Weather Monitoring by IMD | 30 Jan 2024
For Prelims: India Meteorological Department (IMD), INSAT 3D satellite, INSAT 3DR satellite, Infrared, Cyclones, Water Vapour, Clouds, Temperature, Humidity, Tropical Storm
For Mains: Significance of INSAT 3D and INSAT 3DR satellites in revealing the meteorological conditions.
Why in News?
Recently, The India Meteorological Department (IMD) issued a warning about a strong probability of "very dense fog" in Haryana, Chandigarh, and Delhi.
- IMD has also accompanied alerts with maps from the INSAT 3D satellite, and sometimes from the INSAT 3DR satellite.
What is INSAT-3DR?
- About:
- The IMD uses INSAT -3D and INSAT-3DR satellite data for weather forecasting/monitoring purposes.
- INSAT-3DR, similar to INSAT-3D, is an advanced meteorological satellite of India configured with an imaging System and an Atmospheric Sounder.
- An atmospheric sounder measures how the physical properties of a column of air vary with altitude.
- It has several infrared channels from longwave to shortwave bands and one visible band.
- INSAT-3DR, similar to INSAT-3D, is an advanced meteorological satellite of India configured with an imaging System and an Atmospheric Sounder.
- The significant improvements incorporated in INSAT-3DR are:
- Imaging in the Middle Infrared band to provide nighttime pictures of low clouds and fog.
- Imaging in two Thermal Infrared bands for estimation of Sea Surface Temperature (SST) with better accuracy.
- The IMD uses INSAT -3D and INSAT-3DR satellite data for weather forecasting/monitoring purposes.
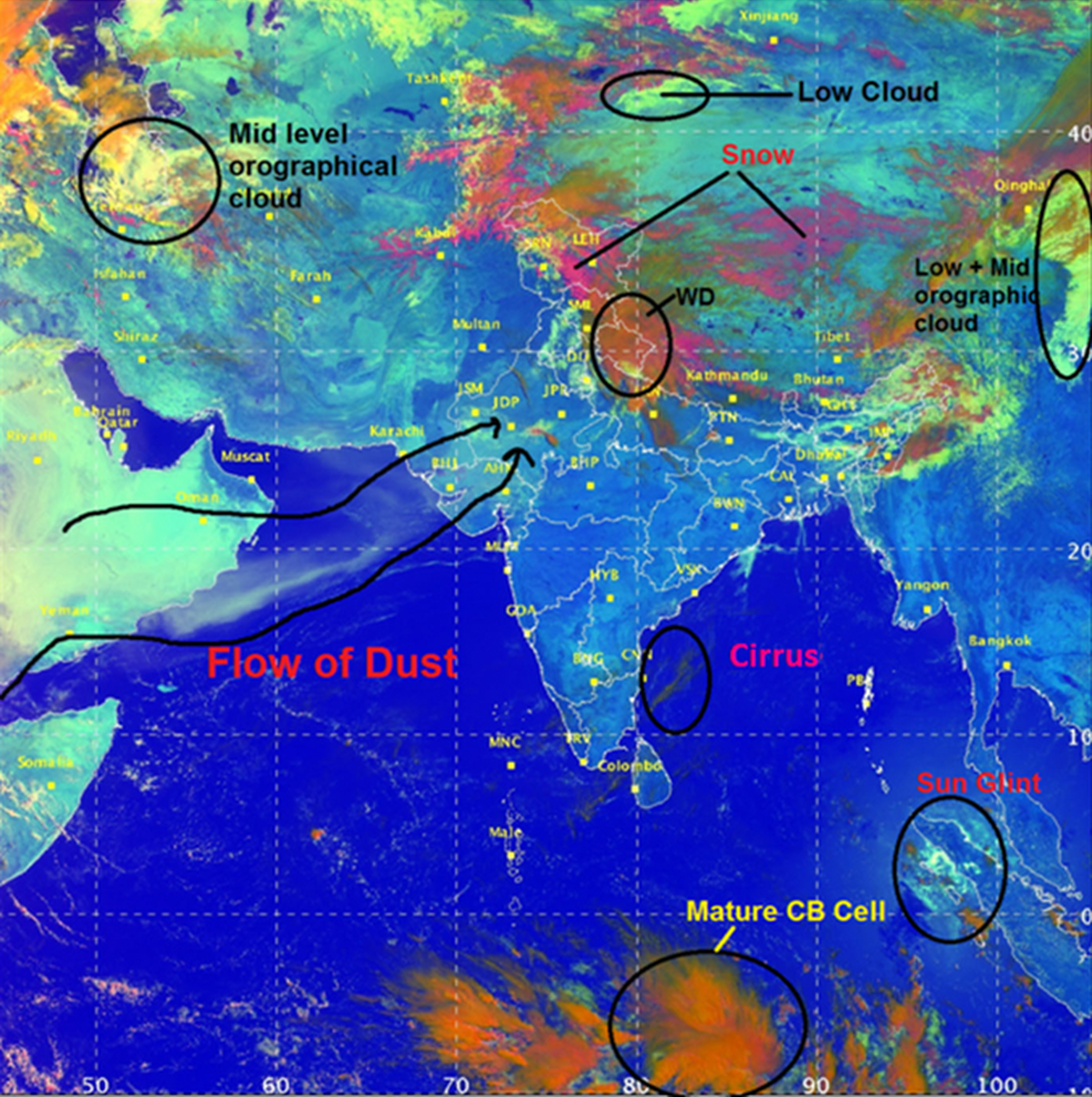
- Mechanism of Imaging System of INSAT-3DR:
- RGB (Red, Green, Blue) Imager: The colouration of images from the RGB imager on the INSAT 3D satellite relies on two factors:
- Solar Reflectance: It is a ratio of the amount of solar energy reflected by a surface and the amount of solar energy incident on it.
