International Relations
Talks Between India & NATO
- 18 Aug 2022
- 3 min read
For Prelims: NATO, Soviet Union.
For Mains: Bilateral Groupings & Agreements, Significance India’s Relations with Other Countries.
Why in News?
It was recently reported India held its first political dialogue with the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) in Brussels on December 12, 2019.
What is NATO?
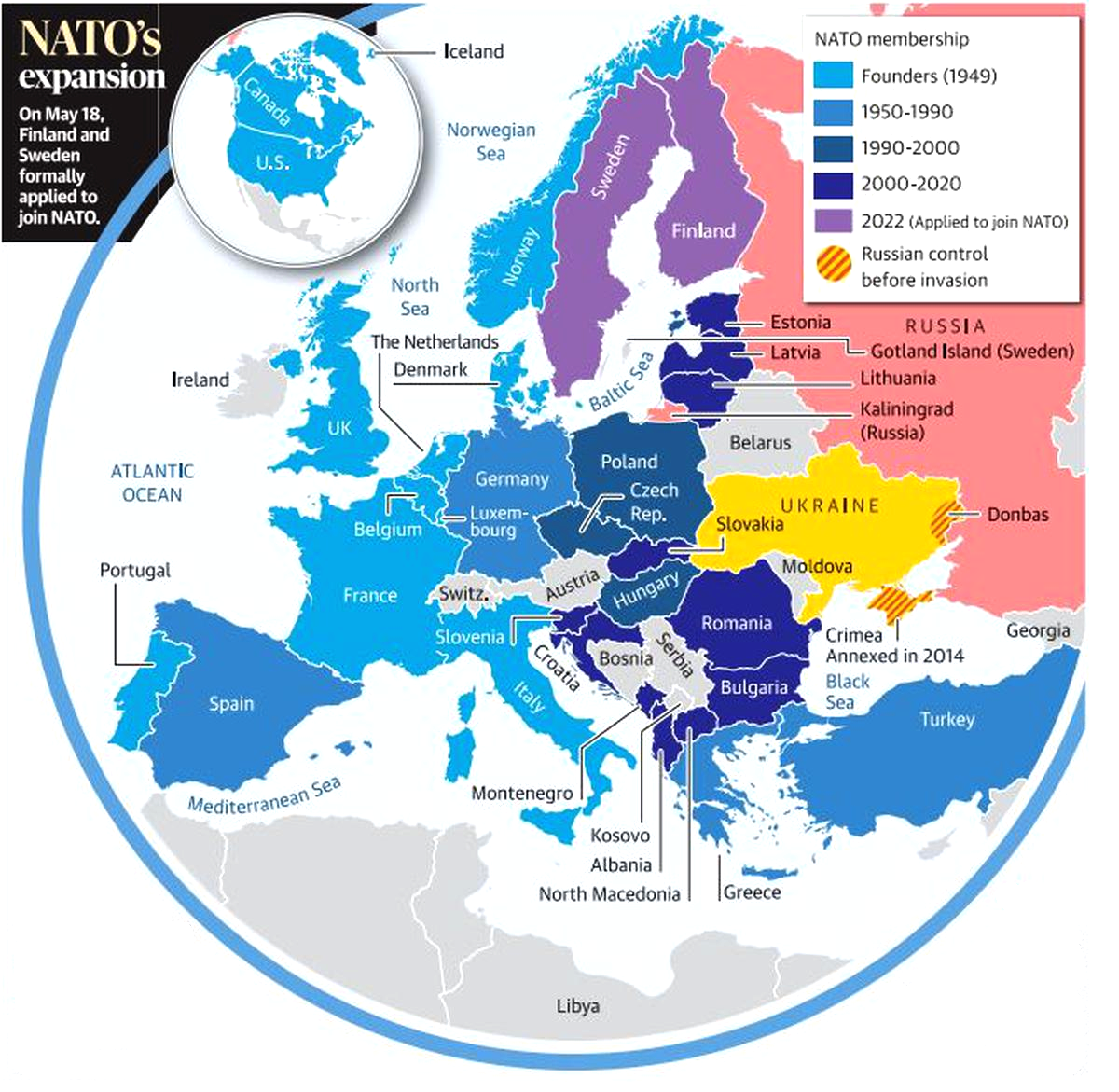
- North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is a military alliance established by the North Atlantic Treaty (also called the Washington Treaty) of April 1949, by the United States, Canada, and several Western European nations to provide collective security against the Soviet Union.
- There are currently 30 member states.
- Original Members:
- Belgium, Canada, Denmark, France, Iceland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Norway, Portugal, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
- Other Countries:
- Greece and Turkey (1952), West Germany (1955, from 1990 as Germany), Spain (1982), the Czech Republic, Hungary, and Poland (1999), Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia, and Slovenia (2004), Albania and Croatia (2009), Montenegro (2017), and North Macedonia (2020).
- France withdrew from the integrated military command of NATO in 1966 but remained a member of the organization, it resumed its position in NATO’s military command in 2009.
- Recently, Finland and Sweden have shown interest to join NATO.
- Original Members:
- Headquarters: Brussels, Belgium.
What is the NATO-India Political Dialogue?
- About:
- India held its first political dialogue with the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) in Brussels on December 12, 2019.
- Significance:
- NATO has been engaging both China and Pakistan in bilateral dialogue.
- While Engaging NATO in a political dialogue would provide India an opportunity to bring about a balance in NATO’s perceptions about the situation in regions and issues of concern to India.
- There is convergence in the perspectives of both India and NATO on China, terrorism, and Afghanistan, including Pakistan’s role in Afghanistan.
- Issues:
- According to NATO’s perspective, the biggest threat it face was not China, but Russia whose aggressive actions are threatening European security.
- Further, NATO had faced difficulties to convene meetings of the NATO-Russia Council due to Russian refusal to place issues such as Ukraine and Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty,
- Given the divergence among NATO countries, its view on China was seen as mixed, while it did deliberate on China’s rise, it presented both a challenge and an opportunity,
- Further, in Afghanistan, NATO saw the Taliban as a political entity.
- Given the divergence among NATO countries, its view on China was seen as mixed, while it did deliberate on China’s rise, it presented both a challenge and an opportunity,
- Further, NATO had faced difficulties to convene meetings of the NATO-Russia Council due to Russian refusal to place issues such as Ukraine and Intermediate-Range Nuclear Forces Treaty,
- According to NATO’s perspective, the biggest threat it face was not China, but Russia whose aggressive actions are threatening European security.
- NATO’S View:
- Dialogue with India would further enhance the cooperation among NATO countries and India’s geo-strategic location shares a unique perspective and enhances international security in India's own region and beyond.