International Relations
Strengthening India-Nepal Cooperation
- 05 Jun 2023
- 9 min read
For Prelims: India and Nepal Relations, Exercise Surya Kiran, 2015 Earthquake, India-Nepal Treaty of Peace and Friendship of 1950, Phukot Karnali Hydro Electric Project, Lower Arun Hydroelectric Project, Gorakhpur-Bhutwal Transmission Line.
For Mains: Areas of Cooperation Between India and Nepal, Recent Major Issues Related to India-Nepal Relations.
Why in News?
India and Nepal have recently unveiled several initiatives and agreements during the 4-day visit of the Prime Minister of Nepal to India to boost their bilateral cooperation in the fields of energy and transport development, aiming to strengthen ties and facilitate regional connectivity.
What are the Major Highlights of Recent Agreement?
- Power Sector Cooperation:
- Long-Term Power Trade Agreement: India and Nepal signed a long-term Power Trade Agreement, targeting the import of 10,000 MW of electricity from Nepal in the coming years.
- Hydropower Projects: Memoranda of Understanding (MoUs) were signed between National Hydroelectric Power Corporation (NHPC), India and Vidyut Utpadan Company Ltd, Nepal for the development of the Phukot Karnali Hydroelectric Project and the Lower Arun Hydroelectric Project.
- Also, the two Prime Ministers expressed their commitment to achieving tangible and time-bound progress on the Pancheshwar multipurpose project, which aims to enhance cooperation in harnessing the shared water resources of the Mahakali River.
Note: Phukot Karnali Hydro Electric Project aims to generate 480 MW of power using the flow from the Karnali River, with an average annual generation of about 2448 GWh. It includes a high RCC( Reinforced Concrete Cement) dam and an underground power house.
- Transport Development:
- Transmission Line and Rail Link: The groundbreaking ceremony for the Gorakhpur-Bhutwal Transmission Line and the inauguration of the Indian Railway cargo train from Bathnaha to Nepal Customs Yard highlighted the focus on enhancing connectivity between the two countries.
- Integrated Checkposts (ICPs): ICPs were inaugurated at Nepalgunj (Nepal) and Rupaidiha (India), promoting smoother cross-border trade and facilitating the movement of goods and people.
- Other Initiatives:
- A plan to extend South Asia’s first cross-border petroleum pipeline from Motihari in India to Amlekhgunj in Nepal by another 69 km up to Chitwan in Nepal.
- Also, a second cross-border petroleum pipeline from Siliguri in India to Jhapa in eastern Nepal.
- A revised Treaty of Transit signed on June 1, 2023, that will give Nepal access to India’s inland waterways.
- This will enable Nepal to use Indian ports such as Haldia, Kolkata, Paradip and Visakhapatnam for its third-country trade.
- It will also reduce transportation costs and time for Nepalese exporters and importers.
- India is also cooperating with Nepal to set up a fertiliser plant, emphasising the importance of collaboration in the agricultural sector.
- A plan to extend South Asia’s first cross-border petroleum pipeline from Motihari in India to Amlekhgunj in Nepal by another 69 km up to Chitwan in Nepal.
What are the Other Areas of Cooperation Between India and Nepal?
- About:
- As close neighbours, India and Nepal share unique ties of friendship and cooperation characterised by an open border and deep-rooted people-to-people contacts of kinship and culture.
- The India-Nepal Treaty of Peace and Friendship of 1950 forms the bedrock of the special relations that exist between India and Nepal.
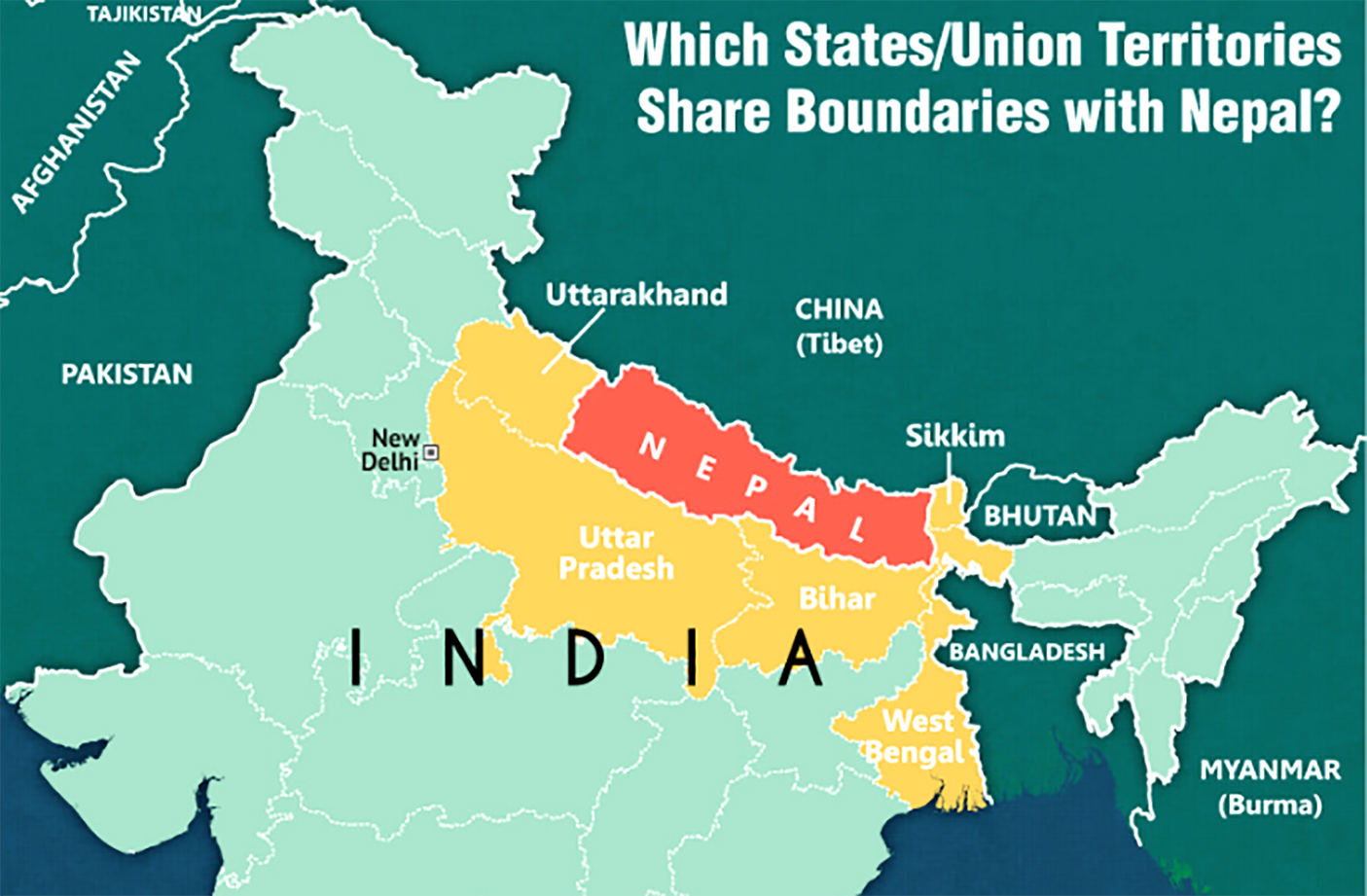
- Nepal shares a border of over 1850 km with five Indian states – Sikkim, West Bengal, Bihar, Uttar Pradesh and Uttarakhand.
- There has been a long tradition of free movement of people across the border.
- As close neighbours, India and Nepal share unique ties of friendship and cooperation characterised by an open border and deep-rooted people-to-people contacts of kinship and culture.
- Defence Cooperation:
- India has been assisting the Nepal Army (NA) in its modernisation by supplying equipment and providing training.
