Indian Economy
Sticky Inflation and RBI's Monetary Policy
- 15 Jun 2024
- 7 min read
For Prelims: Reserve Bank of India, Repo rate, Inflation, Union budget, Sticky Inflation
For Mains: Economic Growth in India, Significance of interest rate in fiscal policy and monetary policy
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) in its latest bi-monthly monetary policy review opted to maintain the repo rate unchanged for the 8th consecutive time, amid discussions on inflation targeting and economic growth.
Why is the RBI not Cutting Interest Rates?
- Persistent Inflation: Despite high repo rates inflation hasn't hit the 4% mark since early 2021. The decline has been gradual, with inflation hovering around 5% in the first four months of 2024. The RBI is concerned about "sticky" inflation trends.
- Durable Inflation Control: The RBI aims for sustained control, not a temporary dip below 4%. RBI Governor emphasises commitment to achieving the 4% target "on a durable basis".
- Strong GDP Growth: India's Gross Domestic Product (GDP) growth has been surprisingly strong, exceeding 7% for four consecutive years. The RBI recently revised the current financial year's GDP forecast upwards to 7.2%. In this scenario, repo rates likely aren't hindering economic growth.
- Upcoming Union Budget: The RBI might be considering the upcoming Union budget, which could impact inflation dynamics and monetary strategies.
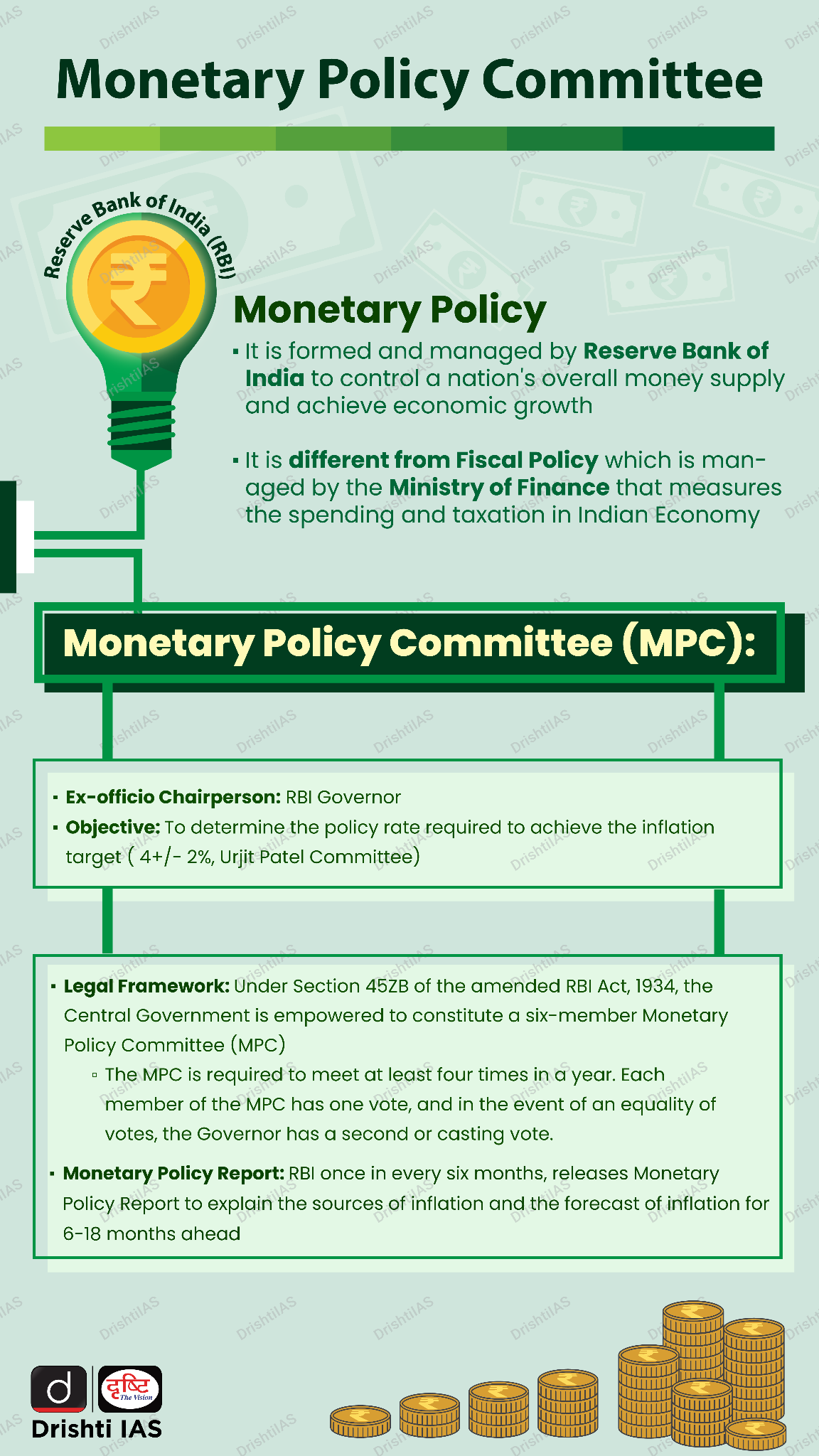
What is RBI's Inflation Targeting?
