Important Facts For Prelims
Sukapaika River
- 25 Oct 2022
- 6 min read
Why in News?
The Sukapaika River which stopped flowing 70 years ago, is set to be rejuvenated as the Odisha government has started working on its revival plan following a recent direction from the National Green Tribunal (NGT).
What are the Key Points of Sukapaika River?
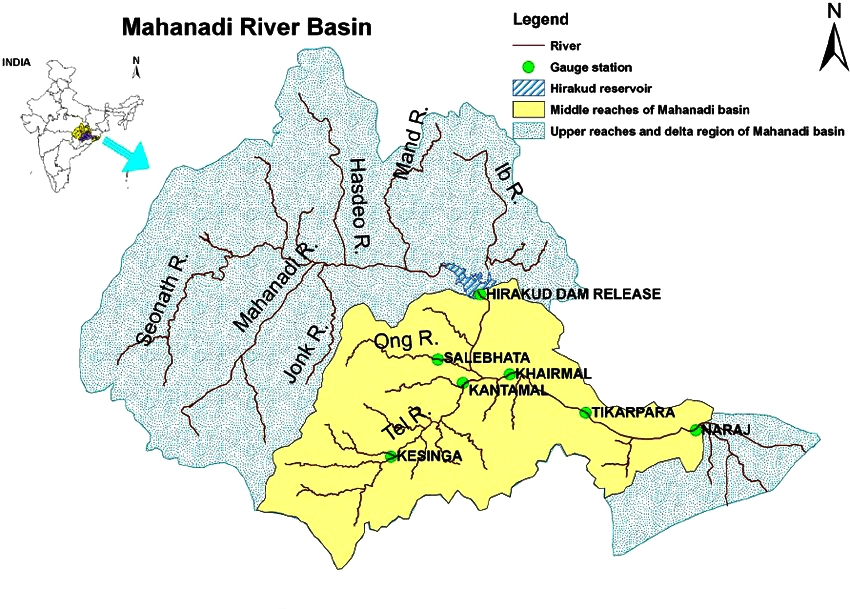
- Sukapaika is one of the several distributaries of the mighty Mahanadi river in Odisha.
- It branches away from the Mahanadi at Ayatpur village in Cuttack district and flows for about 40 kilometres (km) before rejoining its parent river at Tarapur in the same district.
- Sukapaika river is an important system of the Mahanadi to control floodwater and maintain the flow in the river as well as the Bay of Bengal.
What are the Key Points of Mahanadi River?
- About:
- The Mahanadi River system is the third largest of peninsular India after Godavari and Krishna, and the largest river of Odisha state.
- The catchment area of the river extends to Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Jharkhand and Maharashtra.
- Its basin is bounded by the Central India hills on the north, by the Eastern Ghats on the south and east and by the Maikala range in the west.
- Source:
- It rises from a place near Sihawa, in the Dhamtari district of Chhattisgarh.
- Major Tributaries:
- The Seonath, the Hasdeo, the Mand and the Ib joins Mahanadi from left whereas the Ong, the Tel and the Jonk joins it from right.
- Major Dams/Projects on Mahanadi:
- Hirakud Dam: This is the longest dam of India.
- Ravishankar Sagar, Dudhawa Reservoir, Sondur Reservoir, Hasdeo Bango and Tandula are other major projects.
- Industries:
- Mahanadi basin, because of its rich mineral resource and adequate power resource, has a favourable industrial climate.
- Iron and Steel plant at Bhilai
- Aluminium factories at Hirakud and Korba
- Paper mill near Cuttack
- Cement factory at Sundargarh.
- Other industries based primarily on agricultural produce are sugar and textile mills.
- Mining of coal, iron and manganese are other industrial activities.
- Mahanadi basin, because of its rich mineral resource and adequate power resource, has a favourable industrial climate.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question
Q. Consider the following rivers: (2014)
- Barak
- Lohit
- Subansiri
Which of the above flows/flow through Arunachal Pradesh?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
- Barak rises in the Manipur hills and enters the plains near Lakhipur. The River flows through the states of Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram and Assam in India and drains into the Bay of Bengal via Bangladesh. It is being developed as one of the Inland waterways of India. Hence, 1 is not correct.
- Major rivers flowing through Arunachal Pradesh: Subansiri, Lohit/Tellu R, Dihang/Siang, Kameng.
- Lohit is a tributary of Brahmaputra. The river rises in Tibet Autonomous Region, where it is known as the Zayü River. It descends through the mountainous region and surges through Arunachal Pradesh in India for 200 kilometres before entering the plains of Assam where it is known as the Lohit River. Hence, 2 is correct.
- Subansiri rises in the mountains of Tibet. The total length of the Subansiri is about 442 km, out of which 192 km lies in Arunachal Pradesh and 190 km in Assam and the rest part falls in Tibet. Hence, 3 is correct.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2014)
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
- Harike is one of the largest man-made wetlands of Northern India. It came into existence in 1952 after the construction of barrage near the confluence of rivers Satluj and Beas. It was accorded the wetland status in 1990 under the Ramsar Convention. Hence, pair 1 is correctly matched.
- Keoladeo National Park is situated at the confluence of the Gambhir and Banganga rivers in the Bharatpur district of Rajasthan. Hence, pair 2 is not correctly matched.
- Kolleru Lake is located between Krishna and Godavari deltas. Kolleru spreads into two districts –Krishna and West Godavari. Hence, pair 3 is not correctly matched.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.