- Brightness Temperature: It is the relationship between the temperature of an object and the corresponding brightness of its surface.
- Prediction and Monitoring of Snow and Clouds:
- While snow and clouds exhibit similar solar reflectance in the visible spectrum.
- Snow strongly absorbs radiation of the shortwave infrared.
- The INSAT 3D and INSAT 3DR satellites utilise day and night microphysics modes through their RGB imager.
- Day Microphysics: Data from INSAT 3D examines solar reflectance at three wavelengths: 0.5 µm (visible), 1.6 µm (shortwave infrared), and 10.8 µm (thermal infrared).
- The strength of the visible signal determines the amount of green colour.
- The strength of the shortwave infrared signal, the amount of red colour
- The strength of the thermal infrared signal, the amount of blue colour.
- Night Microphysics: This component of the satellite's operation is determined not by a single but by evaluating the strength of the difference between two signals.
- The computer calculates the amount of red colour based on the difference between two thermal infrared signals.
- The quantity of green colour varies according to the difference between a thermal infrared and a middle infrared signal.
- The amount of blue colour is not derived from a difference but is determined by the strength of a thermal infrared signal at a wavelength.
- While snow and clouds exhibit similar solar reflectance in the visible spectrum.
- RGB (Red, Green, Blue) Imager: The colouration of images from the RGB imager on the INSAT 3D satellite relies on two factors:
- Measurement of Temperature, Humidity and Water Vapour:
- By combining day and night microphysics data, the presence of moisture droplets of different shapes and temperature differences over time, can be identified.
- It is helpful in tracking the formation, evolution and depletion of cyclones and other weather events.
- INSAT 3D and INSAT 3DR both use radiometers to make their spectral measurements.
- A radiometer is a device that measures the temperature or electrical activity. Both satellites also carry atmospheric sounders.
- These are devices that measure temperature and humidity, and study water vapor as a function of their heights from the ground.
What are the Other Weather Forecasting Methods?
- Apart from tracking satellite data, IMD collaborates with ISRO for ground-based observations from the Automatic Weather Stations (AWS), the Global Telecommunication System (GTS) that measures temperature, sunshine, wind direction, speed and humidity.
- Meanwhile, the Agro-meteorological Tower (AGROMET) and Doppler Weather Radar (DWR) systems augment the observations.
- In 2021, IMD adopted a new strategy for issuing monthly and seasonal operational forecasts for the southwest monsoon rainfall by modifying the existing two-stage forecasting strategy.
- The new strategy is based on the existing statistical forecasting system and the newly developed Multi-Model Ensemble (MME)-based forecasting system.
- The MME approach uses the coupled global climate models (CGCMs) from different global climate prediction and research centres, including IMD’s Monsoon Mission Climate Forecasting System (MMCFS) model.
- All these technological strides have been possible since the National Monsoon Mission (NMM) was initiated in 2012.
India Meteorological Department
- About:
- IMD was established in 1875. It is the National Meteorological Service of the country and the principal government agency in all matters relating to meteorology and allied subjects.
- It works as an agency of the Ministry of Earth Sciences of the Government of India.
- It is headquartered in New Delhi.
- IMD is also one of the six Regional Specialized Meteorological Centres of the World Meteorological Organization.
- IMD was established in 1875. It is the National Meteorological Service of the country and the principal government agency in all matters relating to meteorology and allied subjects.
- Roles and Responsibilities:
- To take meteorological observations and to provide current and forecast meteorological information for optimum operation of weather-sensitive activities like agriculture, irrigation, shipping, aviation, offshore oil explorations, etc.
- To warn against severe weather phenomena like tropical cyclones, norwesters, dust storms, heavy rains and snow, cold and heat waves, etc., which cause destruction of life and property.
- To provide meteorological statistics required for agriculture, water resource management, industries, oil exploration and other nation-building activities.
- To conduct and promote research in meteorology and allied disciplines.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In the South Atlantic and South-Eastern Pacific regions in tropical latitudes, cyclone does not originate. What is the reason? (2015)
(a) Sea surface temperatures are low
(b) Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone seldom occurs
(c) Coriolis force is too weak
(d) Absence of land in those regions
Ans: (b)
Ans:
- The most proximate reasons for the lack of cyclones in the South Atlantic and South Eastern Pacific ocean is the rare occurrence of the Inter-Tropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ) over the region.
- It becomes very difficult or nearly impossible to have genesis of tropical cyclones, unless synoptic vorticity (it is a clockwise or counterclockwise spin in the troposphere) and convergence (i.e., large scale spin and thunderstorm activity) are provided by ITCZ.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q. The recent cyclone on the east coast of India was called “Phailin”. How are the tropical cyclones named across the world? Elaborate. (2013)
Q. Discuss the meaning of colour-coded weather warnings for cyclone prone areas given by India Meteorological Department. (2022)