Startups | 28 Jul 2022
For Prelims: Startups, Startup India Action Plan, National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations (NIDHI), Promoting and Accelerating Young and Aspiring Innovators and Startups (PRAYAS), Atal Innovation Mission
For Mains: Startup Ecosystem and its Significance
Why in News?
Various reforms and initiatives by the Government have led to booming of the Indian Startup ecosystem.
What are Startups?
- About:
- The term startup refers to a company in the first stages of operations. Startups are founded by one or more entrepreneurs who want to develop a product or service for which they believe there is demand.
- These companies generally start with high costs and limited revenue, which is why they look for capital from a variety of sources such as venture capitalists.
- Growth of Startups in India:
- The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) has recognized startups which are spread across 56 diversified sectors.
- More than 4,500 Startups have been recognized in sectors relating to emerging technologies such as Internet of Things (IoT), robotics, artificial intelligence, analytics, etc.
- Sustained Government efforts in this direction have resulted in increasing the number of recognized Startups from 471 in 2016 to 72,993 in 2022.
- The Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) has recognized startups which are spread across 56 diversified sectors.
How Startup-India Scheme has Facilitated the Growth of Startups in India?
- Various programs undertaken by the Government of India to promote startups under Startup India initiative has facilitated this growth:
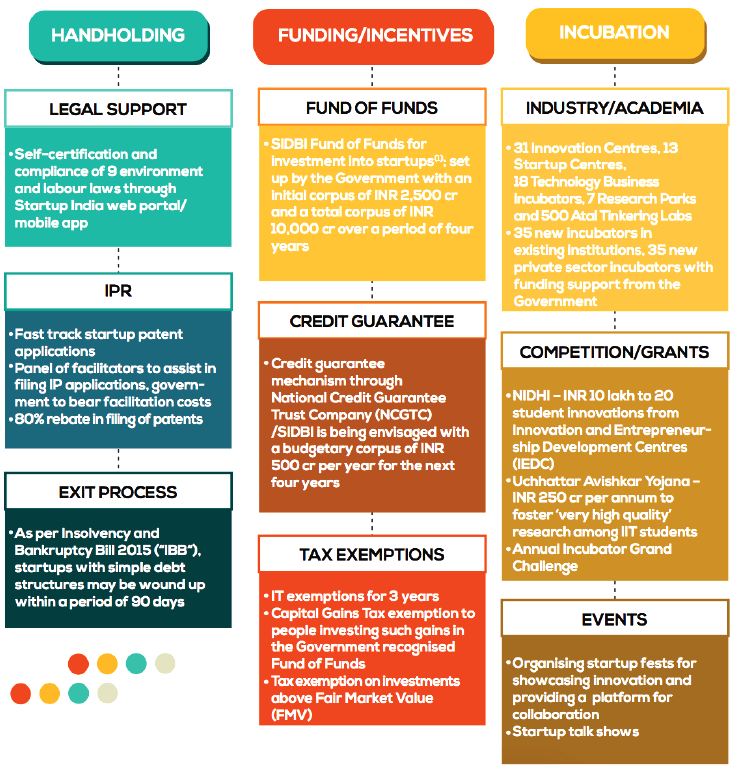
- Startup India Action Plan: It comprises of 19 action items spanning across areas such as Simplification and handholding, Funding support and incentives and Industry- academia partnership and incubation.
- The Action Plan laid the foundation of Government support, schemes and incentives envisaged to create a vibrant startup ecosystem in the country.
- Startup India Hub: It is a one of its kind online platforms for all stakeholders of the entrepreneurial ecosystem in India to discover, connect and engage with each other.
- The Online Hub hosts Startups, Investors, Funds, Mentors, Academic Institutions, Incubators, Accelerators, Corporates, Government Bodies and more.
- Income Tax Exemption for 3 years: Startups incorporated on or after 1st April 2016 Ministerial Board Certificate are exempted from income-tax for a period of 3 consecutive years out of 10 years since incorporation.
- Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS): It aims to provide financial assistance to startups for proof of concept, prototype development, product trials, market entry and commercialization.
- International Market Access to Indian Startups: Startup India has launched bridges with over 15 countries (Brazil, Sweden, Russia, Portugal, UK, Finland, Netherlands, Singapore, Israel, Japan, South Korea, Canada, Croatia, Qatar and UAE) providing a soft- landing platform for startups from the partner nations and aid in promoting cross collaboration.
What Other Factors have Provided Handholding to Startups?
- Government Schemes:
- Department of Science and Technology (DST) had launched an umbrella programme called National Initiative for Developing and Harnessing Innovations (NIDHI) for nurturing ideas and innovations (knowledge-based and technology-driven) into successful startups,
- Promoting and Accelerating Young and Aspiring Innovators and Startups (PRAYAS) program was launched for providing financial support to startups.
- Enhancing Biotechnology:
- To foster biotechnology innovation, the Department of Biotechnology, through the Biotechnology Industry Research Assistance Council (BIRAC), promotes and nurtures biotechnology firms.
- Defense Sector:
- The Department of Defense Production launched the Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) programme to achieve self-reliance and foster innovation and technology development in defence and aerospace by engaging industries, R&D institutes, and academia and providing them with grants to carry out R&D.
- Atal Innovation Mission:
- Under the Atal Innovation Mission, the Government has set up Atal Incubation Centres (AIC) to incubate startups in various sectors.
- It has also launched Atal New India Challenge (ANIC) program to directly aid startups with technology-based innovations that solve sectoral challenges of national importance and societal relevance.
- Role of Forex Flow:
- The inflow of forex especially from leading tech companies such as Facebook, Google, and Microsoft into the Indian start-up ecosystem signals the immense potential of the domestic market.
- Role of Technology:
- With the rise of new technological tools, the startup community is leveraging new-age technologies such as artificial intelligence, internet of things, data analytics, big data, robotics, etc., to bridge wide-ranging gaps that were introduced in the market.
Way Forward
- There is need to create awareness about startups as many enterprising people continue to be discouraged from pursuing their hobbies by their families and social environments and are under pressure to select a job and lifestyle that is seen to provide more stability.
- The willingness to take chances should be rewarded more, and failure should not be seen negatively.
- Furthermore, breaking prejudices is a critical step toward increasing diversity, which would enable today’s big ideas to receive the ecosystem of support they require to succeed.
- The nation’s policymakers, risk-taking corporates and funding agencies need to foster a conducive climate for ensuring easier availability of domestic capital.
- The regulators have to play a more proactive role in formulating appropriate regulations that encourage innovation and support emerging business models.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. What does venture capital mean? (2014)
(a) A short-term capital provided to industries
(b) A long-term start-up capital provided to new entrepreneurs
(c) Funds provided to industries at times of incurring losses
(d) Funds provided for replacement and renovation of industries
Ans: (b)
EXP:
- Venture capital is a form of fund for a new or growing business. It usually comes from venture capital firms that specialize in building high risk financial portfolios.
- With venture capital, the venture capital firm gives funding to the startup company in exchange for equity in the startup.
- The people who invest this money are called venture capitalists (VCs). Venture capital investment is also referred as risk capital or patient risk capital, as it includes the risk of losing the money if the venture does not succeed and takes a medium to long term period for the investments to fructify. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.