Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT) | 19 Jul 2024
Why in News?
Recently, Indian researchers at the Indian Institute of Astrophysics (IIA) in Bengaluru have developed a new online tool to create a comprehensive star catalogue for the Adaptive Optics System (AOS) of the upcoming Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT).
What are the Key Features of Thirty Meter Telescope (TMT)?
- About:
- It is an ambitious international project coming up at Mauna Kea in Hawaii, involving India, the US, Canada, China, and Japan that aims to advance the understanding of the universe significantly.
- India is a key partner in the TMT project, with India TMT Center at IIA leading the national collaboration.
- The TMT is a next-generation astronomical observatory designed to provide unprecedented resolution and sensitivity with its massive 30-meter primary mirror, advanced adaptive optics system, and state-of-the-art instruments.
- The TMT, the Giant Magellan Telescope, and the European Southern Observatory’s Extremely Large Telescope represent the future of ground-based astronomy.
- It is an ambitious international project coming up at Mauna Kea in Hawaii, involving India, the US, Canada, China, and Japan that aims to advance the understanding of the universe significantly.
- Primary Goals:
- Study the early universe and the formation and evolution of the first galaxies and stars after the Big Bang.
- Investigate the formation, structure, and evolution of galaxies across cosmic time.
- Study the relationship between supermassive black holes and their host galaxies.
- Investigate the formation of stars and planetary systems.
- Characterise exoplanets and study their atmospheres.
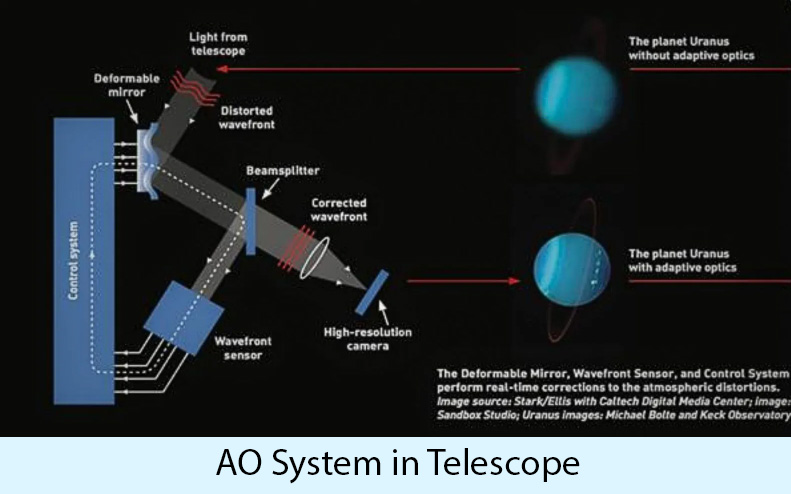
- Adaptive Optics System (AOS) and New Online Tool:
- The TMT’s AOS, known as the Narrow Field Infrared Adaptive Optics System (NFIRAOS), uses deformable mirrors and laser guide stars (LGS) to correct atmospheric turbulence, enhancing image resolution.
- This facility will project up to nine lasers into the sky to create artificial guide stars. However, atmospheric turbulence affects these laser beams, so measuring atmospheric tip-tilt is uncertain.
- To correct these effects, the AO system requires feedback from three real stars, known as Natural Guide Stars (NGS).
- Researchers have developed an automated code that can be used as an online tool to create a catalogue of Near Infrared (NIR) stars.
- The automated code can compute the expected near-infrared magnitudes of stellar sources identified in various optical sky surveys using their optical magnitudes.
Other Major Telescopes
Other Similar Projects India is Part of
- CERN (European Council for Nuclear Research): Project of the “God particle”
- CMS: CMS is one of the experiments that discovered the Higgs Boson, or ‘God particle’
- ALICE: ALICE created conditions that existed at the time of big bang
- International Facility for Antiproton and Ion Research (FAIR): Studying the building blocks of matter and the evolution of the Universe.
- NUSTAR (Nuclear Structure, Astrophysics and Reactions)
-
CBM (Compressed Baryonic Matter)
-
PANDA (Antiproton Annihilation at Darmstadt)
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q1. In the context of modern scientific research, consider the following statements about ‘IceCube’, a particle detector located at South Pole, which was recently in the news: (2015)
- It is the world’s largest neutrino detector, encompassing a cubic kilometre of ice.
- It is a powerful telescope to search for dark matter.
- It is buried deep in the ice.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct ?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q2. In the context of space technology, what is “Bhuvan”, recently in the news? (2010)
(a) A mini-satellite launched by ISRO to promote distance education in India
(b) The name given to the next Moon Impact Probe, for Chandrayan-II
(c) A geoportal of ISRO with 3D imaging capabilities of India
(d) A space telescope developed by India
Ans: C