Disaster Management
Stampede Mitigation
- 28 Dec 2024
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Hypoxia, Hypercapnia, Kumbh Mela, NDMA, Disaster Management Act, 2005, LiDAR.
For Mains: Disaster Management, Strategy to address stampede.
Why in News?
Recently, a surprise appearance by a Telugu actor led to a stampede in Hyderabad, that again revived the concerns related to crowd management and stampede in India.
What is a Stampede?
- About: A stampede is a sudden, uncontrolled rush of a large crowd of people or animals, typically triggered by panic, fear, or excitement.
- It occurs in crowded areas where high density of people restricts movement, causing chaos and potential casualties.
- Causes: Stampedes are caused by human, infrastructure, and organizational factors.
- Human Factors:
- Panic or Fear: Sudden fear (e.g., of a fire, explosion, or perceived threat) can trigger mass hysteria (uncontrollable fear or anxiety).
- Excitement or Euphoria: Overwhelming enthusiasm, such as during concerts or celebrations, may lead to loss of control.
- Impatience or Aggression: Frustration due to long waits, delays, or limited access points can cause people to push and shove.
- Poor Infrastructure:
- Overcrowding: Insufficient space increases the risk of crushing and trampling.
- Insufficient Facilities: Narrow paths, blocked exits, or lack of barriers create bottlenecks.
- Adverse Conditions: Slippery floors, poor lighting, or uneven ground increase the chance of falling.
- Organizational Factors:
- Inadequate Crowd Management: Lack of trained personnel to control or direct crowds.
- Insufficient Planning: Poor venue design, limited entry/exit points, or inadequate emergency planning.
- Failure in Communication: Absence of clear instructions leads to confusion and panic.
- Human Factors:
- Cause of Death: During a stampede, crushing pressure on the chest restricts the ability of the diaphragm (base of lungs) to contract and expand properly. The body cannot take in enough air or expel carbon dioxide.
- This leads to hypoxia (lack of oxygen) and hypercapnia (excess carbon dioxide), both of which are life-threatening conditions.
- Impact:
- Physical Impacts: Stampedes can result in high fatality rates. It often results in bruises, fractures, and broken bones due to people being pushed, trampled, or crushed.
- Psychological Impacts: Stampede survivors or witnesses may experience psychological trauma, Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), anxiety, panic attacks, and long-term emotional scars.
- Legal Impacts: A major stampede can prompt calls for stricter regulations and improved crowd management for enhanced safety standards for public events and gatherings.
- Impact on Infrastructure: It can damage physical infrastructure, including barriers and buildings, leading to significant repair and upgrade costs.
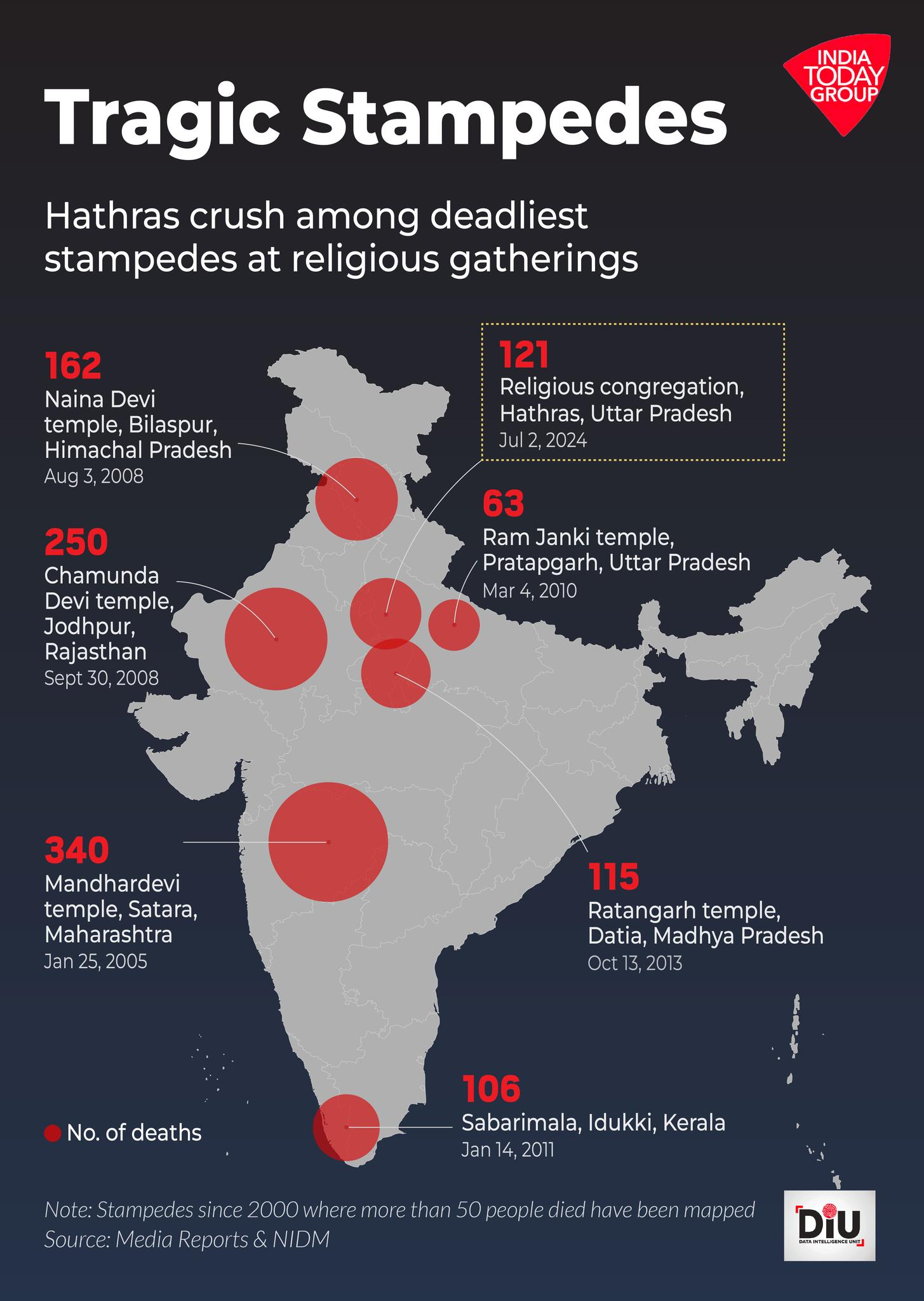
Deadly Stampedes in India
- Hathras (2024): At least 121 people, mostly women and children, were killed in a stampede during a religious event in Hathras, Uttar Pradesh.
