Place In News
`Thar Desert
- 11 Apr 2025
- 2 min read
According to a new study, the Thar Desert in India has experienced a 38% annual increase in greening over the past two decades, driven by significant monsoon rainfall and agricultural expansion.
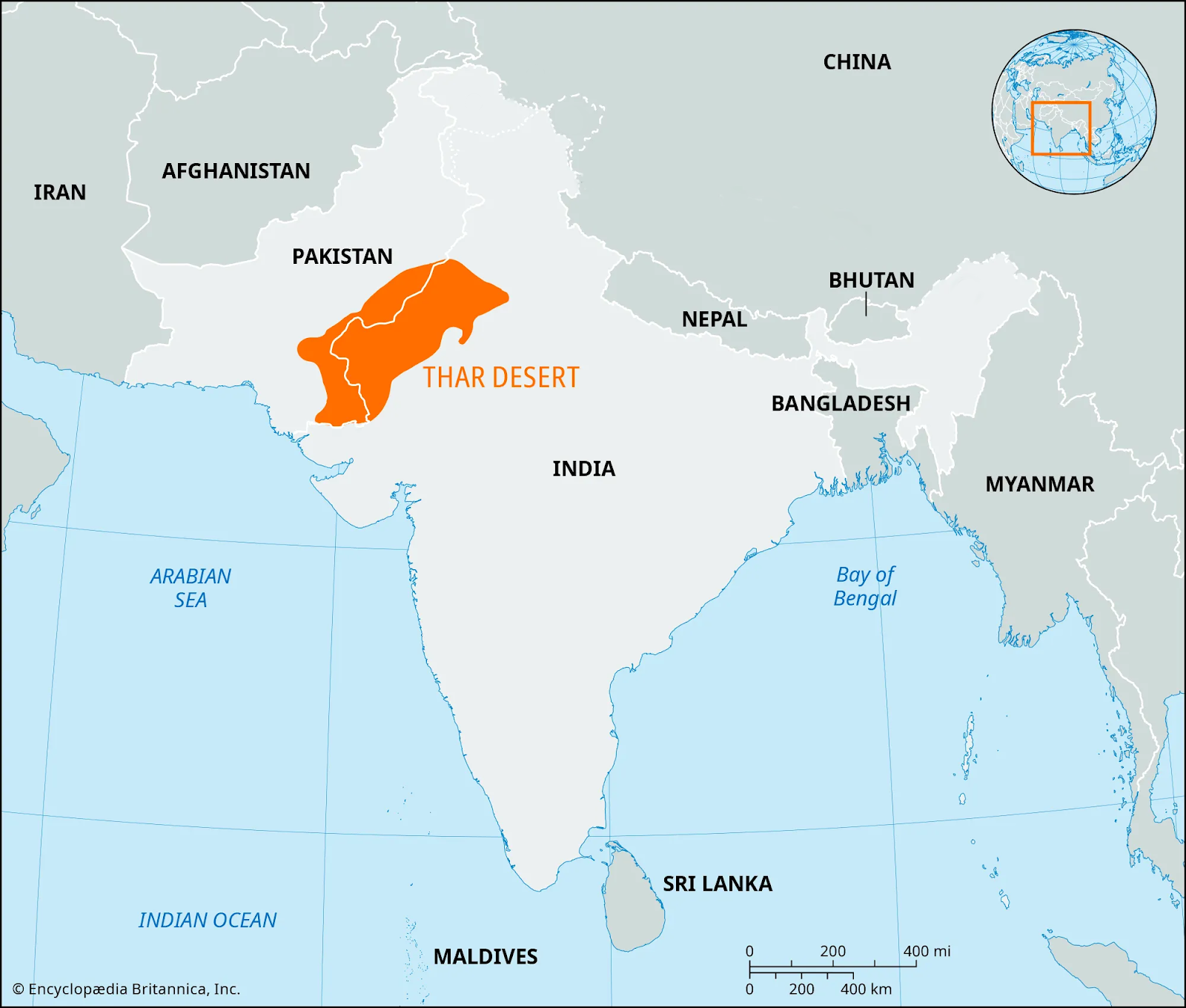
- Location of Thar Desert (The Great Indian Desert): It is an arid region of rolling sand hills on the Indian subcontinent. It spans an area of 200,000 sq kms across northwestern India (Rajasthan, Gujarat, Punjab, and Haryana) and southeastern Pakistan (Sindh and Punjab provinces).
- Geography & Climate: It is bordered by the Indus River plain to the west, the Punjab Plain to the north and northeast, the Aravalli Range to the southeast, and the Rann of Kachchh to the south.
- The desert experiences a subtropical desert climate, characterized by persistent high pressure and subsidence.
- Soil Composition: The desert's soils include Desert, Red Desertic, Sierozems, Red and Yellow, Saline, Lithosols, and Regosols.
- These soils are coarse-textured, well-drained, and calcareous (calcium-bearing), supporting specific vegetation and agriculture.
- Biodiversity: Supports a relatively rich biodiversity, including Blue Bull (Nilgai), Blackbuck, Great Indian Bustard (GIB) and Indian Gazelle (Chinkara).
- It is home to one of the largest national parks in India– Desert National Park (Rajasthan).
- Mineral Resources: The Desert houses one of the world's largest lignite coal reserves.
- It is rich in gypsum, and salt (with saltwater lakes– Sambhar and Kuchaman).
| Read More: Thar Desert |