- About: RBI's Inflation Targeting is a monetary policy framework implemented to maintain price stability in the economy.
- The RBI targets a specific inflation rate, currently set at 4% per year. This target is a long-term average and not a rigid ceiling or floor.
- The target is accompanied by a tolerance band of +/- 2 percentage points. This means the RBI considers inflation acceptable as long as it falls within the range of 2% to 6%.
- Goal: The main aim of inflation targeting is to achieve and maintain price stability, promoting economic growth, protecting the value of the rupee, and ensuring fair resource allocation in the economy.
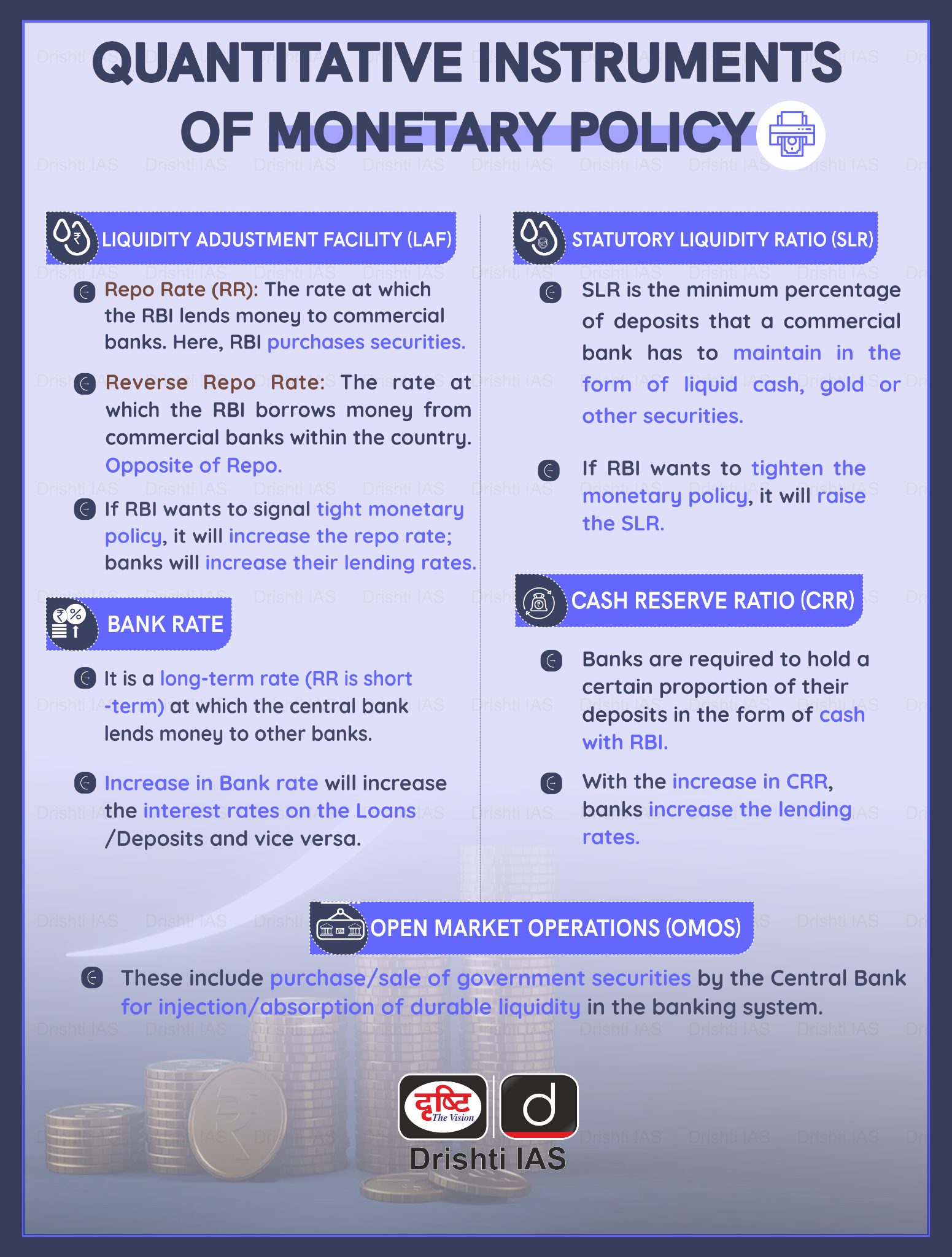
- Mechanism: The RBI uses monetary policy tools, primarily the repo rate, to influence inflation.
- The repo rate is the interest rate at which the RBI lends money to commercial banks.
- By raising the repo rate, the RBI makes borrowing more expensive, which discourages spending and investment, ultimately slowing down inflation.
- Conversely, lowering the repo rate encourages borrowing and spending, boosting economic activity but potentially increasing inflationary pressures.
- Limitations: Inflation targeting may not effectively address supply-side shocks or structural constraints like inadequate infrastructure, thus leading to higher inflation.
- It can also cause exchange rate volatility in open economies and have social and economic impacts on vulnerable populations.
- Additionally, accurate and timely data on inflation and other macroeconomic variables may not be available in all countries, including India.
What is Sticky Inflation?
- About: Sticky inflation refers to a persistent economic phenomenon where prices for goods and services do not adjust quickly to changes in supply and demand dynamics.
- Generally, prices for goods or services that don’t appear to be coming down anytime soon are considered sticky.
- This "stickiness" makes it difficult for inflation to return to a desired level, such as the RBI's target of 4% in India.