- The ‘Indo-Nepal Battalion-level Joint Military Exercise Surya Kiran’ is conducted alternately in India and in Nepal.
- Also, Currently, about 32,000 Gorkha Soldiers from Nepal are serving in the Indian Army.
- Economic Cooperation:
- India is the largest trading partner of Nepal. Nepal is also India’s 11th largest export destination.
- In 2022-23, India exported goods worth USD 8 billion to Nepal while its imports were at USD 840 million.
- Indian firms are among the largest investors in Nepal, accounting for more than 30% of the total approved foreign direct investments.
- India is the largest trading partner of Nepal. Nepal is also India’s 11th largest export destination.
- Cultural Cooperation:
- India and Nepal share similar ties in terms of Hinduism and Buddhism with Buddha’s birthplace Lumbini located in present day Nepal.
- The Swami Vivekananda Centre for Indian Culture was set up in Kathmandu in August 2007 to showcase the best of Indian culture.
- The Nepal-Bharat Library was founded in 1951 in Kathmandu. It is regarded as the first foreign library in Nepal.
- Humanitarian Assistance:
- India has provided 1.54 billion Nepalese Rupees (INR nearly 96 crore) to Nepal as part of its commitment towards assistance and rehabilitation after the 2015 earthquake .
What are Recent Major Issues Related to India-Nepal Relations?
- Boundary Dispute: The boundary dispute is one of the contentious issues that has strained India-Nepal relations in recent years. The dispute mainly involves two segments:
- Kalapani-Limpiyadhura-Lipulekh trijunction area in western Nepal and Susta area in southern Nepal.
- Both countries claim these areas as part of their territory based on different historical maps and treaties.
- The dispute flared up in 2020 when India inaugurated a road linking Dharchula in Uttarakhand with Lipulekh pass near the China border, which Nepal objected to as a violation of its sovereignty.
- Nepal then issued a new political map that shows Kalapani-Limpiyadhura-Lipulekh as part of its territory. India rejected this map as “artificial enlargement” of Nepalese claims.
- Kalapani-Limpiyadhura-Lipulekh trijunction area in western Nepal and Susta area in southern Nepal.
- China’s Rising Footprints:
- The rise of China’s influence in Nepal has raised concerns in India about its strategic interests in the region. China has increased its economic engagement with Nepal through projects under its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) such as railways, highways, hydropower plants etc.
- Rising Nepal and China cooperation can undermine Nepal’s distinction of a buffer state between India and China.
- The rise of China’s influence in Nepal has raised concerns in India about its strategic interests in the region. China has increased its economic engagement with Nepal through projects under its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) such as railways, highways, hydropower plants etc.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Digital Connectivity: Emphasizing digital connectivity initiatives can provide an innovative way to engage with Nepal.
- India can support the development of Nepal's digital infrastructure, promote e-governance initiatives, and foster cross-border digital collaborations. This can enhance connectivity, create economic opportunities, and strengthen bilateral relations.
- Strategic Partnerships: India should actively seek strategic partnerships with Nepal on regional and global platforms. By aligning their interests and jointly addressing common challenges, such as climate change, disaster management, and regional security, both countries can demonstrate their commitment to shared values and interests.
- This will not only counterbalance China's influence but also strengthen the regional stability. Also, organizing joint cultural events, film festivals, and wellness retreats to showcase India's rich heritage can influence public opinion.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2016)
Community sometimes In the affairs of mentioned in the news
- Kurd — Bangladesh
- Madhesi — Nepal
- Rohingya — Myanmar
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
Ans: (c)