Type 1 Diabetes | 31 Mar 2023
Why in News?
The National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR) has written to all States and Union Territories, suggesting that children with Type 1 diabetes (T1D) are provided with proper care and required facilities.
What is T1D?
- About:
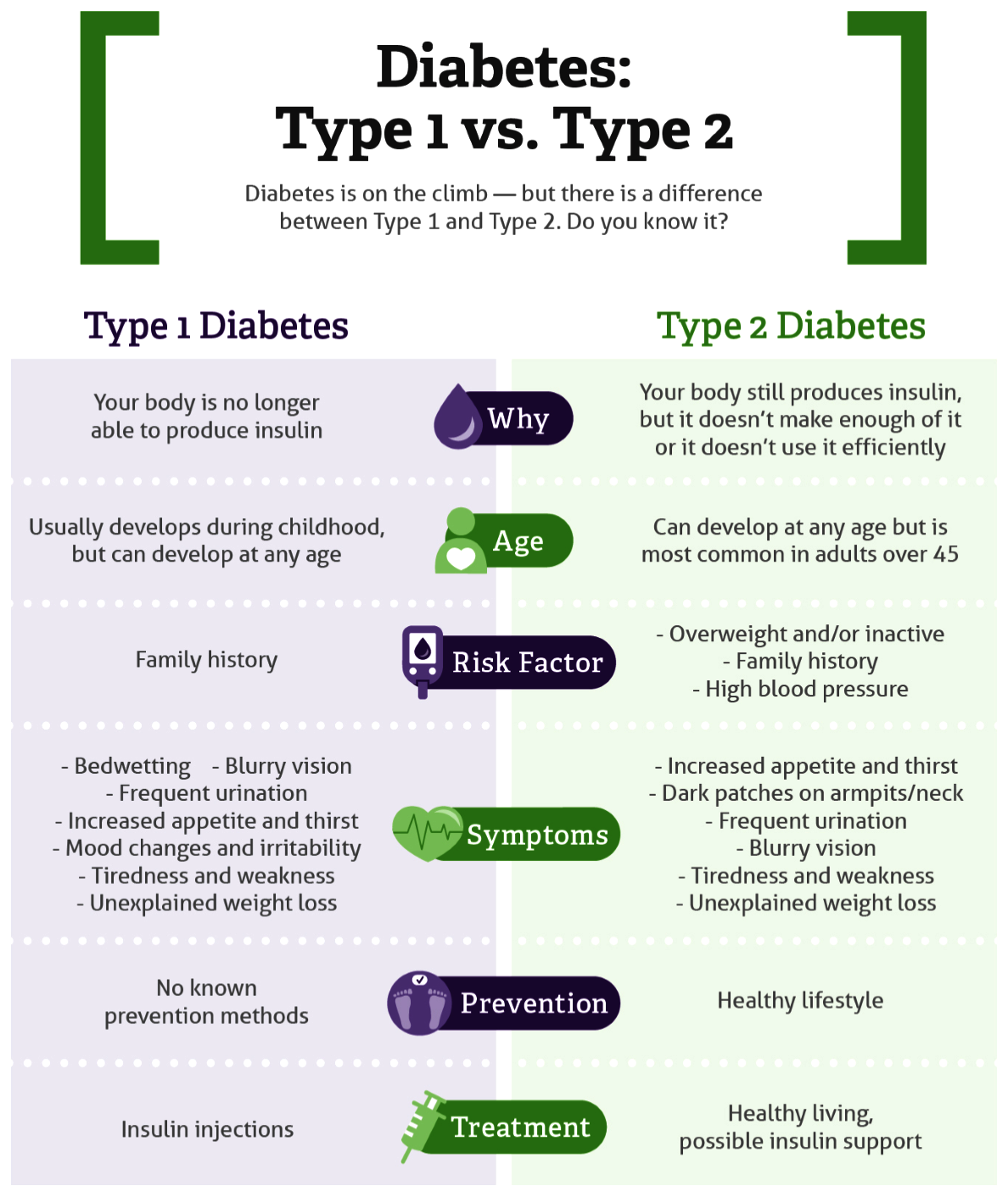
- T1D is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin, which is a hormone needed to regulate blood sugar levels. This type of diabetes usually occurs in children and young adults, although it can occur at any age.
- According to data from the International Diabetes Federation Atlas 2021, India has the world’s highest number of children and adolescents living with Type I Diabetes Mellitus (TIDM), at over 2.4 lakh, in the southeast Asia region.
- It is an autoimmune disorder, which means that the body's immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. The exact cause of this condition is not known, but genetic and environmental factors are thought to play a role.
- T1D is a chronic condition in which the pancreas produces little or no insulin, which is a hormone needed to regulate blood sugar levels. This type of diabetes usually occurs in children and young adults, although it can occur at any age.
- Treatment:
- Type 1 diabetes typically require insulin injections or an insulin pump to manage the blood sugar levels.
- Complications in Children:
- Complications of type 1 diabetes in children can include hypoglycemia (low blood sugar), hyperglycemia (high blood sugar), ketoacidosis (a potentially life-threatening condition that occurs when the body breaks down fat for energy instead of glucose), and long-term complications such as eye, kidney, nerve, and cardiovascular damage.
What are the other Types of Diabetes?
- Type 2 Diabetes:
- It affects the way the body uses insulin. While the body still makes insulin.
- Type 2 diabetes can occur at any age, even during childhood. However, this type of diabetes occurs most often in middle-aged and older people.
- Gestational Diabetes:
- This type occurs in women during pregnancy when the body sometimes becomes less sensitive to insulin. Gestational diabetes does not occur in all women and usually resolves after giving birth.
What are Related Initiatives?
- National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases and Stroke (NPCDCS):
- In order to prevent and control major NCDs, this initiative was launched by India in 2010 with focus on strengthening infrastructure, human resource development, health promotion, early diagnosis, management and referral.
- World Diabetes Day:
- It is observed on 14th November every year. The 2022 campaign focus on access to diabetes education.
- Global Diabetes Compact:
- WHO launched a Global Diabetes Compact to better fight the disease while marking the centenary of the discovery of insulin.
What is the National Commission for Protection of Child Rights?
- NCPCR is a statutory body set up in March 2007 under the Commissions for Protection of Child Rights (CPCR) Act, 2005.
- It is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Women & Child Development.
- The Commission's mandate is to ensure that all laws, policies, programmes, and administrative mechanisms are in consonance with the child rights perspective as enshrined in the Constitution of India and also the UN Convention on the Rights of the Child.
- It inquires into complaints relating to a child's right to free and compulsory education under the Right to Education Act, 2009.
- It monitors the implementation of Protection of Children from Sexual Offences (POCSO) Act, 2012.