Governance
Website Blocking by the Government
- 11 Jan 2024
- 6 min read
For Prelims: Section 69A of the Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000, Right to Information (RTI), Terrorism, Hate Speech, Freedom of Expression.
For Mains: Website Blocking by the Government, Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Why in News?
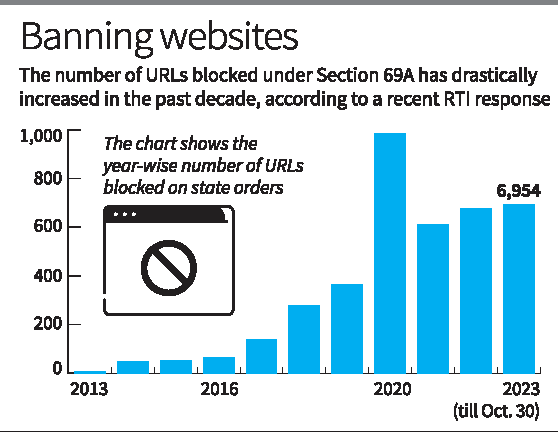
Website blocking orders have grown over a 100-fold from 2013 to October 2023, shows a reply to a Right to Information (RTI) application.
What are the Trends of the Website Blocking Orders in India?
- The Union government issued 62 website blocking orders in 2013, and in 2023, 6,954 till October.
- These orders are issued under Section 69A of the Information Technology (IT) Act, 2000.
- The increase in website blocking orders has occurred alongside a significant rise in internet use, especially since the substantial reduction in mobile data prices in 2016.
- Most of the web pages blocked are likely to be individual posts, videos or profiles.
- Location of web/application servers are traced on immediate basis as and when required or in case they are not complying with the laws of the land or they are required to be blocked as per court orders.
What is the Legal Framework within the Government to Block Websites or Online Contents?
- Information Technology Act, 2000:
- In India, the IT Act, 2000, as amended from time to time, governs all activities related to the use of computer resources.
- It covers all ‘intermediaries’ who play a role in the use of computer resources and electronic records.
- The Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules 2021 issued by the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology, under IT Act 2000 regulates the content and conduct of intermediaries and digital media platforms, and have resulted in the blocking of several websites and channels that allegedly violate the rules.
- Section 69 of the IT Act:
- It confers on the Central and State governments the power to issue directions “to intercept, monitor or decrypt any information generated, transmitted, received or stored in any computer resource”.
- The grounds on which these powers may be exercised are:
- In the interest of the sovereignty or integrity of India, defence of India, the security of the state.
- Friendly relations with foreign states.
- Public order, or for preventing incitement to the commission of any cognizable offence relating to these.
- For investigating any offence.
Why the Government Blocks Websites and what are the Challenges in Blocking them?
- Government website blocking is primarily driven by concerns related to national security, public order, and legal regulations.
- It aims to counter threats such as Terrorism, Hate Speech, or illegal content.
- However, this practice encounters various challenges. Users can easily circumvent blocks using tools like VPNs, making enforcement difficult.
- VPN stands for "Virtual Private Network" and describes the opportunity to establish a protected network connection when using public networks.
- Website blocking has become much harder due to evolutions in the encryption technologies used by Web browsers and firms, increasingly blurring the level of visibility that Internet providers have on their users’ activity.
What are the Implications of Blocking Websites by the Government?
- Impact on Freedom of Expression:
- Website blocking, especially when not transparently justified, can raise concerns about Freedom of Expression. It is crucial to strike a balance between protecting national interests and safeguarding citizens' rights to express their opinions.
- Impact on Information Access:
- Blocking websites may hinder access to valuable information and diverse perspectives. This can limit the public's ability to stay informed about various issues and make well-rounded decisions.
- If the government blocks websites without due diligence, it may unintentionally impede the dissemination of knowledge and hinder the public's right to access information.
- Economic Consequences:
- Blocking websites can have economic repercussions, especially if it disrupts the operations of legitimate businesses hosted on those platforms.
- Businesses and entrepreneurs may face challenges if their websites are blocked, impacting not only their revenue but also potentially stifling innovation and economic growth.
- Public Perception and Trust:
- The government's decisions to block websites can shape public perception and trust in its ability to uphold democratic values.
- If the public perceives website blocking as arbitrary or unjustified, it can lead to a loss of trust in government institutions, potentially impacting overall civic engagement.
Way Forward
- To enhance the efficiency of website blocking, collaboration with major CDNs (Content Delivery Network), such as Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, and Cloudflare, could be explored. CDNs play a significant role in content distribution and may provide more effective mechanisms for blocking specific content.
- While governments seek to address genuine threats through website blocking, careful consideration and transparent, accountable processes are essential to mitigate the potential adverse impacts on freedom of expression, businesses, and public trust.





-min.jpg)