Tissue Culture Laboratory at the Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary | 09 Apr 2024
Why in News?
Recently, the Delhi forest department has initiated the establishment of a tissue culture laboratory at the Asola Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary to conserve rare native trees.
- The primary goal of the laboratory is to grow endangered native Delhi trees in a controlled environment and regenerate saplings of species facing regeneration challenges due to invasive species.
What are key Facts about the Tissue Culture Laboratory?
- Tissue Culture Laboratory:
- The lab will be able to extract plant tissue from an in-vitro fully grown plant, generating multiple trees from the same tree.
- The forest department will take assistance from botanists and scientists from the Indian Council of Forestry Research and Education (ICFRE) and the Forest Research Institute (FRI).
- Other Similar Laboratories:
- The National Facility for Plant Tissue Culture Repository (NFPTCR) was established in Delhi at the National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR) in 1986.
- They carry out tissue culture experiments and research on five plant types -- tubers, bulbs, spices, plantation crops, horticultural crops, and medicinal and aromatic plants.
- The National Facility for Plant Tissue Culture Repository (NFPTCR) was established in Delhi at the National Bureau of Plant Genetic Resources (NBPGR) in 1986.
- Application:
- The Aravalli Plan:
- The regeneration of ridge species like Kulu (ghost tree), palash, doodhi, and dhau is hindered by invasive species, resulting in poor survival rates, with large-scale multiplication achievable only through tissue culture, particularly shoot culture.
- The lab will also be useful in culturing endangered medicinal plants.
- Success Stories:
- Tissue culture has proven highly effective in agriculture, particularly with crops such as bananas, apples, pomegranates, and jatropha, offering higher yields compared to traditional farming methods.
- The Aravalli Plan:
- Issues:
- Biodiversity experts have contended that cloning should be limited to "extremely rare trees" to avoid genetic homogeneity and vulnerability to specific diseases.
- Cloning can result in restricted genetic diversity, with the trees being clones of a single tree or plant.
- To avoid this, one should not restrict oneself to a single seed variety; instead, use different parent seeds or seed varieties to prevent having multiple cloned trees.
- Cloning can result in restricted genetic diversity, with the trees being clones of a single tree or plant.
- Experts believe that commonly found species like khair, dhak and desi babool in the Aravallis could waste public funds, despite potential benefits for endangered or nearly extinct species.
- Biodiversity experts have contended that cloning should be limited to "extremely rare trees" to avoid genetic homogeneity and vulnerability to specific diseases.
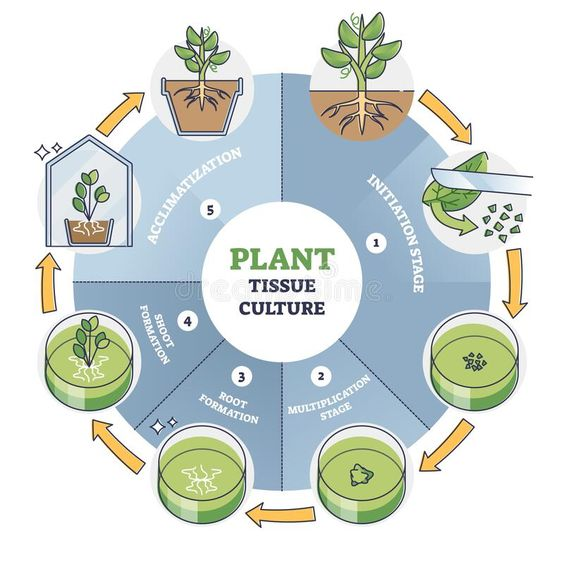
What is Tissue Culture?
- Tissue culture, also known as micro-propagation, allows multiple plants to be produced from a parent plant using in-vitro tissue, which is incubated under a controlled environment.
- Types of Plant Tissue culture:
- Callus Culture: Involves cultivating undifferentiated masses of cells (callus) from explants.
- Cell Suspension Culture: Cultures individual cells or small aggregates of cells in a liquid medium.
- Anther/Microspore Culture: Used for producing haploid plants from pollen grains or anthers.
- Protoplast Culture: Cultures isolated plant cells without cell walls.
- Applications of Plant Tissue Culture:
- Micropropagation: Rapid clonal propagation of plants by culturing small pieces of plant tissue.
- Soma-clonal Variation: Studying genetic variation among plant cells in culture.
- Transgenic Plants: Introducing and expressing foreign genes (transgenes) in plant cells.
- Induction and Selection of Mutations: Using mutagens to induce mutations for specific traits.
Animal Tissue Culture:
- Animal tissue culture is the in vitro maintenance and propagation of isolated cells, tissues, or organs from animals in an appropriate artificial environment.
- Cells used in animal tissue culture are usually obtained from multicellular eukaryotes and their established cell lines.
- This technique allows the study of cell functions, mechanisms, and applications.
- Animal cell culture has revolutionised research and biotechnology, providing insights into cell behaviour and applications across various fields.
Asola Wildlife Sanctuary
- Asola-Bhatti Wildlife Sanctuary is located at the end of an important wildlife corridor that starts from Sariska National Park in Alwar and passes through Mewat, Faridabad and Gurugram districts of Haryana.
- The region has a semiarid climate with notable diurnal temperature variations.
- The vegetation in the Wildlife Sanctuary is predominantly an open canopied thorny scrub. The native plants exhibit xerophytic adaptations such as thorny appendages, and wax-coated, succulent, and tomentose leaves.
- Major wildlife species include Peafowl, Common Woodshrike, Sirkeer Malkoha, Nilgai, Golden Jackals, Spotted deer, etc.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the current trends in the cultivation of sugarcane in India, consider the following statements: (2020)
1. A substantial saving in seed material is made when ‘bud chip settlings’ are raised in a nurse, and transplanted in the main field.
2. When direct planting of setts is done, the germination percentage is better with single-budded setts as compared to setts with many buds.
3. If bad weather conditions prevail when setts are directly planted, single-budded setts have better survival as compared to large setts.
4. Sugarcane can be cultivated using settlings prepared from tissue culture.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
Ans: (c )
Q. Consider the following statements: (2009)
1. Sweet orange plant is propagated by grafting technique.
2. Jasmine plant is propagated by layering technique.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)