Subclinical Tuberculosis | 19 Aug 2024
Why in News?
Subclinical Tuberculosis (TB) is a growing concern in India, contributing to the slow decline in TB incidence rates despite advances in detection and treatment.
What is Subclinical Tuberculosis?
- Definition: Subclinical TB refers to a form of TB infection where individuals do not exhibit the typical symptoms of the disease, such as a persistent cough.
- This makes it harder to detect compared to active TB, which presents with more apparent symptoms.
- Detection: It is often identified through imaging techniques like chest X-rays or molecular tests, as it may not be noticeable through routine symptom-based screenings.
- Prevalence: Subclinical TB accounted for 42.6% of cases in the National TB Prevalence Survey (2019-2021), with similar findings in Tamil Nadu (39%).
- Although asymptomatic, individuals with subclinical TB can still spread the bacteria to others.
- High-burden countries, including India, have a considerable proportion of subclinical TB, which remains largely undetected, thus sustaining the transmission of the disease.
- Countries like Vietnam have successfully reduced TB prevalence by screening entire populations using X-rays and molecular tests, regardless of symptoms.
- Implementing similar large-scale screening in India would require strategic shifts, including mobile units and community engagement.
- Impact: This form of TB can contribute to the slow decline in overall TB incidence rates, as it remains largely undetected and untreated.
What are the Key Facts About Tuberculosis?
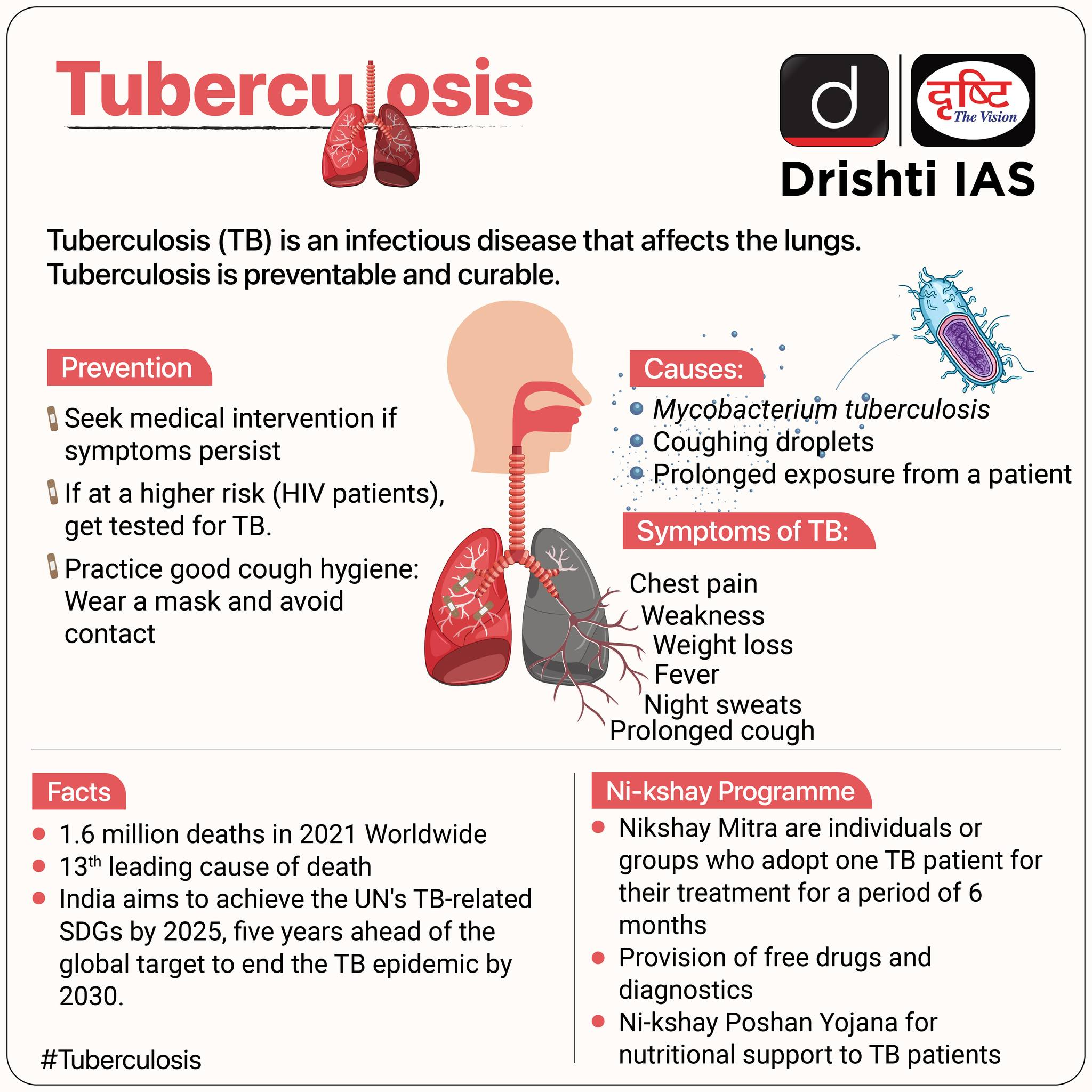
- About: TB is an infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis, that mainly affects the lungs. It spreads through the air when infected people cough, sneeze or spit.
- Symptoms: Prolonged cough, chest pain, weakness, fatigue, weight loss, fever, and night sweats.
- Diabetes, weakened immune system, malnutrition, tobacco use can increase the risk of TB disease.
- Prevention: Seek medical attention, get tested if at risk, early treatment. The Bacille Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine helps prevent TB outside the lungs but not in the lungs.
- Prevalence and Treatment: About 25% of the global population has been infected with TB bacteria. 5-10% of these infections progress to active TB disease.