- Mumbai Pedestrian Bridge (2017): 22 died in a stampede during rush hour.
- Allahabad Train Station (2013): 36 killed due to a platform change during Kumbh Mela.
- Naina Devi Temple (2008): Around 145 Hindu pilgrims were killed in a stampede at the Naina Devi temple in Himachal Pradesh, triggered by rumors of a landslide.
- Mandhardevi Temple (2005): More than 265 Hindu devotees lost their lives and hundreds were injured at the Mandhardevi temple in Maharashtra.
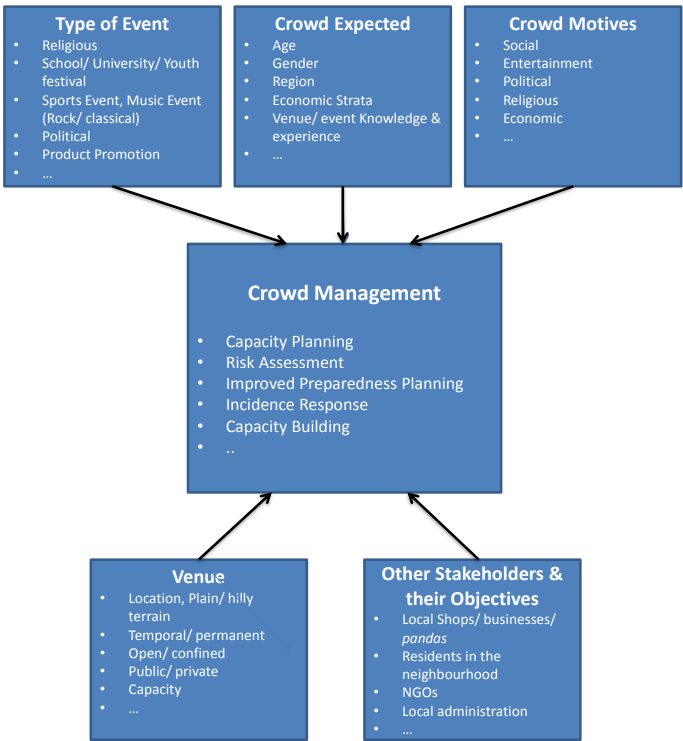
What are NDMA Guidelines to Control Stampedes?
- Infrastructure Development: Ensuring venues and access routes can handle large crowds, especially in disaster-prone areas like hilly terrain and narrow pathways.
- Encouraging separate routes for normal, express, and emergency flows helps manage the movement of vulnerable groups like children, the elderly, and the disabled.
- Panic Management: In case of incidents like rumors or sudden events (e.g., a loud noise), the NDMA advises quick intervention by trained personnel to prevent stampedes.
- Crowd Control: The NDMA advocates a community-based approach to crowd control, focusing on clear communication and understanding rather than relying solely on force.
- Demand Management: This involves analyzing historical crowd data, arrival patterns, and peak periods. Advanced ticketing or registration can help manage crowd inflow.
- Fire Safety: NDMA highlights precautions such as safe electrical wiring, monitoring LPG cylinder usage, and caution with fireworks to prevent fires.
National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA)
- About: NDMA headed by the Prime Minister of India, is the country's highest statutory body for managing disasters.
- Establishment and Purpose: It was established under the Disaster Management Act, 2005 to build institutional mechanisms at both the State and District levels for effective disaster management.
- Responsibilities: NDMA is tasked with formulating policies, plans, and guidelines for disaster management, emphasizing prevention, mitigation, preparedness, and response.
- Vision and Goals: The authority aims to create a safer and disaster-resilient India through a proactive approach and sustainable development strategies.
Way Forward
- Live Crowd Tracking: Deploy thermal and LiDAR sensors to track crowd density, feeding data into AI models to predict surges and trigger early warnings.
- Communication Tools: Install interactive displays showing wait times, evacuation routes, and information in multiple languages.
- Lighting and Pathway Systems: Implement crowd-responsive lighting that adjusts brightness and color based on density to guide movement or calm situations.
- Use bioluminescent pathways that glow brighter during emergencies to guide movement in low light.
- Public Awareness and Education: Launch campaigns to educate the public on crowd safety protocols and appropriate behavior at large gatherings.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the major causes of stampedes and suggest effective measures to prevent such incidents. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q. Discuss the recent measures initiated in disaster management by the Government of India departing from the earlier reactive approach. (2020)