Important Facts For Prelims
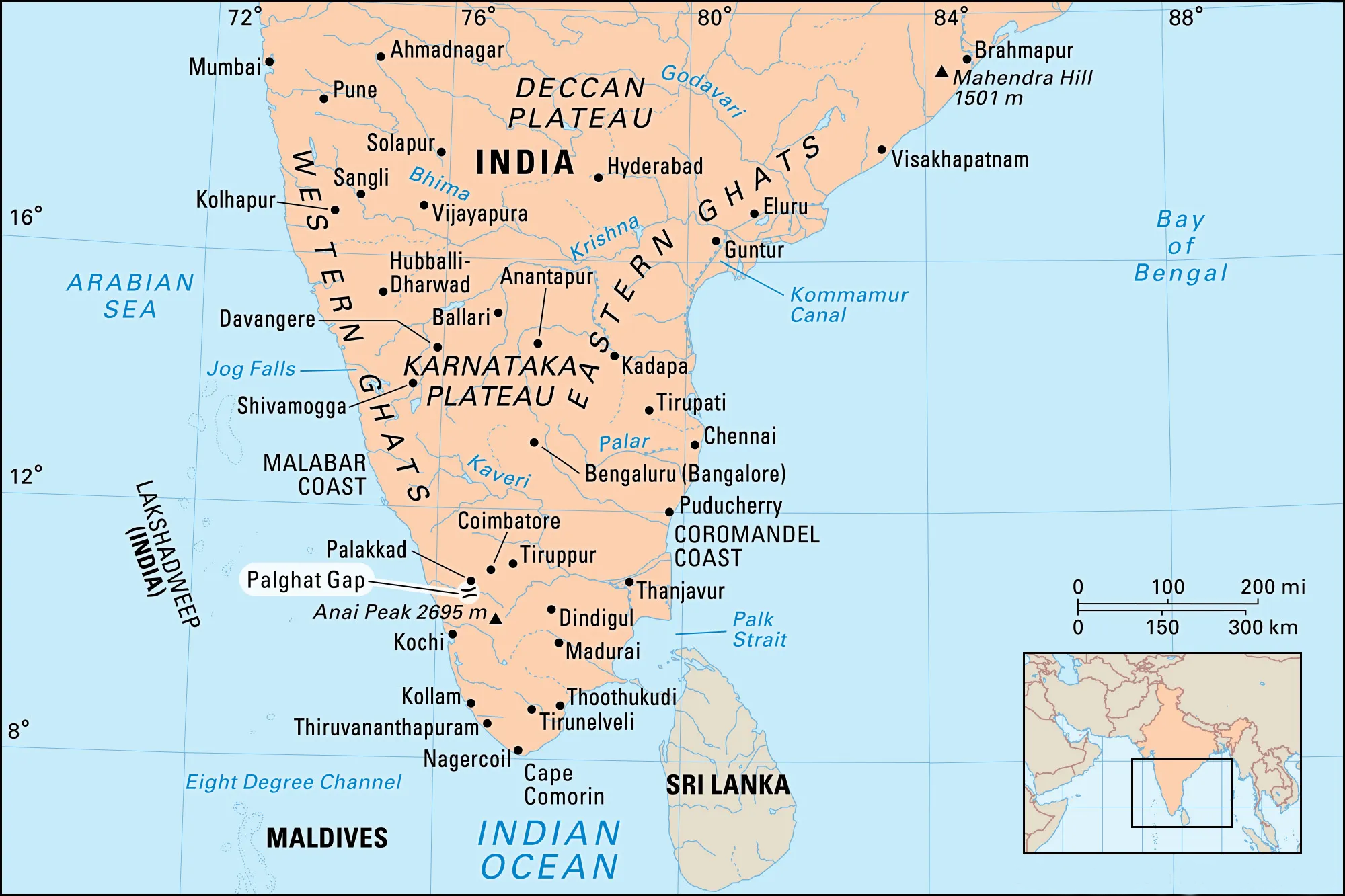
The Palghat Gap
- 16 May 2023
- 4 min read
Why in News?
Often called as a significant discontinuity in the Western Ghats, the Palghat Gap is a geographical marvel spanning approximately 40 km in width, separating the Nilgiris and Anamalai hills, both towering above 2,000 meters above sea level.
What is the Significance of Palghat Gap?
- Origin and Formation: The Palghat Gap originated due to the drift of continental shelves after the separation of Australia and Africa from the Gondwana landmass.
- The splitting of India and Madagascar led to the formation of the Gap approximately 100 million years ago.
- Vegetation: In contrast to the tropical rainforests of the Western Ghats, the vegetation in the Palghat Gap is classified as dry evergreen forest.
- Significance:
- Historical:
- Gateway to Kerala: The Palghat Gap has historically served as a vital entry point into Kerala, facilitating both road and rail transportation between Coimbatore and Palakkad.
- Also, the Bharathappuzha river flows through the Palghat Gap, enhancing its importance as a transportation route.
- Gateway to Kerala: The Palghat Gap has historically served as a vital entry point into Kerala, facilitating both road and rail transportation between Coimbatore and Palakkad.
- Geographical:
- Shear Zone: The Palghat Gap is a geological shear zone, running from east to west, which represents a weak region in the earth's crust.
- This geological characteristic can explain occasional tremors experienced in the Coimbatore region.
- Climate: While the Western Ghats north of the Palghat Gap receive more annual rainfall, the southern region experiences more evenly distributed rainfall throughout the year.
- Shear Zone: The Palghat Gap is a geological shear zone, running from east to west, which represents a weak region in the earth's crust.
- Ecological:
- Biogeographic Distinctions: The distinct flora and fauna on either side of the Palghat Gap are believed to be a consequence of ancient river systems or past incursions of the sea.
- Genetic Variations: Genetic studies have revealed differences in the mitochondrial DNA of elephant populations residing on the Nilgiris side compared to those in the Anamalai and Periyar sanctuaries.
- Bird Species Variation: Research conducted by IISc Bangalore highlighted genetic divergence in the White-bellied Shortwing, an endemic and threatened bird species.
- The Nilgiri blue robin and White-bellied blue robin populations exhibit slight variations in appearance based on their location around Ooty and the Anamalai hills.
- Species Richness and Phylogenetic Diversity: A recent study conducted by groups from CCMB at Hyderabad and other institutions revealed that the southern region of the Western Ghats, located south of the Palghat Gap, boasts abundant species richness and phylogenetic diversity.
- This region is home to more than 450 tree species, including ancient species like Magnolia champaca (Champa; Tamil: Sambagan), which have thrived for over 130 million years.
- Historical:
- Other Gaps:
- Thalghat (Mumbai and Nashik)
- Bhorghat( Mumbai and Pune)
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. ‘Gadgil Committee Report’ and ‘Kasturirangan Committee Report’, sometimes seen in the news, are related to (2016)
(a) constitutional reforms
(b) Ganga Action Plan
(c) linking of rivers
(d) protection of Western Ghats
Ans: (d)