Internal Security
Surveillance Balloon
- 06 Feb 2023
- 6 min read
For Prelims: Surveillance Balloon, Human Intelligence, Outer Space Treaty 1967.
For Mains: Ways of Surveillance Techniques, Air Space and Related Laws.
Why in News?
The United States (US) shot down a Chinese surveillance balloon that has been spotted over US airspace for a couple of days.
What is a Surveillance Balloon?
- About:
- These cheap, quiet and hard-to-reach balloons have been used for reconnaissance purposes, including in conflicts like the American Civil War.
- The practice became widespread during World War I and was used extensively during the Cold War when the US launched hundreds of balloons to gather intelligence on the Soviet Union and China.
- While their use has declined with the rise of unmanned drones and satellites, many countries still employ spy balloons.
- The Purpose of Sending the Balloon:
- China has for decades complained about US surveillance by ships and spy planes near its own territory, leading to occasional confrontations over the years. According to China, the balloon was for research but got off track.
Why do Governments use Surveillance Balloons?
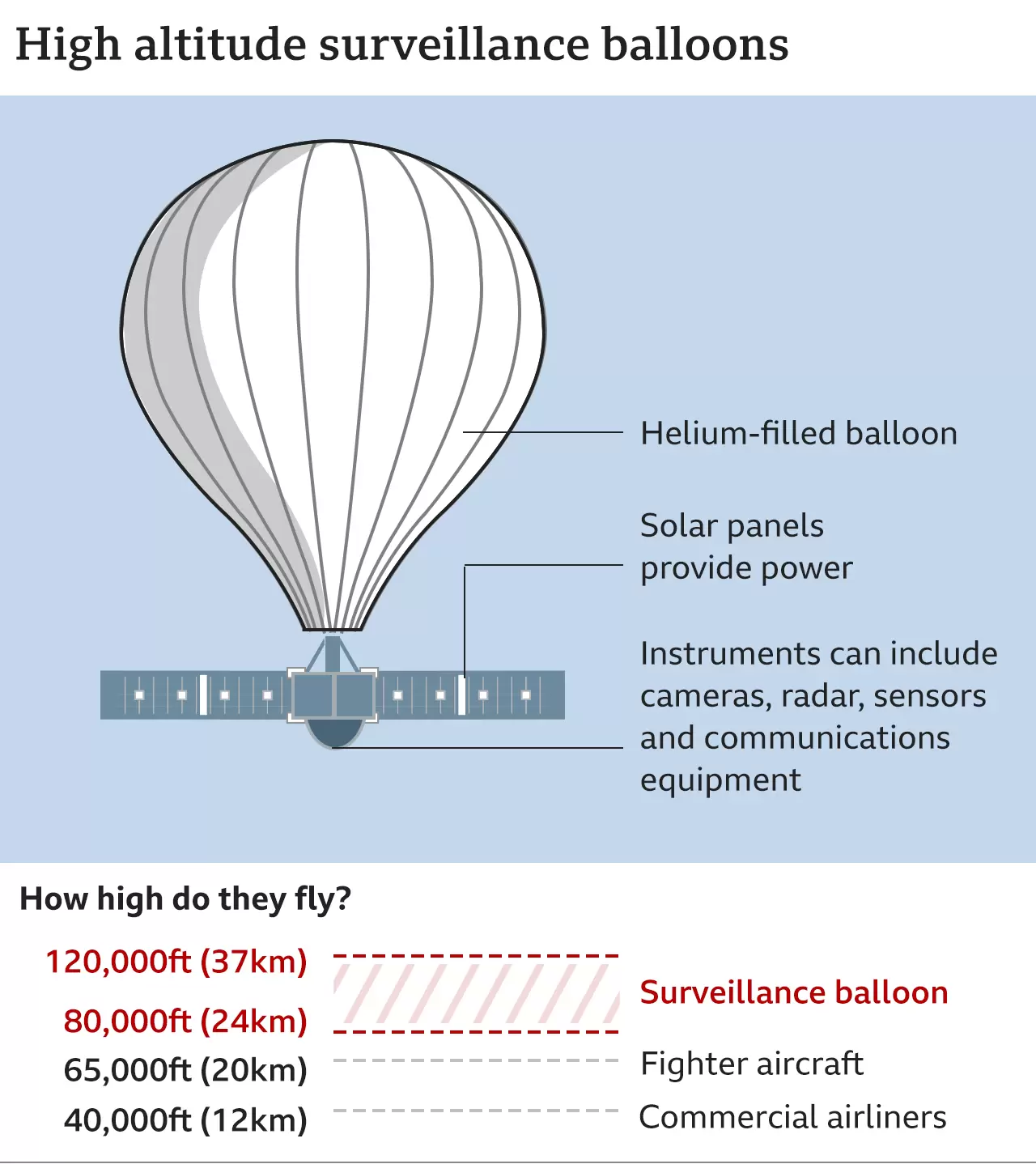
- Close-range Monitoring: In the age of satellites, surveillance balloons which are typically advanced balloons equipped with high-tech, downward-pointing imaging gear offer close-range monitoring.
- Image Quality: The lower-flying balloons, which hover at about the same height as commercial airlines fly, can typically take clearer images than the lowest orbiting satellites.
- Satellites that rotate in sync with Earth capture continuous but hazier images due to farther orbit.
- Intercepting Communication: Surveillance balloons can also be capable of “gathering electronic signals” and intercepting communications.
What are the Other Ways of Surveillance Techniques?
- Electronic Surveillance: It can be used in intercepting communication signals, tapping phone calls, and monitoring emails and other forms of digital communication.
- Human Intelligence (HUMINT): It is one of the main components used in surveillance by recruiting individuals with access to sensitive information, such as embassy staff, military personnel, or government officials.
- Cyber Espionage: It is a form of cyber-attack that steals classified, sensitive data or intellectual property to gain an advantage over a competitive company or government entity.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites are sometimes used to gather information about foreign countries.