- Features of Sticky Inflation: Prices remain high despite fluctuations in supply and demand. Certain sectors like medical services, education, and housing are particularly prone to sticky inflation.
- Erodes purchasing power and affordability, especially in essential goods and services.
- Poses difficulties for central banks in controlling inflation without causing adverse economic impacts.
- Causes of Sticky Inflation: Prices may not respond immediately to changes in market conditions due to factors like rigid pricing mechanisms.
- Rising wages can lead to higher costs for businesses, contributing to inflation stickiness.
- Unique characteristics of sectors such as healthcare and housing contribute to persistent inflationary pressures.
- Managing Sticky Inflation: Central banks often raise interest rates to curb inflation, though balancing rate adjustments is critical to avoiding economic downturns.
- Targeted policies addressing specific sectors experiencing inflation stickiness can help mitigate its impact.
- Regular assessment and adjustment of economic forecasts and policies are crucial to managing sticky inflation effectively.
Read more: Global Economic Prospects Report 2024
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Analyse sticky inflation trends in India and elaborate on its impact on economic stability and policy management in India. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q1. Concerning the Indian economy, consider the following: (2015
- Bank rate
- Open market operations
- Public debt
- Public revenue
Which of the above is/are component/ components of Monetary Policy?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Ans: c
Q2. If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following would it not do? (2020)
- Cut and optimize the Statutory Liquidity Ratio
- Increase the Marginal Standing Facility Rate
- Cut the Bank Rate and Repo Rate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. Do you agree that the Indian economy has recently experienced V-shaped recovery? Give reasons in support of your answer. (2021)