- TB is preventable and curable with antibiotics, typically including isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol, and streptomycin.
- Multidrug-resistant TB (MDR-TB) is caused by bacteria resistant to first-line drugs, treatable with costly and toxic second-line drugs.
- MDR-TB remains a public health crisis, with only about 2 in 5 people accessing treatment in 2022.
- TB and HIV: People living with HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) are 16 times more likely to develop TB. TB is the leading cause of death among people with HIV.
- Without proper treatment, 60% of HIV-negative people with TB and nearly all HIV-positive people with TB will die.
- Impact: TB disproportionately affects adults in low and middle-income countries, with over 80% of cases and deaths occurring in these regions. The highest burden is in the World Health Organization’s (WHO) South-East Asian and African Regions.
- A total of 1.3 million people died from TB in 2022 (including 167 000 people with HIV). Worldwide, TB is the second leading infectious killer after Covid-19.
- Initiatives Related to TB:
- India:
- The National TB Elimination Programme (NTEP) to Eliminate TB by 2025.
- Ni-kshay Mitra Initiative.
- Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) provided to TB patients.
- TB-Mukt Panchayat Initiative: Launched to leverage the support of over 2.5 lakh Gram Panchayats to increase TB awareness, eliminate stigma, and improve service uptake.
- Pradhan Mantri TB Mukt Bharat Abhiyan (PMTBMBA)
- India:
-
Global:
-
The Global Tuberculosis Programme by the World Health Organization works towards the goal of a world free of TB, with zero deaths, disease and suffering due to the disease.
-
Global Plan to End TB 2023-2030 is a plan to end tuberculosis as a public health challenge by 2030, in line with the UN Sustainable Development Goals.
- SDG 3 aims to prevent needless suffering from preventable diseases and premature death by focusing on key targets that boost the health of a country's overall population.
- Global Tuberculosis Report.
-
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following diseases can be transmitted from one person to another through tattooing? (2013)
- Chikungunya
- Hepatitis B
- HIV-AIDS
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)