- Drone Technology: Drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) can be used for surveillance and espionage purposes. Drones equipped with cameras, listening devices, and other sensors can fly over foreign territories and gather intelligence.
What is Air Space and its Related Laws?
- About:
- Air space, in international law, is the space above a particular national territory, treated as belonging to the government controlling the territory.
- It does not include outer space, which, under the Outer Space Treaty of 1967 is declared to be free and not subject to national appropriation.
- The treaty, however, did not define the altitude at which outer space begins and air space ends.
- Air Sovereignty:
- It is the fundamental right of a sovereign state to regulate the use of its air space and enforce its own aviation law.
- The State controls the entry of foreign aircraft into its territory and that persons within its territory are subject to its laws.
- The principle of air space sovereignty is established through the Paris Convention on the Regulation of Aerial Navigation (1919) and subsequently by other multilateral treaties.
- Under the 1944 Chicago Convention, contracting states agree to permit aircraft registered in the other contracting states and engaged in commercial non-scheduled flights to fly into their territory without prior diplomatic permission and, moreover, to pick up and discharge passengers, cargo, and mail.
- This provision, in practice, has become a dead letter.
- Prohibited Air Space:
- It refers to an area of air space within which flight of aircraft is not allowed, usually due to security concerns. It is one of many types of special use airspace designations and is depicted on aeronautical charts with the letter "P" followed by a serial number.
- Restricted Air Space:
- Different from prohibited air space, in this space, entry is typically forbidden for all aircraft and is not subjected to clearance from ATC (Air Traffic Control) or the air space's controlling body.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. International civil aviation laws provide all countries complete and exclusive sovereignty over the airspace above their territory. What do you understand by ‘airspace’? What are the implications of these laws on the space above this airspace? Discuss the challenges which this poses and suggest ways to contain the threat. (2014)