Ultra-Conserved Elements | 01 Mar 2025
Why in News?
A study found that Ultra-Conserved Elements (UCEs) in the Tra2b (Transformer-2 beta) gene have remained unchanged for 80 million years due to their role in preventing infertility by regulating protein levels.
What are Key Findings of the Study on Ultra-Conserved Elements?
- Findings of the Study: Deleting the UCE in mouse testes caused excess Tra2β protein, sperm cell death, and infertility.
- A UCE in the Tra2b gene regulates Tra2β protein production by acting as a poison exon.
- When Tra2β protein levels are too high, the UCE triggers an extra exon in the gene’s RNA, introducing a stop codon that halts protein synthesis, preventing overproduction.
- Mutations disrupting UCE's protein-limiting function cause infertility, preventing inheritance. Thus Natural selection has preserved UCEs across species for millions of years.
- A UCE in the Tra2b gene regulates Tra2β protein production by acting as a poison exon.
- Ultra-Conserved Elements: UCEs are Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) sequences of at least 200 base-pairs that have remained completely unchanged across multiple species for 80 million years or more.
- These sequences are found in humans, mice, rats, chickens, and even fish, indicating their critical biological importance.
- Across the human genome (an entire set of DNA instructions found in a cell), there are nearly 500 UCEs.
- Characteristics of UCEs: UCEs exhibit nearly identical DNA sequences across diverse species, even those that are evolutionarily distant.
- Functions of UCEs: They do not usually code for proteins but are involved in gene regulation.
- These sequences are found in humans, mice, rats, chickens, and even fish, indicating their critical biological importance.
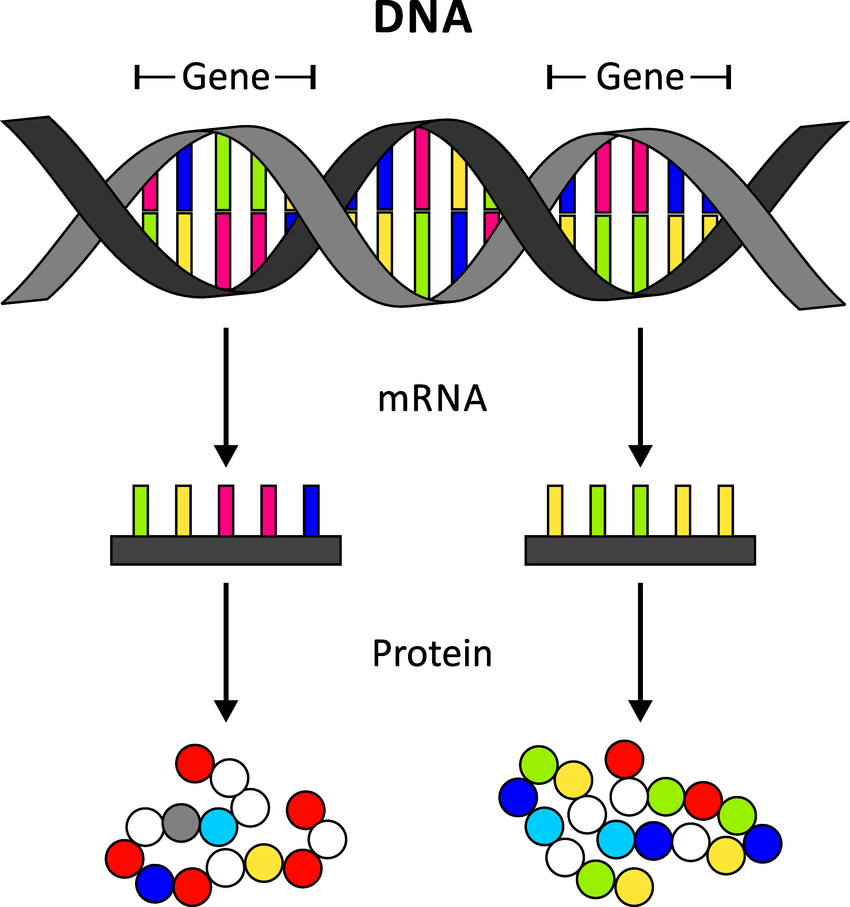
DNA to Protein Conversion
- DNA Structure: DNA is a double-helix molecule, with each strand consisting of four bases that pair up to hold the strands together.
- Gene: A gene is a short segment of DNA, typically a few thousand base-pairs long, that carries instructions for making proteins.
- Transcription: When a gene is expressed (information encoded in a gene is turned into a function), the cell transcribes its DNA sequence into messenger RNA (mRNA).
- Ribosomes read the mRNA sequence and assemble amino acids to form a protein (Protein Synthesis). The process halts at a stop codon, signaling the completion of protein synthesis.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. What is Cas9 protein that is often mentioned in news? (2019)
(a) A molecular scissors used in targeted gene editing
(b) A biosensor used in the accurate detection of pathogens in patients
(c) A gene that makes plants pest-resistant
(d) A herbicidal substance synthesised in genetically modified crops
Ans: (a)