Indian Economy
Surplus Liquidity
- 08 Jun 2023
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Repo rate, reverse rapo rate, monetary policy committee, concepts related to inflation
For Mains: Impact of increased liquidity, factors leading to increase in liquidity in the market
Why in News?
Recently, the net liquidity in the banking system in India increased to Rs 2.59 lakh crore on June 4, 2023. However, the surplus liquidity in the banking system is likely to decline to around Rs 1.5 lakh crore over the next few days from the current level of Rs 2.1 lakh crore.
- The net liquidity in the banking system is represented by the amount of money absorbed by the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) from the system.
What is Surplus Liquidity?
- About:
- Surplus liquidity occurs where cashflows into the banking system persistently exceed withdrawals of liquidity from the market by the central bank.
- Liquidity in the banking system refers to readily available cash that banks need to meet short-term business and financial needs.
- Surplus liquidity occurs where cashflows into the banking system persistently exceed withdrawals of liquidity from the market by the central bank.
- Causes of Increased Liquidity:
- Advance tax and goods and services tax (GST) payments,
- The deposit of withdrawn Rs 2,000 notes,
- Redemption of government bonds,
- Higher government spending,
- The sale of dollars by the RBI to defend the rupee from depreciation.
- Impact of Increased liquidity:
- It may lead to increased levels of inflation.
- Interest rates in the market will remain low.
- RBI's Measures:
- The RBI takes action if liquidity levels deviate from its comfort range.
- The RBI, under its Liquidity Adjustment Facility, infuses liquidity in the banking system via repos and sucks it out using reverse repos after assessing liquidity conditions.
- The RBI also uses a 14-day variable rate repo and/or reverse repo operation.
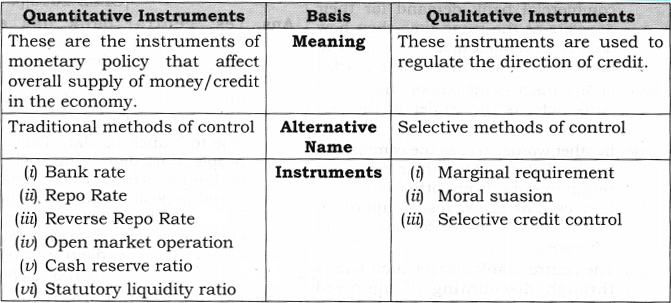
What are the Tools Used by RBI to control Money Supply?
| Various Instruments of Monetary Policy | |
| Repo Rate: |
|
|
Reverse Repo Rate: |
|
|
Liquidity Adjustment Facility (LAF): |
|
|
Marginal Standing Facility (MSF): |
|
| Corridor: |
|
|
Bank Rate: |
|
|
|
|
Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR): |
|
|
Open Market Operations (OMOs):
|
|
|
Market Stabilisation Scheme (MSS):
|
|
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. The money multiplier in an economy increases with which one of the following?(2021)
(a) Increase in the Cash Reserve Ratio in the banks
(b) Increase in the Statutory Liquidity Ratio in the banks
(c) Increase in the banking habit of the people
(d) Increase in the population of the country
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- In macroeconomics, the money multiplier is important because it determines the money supply.
- Money multiplier shows the magnified change in the money supply that results from the infusion of additional reserves into the banking system.
- The most basic multiplier used in computing the multiplier effect is calculated as change in income / change in spending.
- The money multiplier effect can be seen in a country’s banking system. An increase in bank lending should translate to an expansion of a country’s money supply. Thus, the money multiplier in an economy increases with an increase in the banking habits of the people.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Mains
Question: Do you agree with the view thatsteady GDP growth and low inflation have left the Indian economyin good shape? Give reasons in support of your arguments. (2019)





-min.jpg)