Agriculture
Western Disturbance Threatens India's Wheat Crop
- 12 Apr 2023
- 5 min read
For Prelims: Food inflation, Wheat, Food Crops.
For Mains: Effects of Weather in Food Production, Foodgrain Security.
Why in News?
Recent inclement weather conditions, including an unusual rise in mercury in February and untimely spells of widespread rain, gusty winds, and hails during March under the influence of western disturbances in key wheat-producing states have left farmers worried about a potential drop in yield, output, and quality of wheat.
What is the Impact of Untimely Rains and Winds on Wheat Crops in India?
- Impact of Untimely Rains and Winds:
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD) reported that the rains, along with stormy winds between 40-50 kilometers per hour, could be detrimental to the crop's health, especially if they occur close to the ripening and harvesting stage. Unfortunately, there have been instances of crop flattening and waterlogging in fields, which could further damage the ready-to-harvest wheat crop.
- Impact on Production:
- According to the researchers, with the recent untimely rains, India's wheat production in the agriculture year 2022-23 is likely to be 102.9 MT, which is less than the Union government's estimate of 112 MT. However, the Centre remains optimistic that wheat production will be close to 112 MT due to increased acreage and better yield this season, despite a slight production loss due to recent adverse weather conditions.
- Impact on Price and Foodgrain Security:
- If India's wheat production drops below the government's estimate, it could lead to a hike in the prices of wheat and wheat-based products in the domestic market.
- Additionally, any decline in wheat production could lead to a potential foodgrain security issue.
What are the Key Points related to Wheat?
- About:
- This is the second most important cereal crop in India after rice.
- It is the main food crop, in the north and north-western part of the country.
- Wheat is a rabi crop that requires a cool growing season and bright sunshine at the time of ripening.
- Success of the Green Revolution contributed to the growth of Rabi crops, especially wheat.
- Temperature:
- Between 10-15°C (Sowing time) and 21-26°C (Ripening & Harvesting) with bright sunlight.
- Rainfall:
- Around 75-100 cm.
- Soil Type:
- Well-drained fertile loamy and clayey loamy (Ganga-Satluj plains and black soil region of the Deccan).
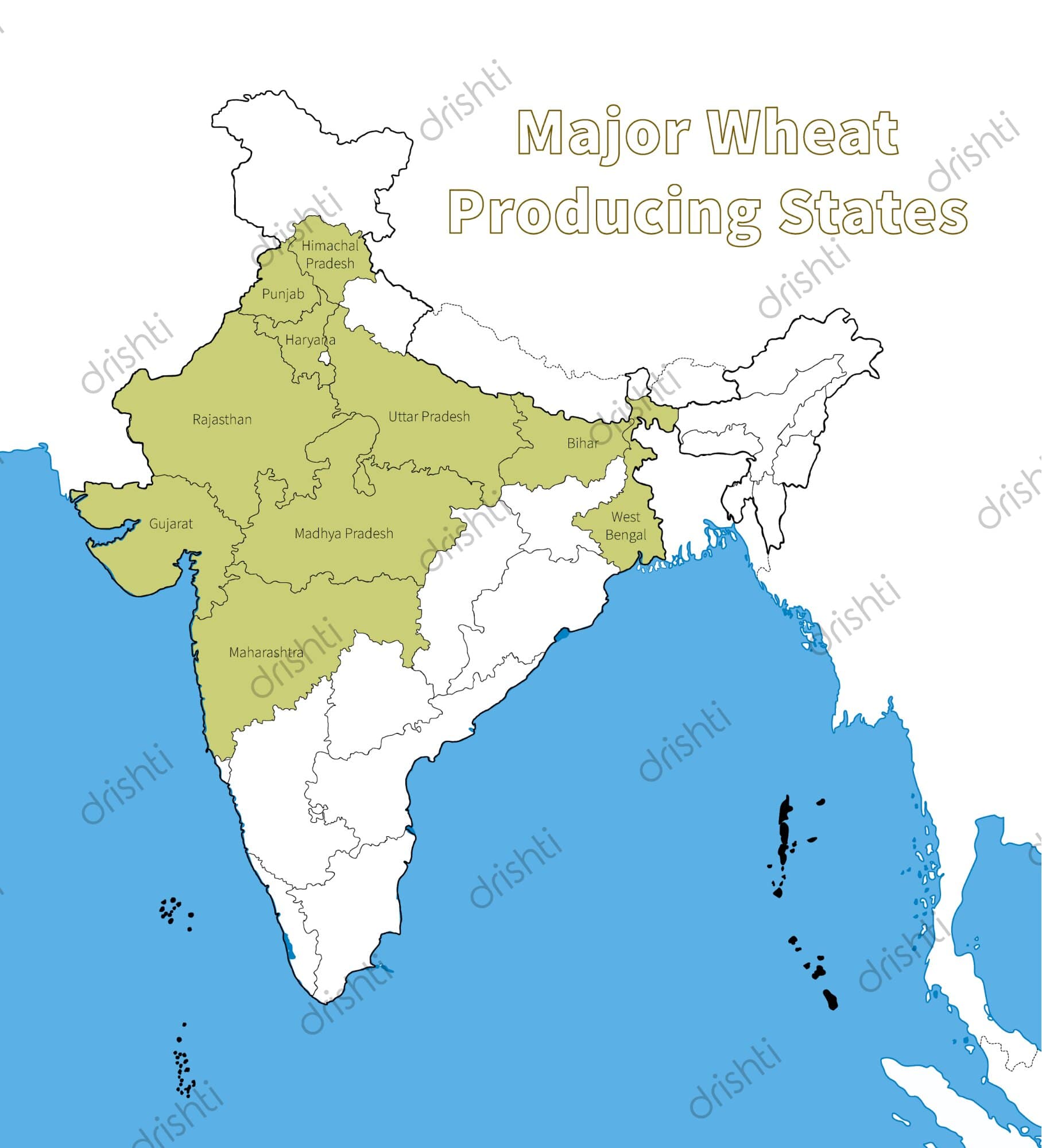
- Top Wheat Producing States:
- Uttar Pradesh, Punjab, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Bihar, Gujarat.
- Status of Indian Wheat Production and Export:
- India is the world's second-biggest wheat producer after China. But it accounts for less than 1% of the global wheat trade. It keeps a lot of it to provide subsidised food for the poor.
- Its top export markets are Bangladesh, Nepal and Sri Lanka - as well as the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
- Government Initiatives:
- Macro Management Mode of Agriculture, National Food Security Mission and Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana are few government initiatives to support wheat cultivation.
What are Western Disturbances?
- Western disturbances are storms that originate in the Caspian or Mediterranean Sea, and bring non-monsoonal rainfall to northwest India, according to the India Meteorological Department (IMD).
- They are labelled as an extra-tropical storm originating in the Mediterranean, is an area of low pressure that brings sudden showers, snow and fog in northwest India.
- It arrives with rain and snow in Pakistan and northern India. The moisture which WDs carry with them comes from the Mediterranean Sea and/or from the Atlantic Ocean.
- WD brings winter and pre-monsoon rain and is important for the development of the Rabi crop in the Northern subcontinent.
- The WDs are not always the harbingers of good weather. Sometimes WDs can cause extreme weather events like floods, flash floods, landslides, dust storms, hailstorms and cold waves killing people, destroying infrastructure and impacting livelihoods.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following crops:
- Cotton
- Groundnut
- Rice
- Wheat
Which of these are Kharif crops?
(a) 1 and 3
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)