Report (ISFR) 2021 published by the Forest Survey of India (FSI), 35.47% of the forest cover is prone to fire.
What are the Causes and Impacts of Frequent Wildfires in California?
- Natural Causes:
- Lightning Strikes: Lightning Strikes ignite dry vegetation like trees and grass, triggering uncontrollable fires, especially when combined with strong winds. This is common during dry seasons.
- Climate Change: California, in the last two winters (2022 and 2023) saw heavy rainfall, promoting vegetation growth.
- The unusually dry winters of 2024-2025 have dried out vegetation in Los Angeles, turning it into fuel for wildfires.
- Global warming has also exacerbated dry and wet seasons, leading to prolonged droughts and reduced moisture in vegetation, which has led to a rise in frequency and severity of wildfires.
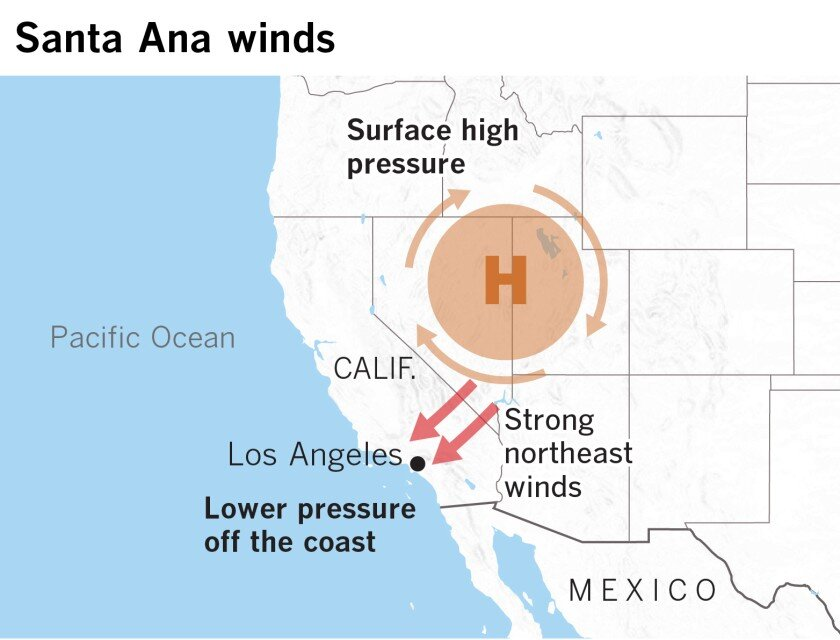
- Santa Ana Winds: The Santa Ana winds in California, typically strong between October and January, have been exceptionally powerful in 2025.
- The winds originate from high-pressure systems in the Great Basin and blow hot, dry air from east to west, flowing down towards the Pacific coast.
- As air descends the Sierra Nevada and Santa Ana mountains and passes through valleys, it gets compressed, which raises its temperature and reduces humidity.
- In Southern California, these winds exacerbate wildfires by rapidly spreading flames across dry vegetation, power lines, and buildings.
- Human Intervention: According to the US National Park Service, human activities account for approximately 85% of wildfires in the US.
- Campfires: Unattended or improperly extinguished campfires are major human-induced causes of wildfires.
- Roadside Ignition: Sparks from vehicles, such as dragging chains or malfunctioning catalytic converters, can ignite fires along highways.
- Power Lines: Faulty or wind-disturbed power lines often trigger wildfires.
- Other Human Activities: Equipment malfunctions, arson, and discarded cigarettes also contribute to wildfire outbreaks.
- Sometimes smugglers and wildlife traffickers ignite wildfires to divert the attention of security forces or to destroy the evidence of crime.
- Impact of Wildfires:
- Economic loss from destruction of life and property.
- Air pollution by small particulate matter and also acids, organic chemicals, and metals along with dust and allergens.
- Land degradation as high temperatures consume all nutrients and vegetation from a land, leaving it barren and infertile.
- Loss of biodiversity
What is Pink Fire Retardant?
- About:
- It is a chemical mix used to slow or extinguish wildfires.
- It primarily contains ammonium phosphate-based slurry with salts like ammonium polyphosphate and toxic metals like chromium and cadmium.
- A commonly used fire retardant in the US is Phos-Chek.
- Phos-Chek is a mixture of water, ammonium phosphate-based fertilizers (diammonium phosphate and ammonium polyphosphate), and a red dye (iron oxide) for visibility.
- It also includes thickening agents to enhance its stickiness and prevent drift during aerial application.
- Function: It is sprayed ahead of fire that coats vegetation to prevent oxygen from aiding combustion.
- Pink is chosen because it is highly visible, helping firefighters target fire lines more effectively.
- Concerns: Toxic metals like chromium and cadmium cause cancer and organ damage, and pose severe risks to aquatic life when they contaminate waterways.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following: (2019)
- Carbon monoxide
- Methane
- Ozone
- Sulphur dioxide
Which of the above are released into atmosphere due to the burning of crop/biomass residue?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)