International Relations
Ukraine’s Counter-Offensive
- 15 Sep 2022
- 4 min read
For Prelims: Russia-Ukraine Conflict, Regions of Kharkiv Oblast, NATO, Minsk Protocols
For Mains: Ukraine-Russia Conflict and India’s Interests in Ukraine and Russia, Implications of Conflict on India
Why in News?
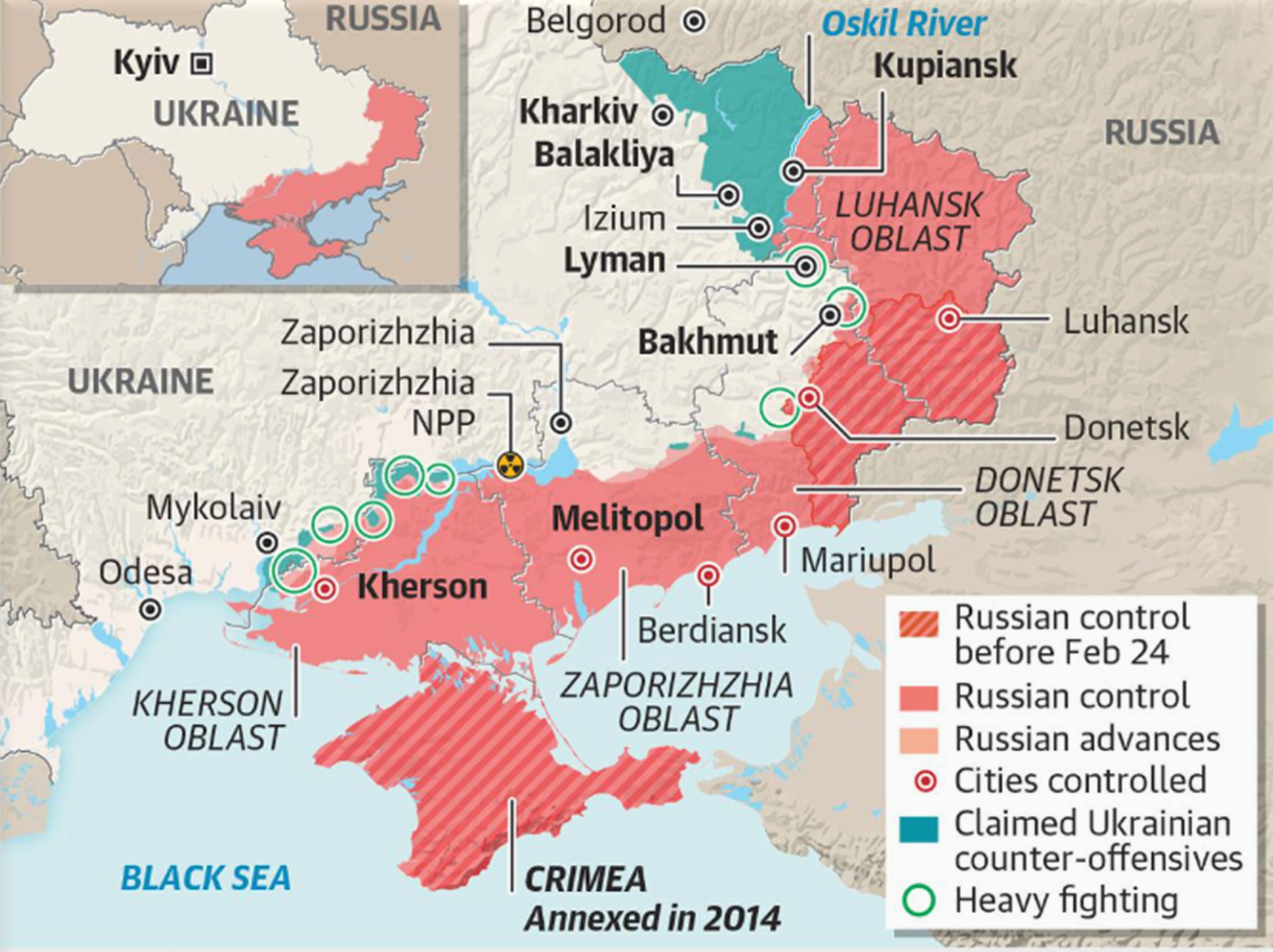
Recently, Ukraine has launched a lightning counter-offensive in the country’s northeast that saw surprising territorial gains.
- Its forces have pushed back Russian soldiers from most of Kharkiv Oblast, retaking thousands of square kilometres of territory.
- This is the first time that Ukrainian troops have pushed back the Russians through combat since the Russia Ukraine conflict began.
How did Ukraine Push Back Russia in Kharkiv Oblast?
- Halt of Russian Forces:
- After capturing Lysychansk in July 2022 and taking the whole of Luhansk province coming under its control, Russia’s battlefield combat came to a halt.
- Russia was controlling almost 25% of Ukraine at this time.
- The halt of Russian forces opened a window opportunity for Ukraine to move ahead with its counter-offensive plans.
- After capturing Lysychansk in July 2022 and taking the whole of Luhansk province coming under its control, Russia’s battlefield combat came to a halt.
- Help from US:
- Advanced mid-range rocket systems such as High Mobility Artillery Rocket Systems (HIMARS).
- Military assistance worth more than USD 14.5 billion.
- U.S. intelligence agencies also provided information to Ukraine on the weak links of the Russian defence.
- Sanctions on Russia:
- Russia was being faced with sanctions which made it difficult to make sure their supply was intact and they had to turn to Iran and North Korea.
- Ukraine’s Attacks:
- Ukraine started attacks in southern Ukraine in Kherson and sabotage hits in Crimea, which Russia annexed in 2014.
- Russia, faced with the Ukrainian attacks in the south, bolstered the defences of Kherson and Zaporizhzhia.
- Ukraine broke into the relatively weaker defence lines in the northeast and successfully pushed the Russians back.
What do we need to know about the Russia Ukraine Conflict?
- History:
- In 2014, Russia had annexed Crimea from Ukraine following a hastily called referendum, a move that sparked fighting between Russia-backed separatists and government forces in eastern Ukraine.
- Ukraine urged the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) to speed up the country’s membership in the alliance.
- Russia declared such a move a “red line”, and worried about the consequences of the US-led military alliances expanding right up to its doorstep.
- This has led to the present war between Russia and Ukraine.
- Invasion of Ukraine:
- The conflict is now the largest attack by one state on another in Europe since the Second World War, and the first since the Balkan conflict in the 1990s.
- With the invasion of Ukraine, agreements like the Minsk Protocols of 2014, and the Russia-NATO Act of 1997 stand all but voided.
- Stand of Other Countries:
- Global:
- The G7 nations strongly condemned Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
- Sanctions have been imposed on Russia by the U.S., the European Union (EU), the UK, Australia, Canada and Japan.
- China rejected calling Russia’s moves on Ukraine an “invasion” and urged all sides to exercise restraint.
- The G7 nations strongly condemned Russia’s invasion of Ukraine.
- India’s Stand:
- India did not join the Western powers’ condemnation of Russia’s intervention in Crimea and kept a low profile on the issue.
- However, in August 2022, India voted against Russia during a “procedural vote” at the United Nations Security Council on Ukraine.
- India did not join the Western powers’ condemnation of Russia’s intervention in Crimea and kept a low profile on the issue.
- Global: