SIPRI Report on Global Arms Producers | 21 Dec 2024
For Prelims: Hindustan Aeronautics Limited, Bharat Electronics Limited, Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Ltd, Gaza, Ukraine, BrahMos, ASEAN, Akash Air Defence Missile System, Pinaka, FDI, Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP)-2020, Positive Indigenization List, Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) Scheme, Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs), Defence Industrial Corridors.
For Mains: Global performance of India;s defence sector, growth drivers of India's defense exports.
Why in News?
Recently, the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI) released its annual report on the world’s 100 largest arms producers with three Indian firms among the top global arms manufacturers.
What are the Key Findings of the SIPRI Report?
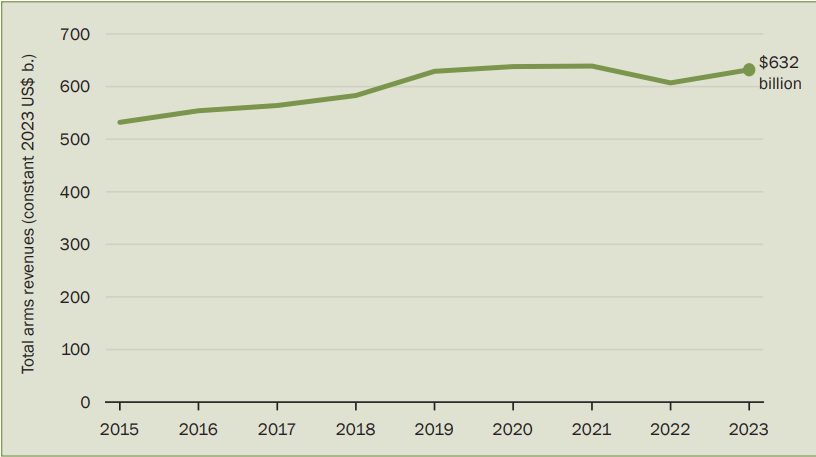
- Global Arms Revenue: Global arms revenues reached USD 632 billion in 2023, a 4.2% rise driven by wars, regional tensions, and rearmament.
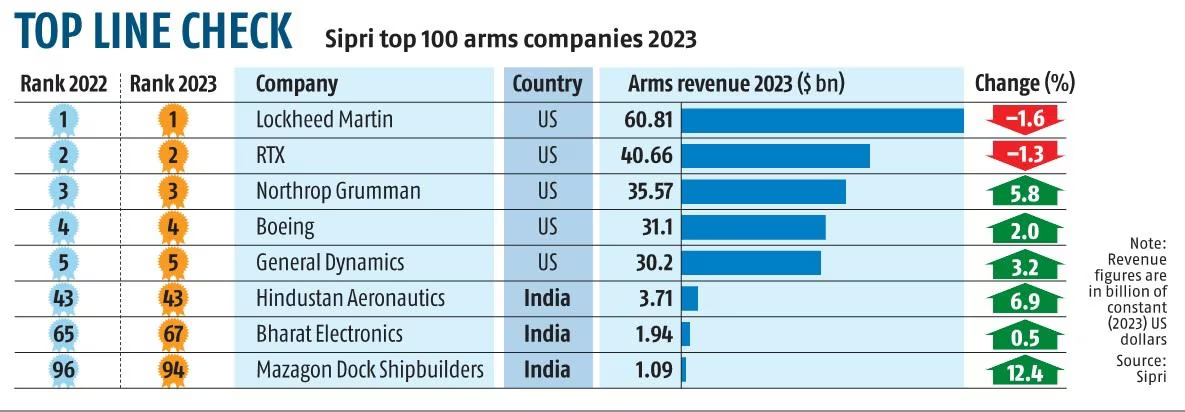
- Performance of Indian Companies: Three Indian companies namely Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (Rank 43), Bharat Electronics Limited (Rank 67), and Mazagon Dock Shipbuilders Ltd (Rank 94) ranked among the Top 100 global arms producers.
- The combined revenues of these companies rose by 5.8%, from USD 6.37 billion in 2022 to USD 6.74 billion (Rs 56,769 crore) in 2023.
- Major Global Producers:
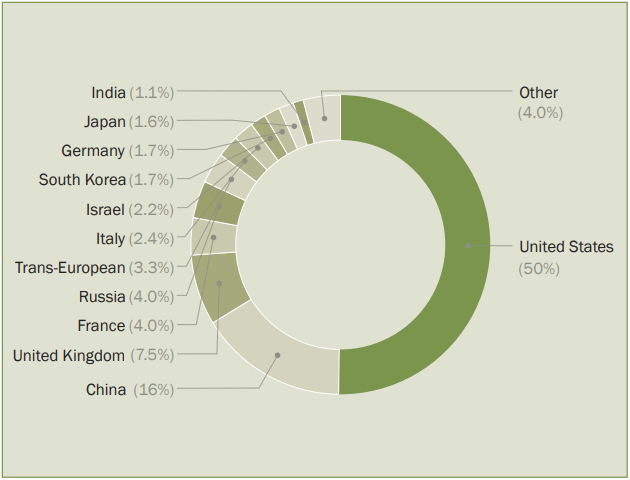
- US: The 41 US companies in the Top 100 earned USD 317 billion in 2023, half of global arms revenues, with the top five producers being US-based.
- China: The nine Chinese companies in the Top 100 recorded a total revenue of USD 103 billion in 2023.
- Russia: The arms revenues of the two Russian companies for which data was available went up by 40% to an estimated USD 25.5 billion due to a significant increase in orders and production.
- Regional Highlights: Growth in arms revenue was seen in all regions of the world, with particularly sharp rises among companies based in Russia and the Middle East (West Asia).
- Reasons for Arms Revenue Growth: Increased demand was driven by wars in Gaza and Ukraine, growing tensions in East Asia, and expanded rearmament programs globally.
- Smaller arms producers were more efficient in responding to increased demand from conflict zones.
- Outlook for 2024: Arms revenues rose in 2023 and are expected to grow in 2024. Companies are recruiting more, showing optimism about future sales.
Note: Arms revenues refer to revenues generated from the sales of military goods and services to military customers domestically and abroad.
Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI)
- SIPRI is an independent international institute dedicated to research into conflict, armaments, arms control and disarmament.
- Established in 1966, SIPRI provides data, analysis and recommendations, based on open sources, to policymakers, researchers, media and the interested public.
What are Key Items in India's Defence Exports?
- BrahMos Missiles: India delivered the first batch of BrahMos supersonic cruise missiles to the Philippines, following a USD 375-million deal for three shore-based, anti-ship missile batteries.
- ASEAN countries and some Gulf nations are showing increasing interest in acquiring BrahMos missiles.
- Dornier-228 Aircraft: India exports the Dornier-228 aircraft, a versatile and reliable aircraft for defense and civilian applications to various countries.
- Subsidiary Aircraft Parts: India exports subsidiary aircraft parts like fuselage and wings to defense giants such as Boeing and Lockheed Martin as part of the global supply chain and offset commitments.
- Software and Electronic Equipment: India exports software and electronic equipment for defense applications to France.
- 155mm Artillery Guns: India has been exporting 155mm artillery guns to countries like Armenia, highlighting its capabilities in producing advanced artillery systems.
- Akash Missile System: The Akash air defence missile system, including its variant Akash-1S, has been a major export, with Armenia being the first international customer.
- Pinaka: Pinaka multi-launch rocket systems have been exported, with Armenia being a significant buyer.
India’s Achievements
- Arms Production: India's annual defence production hit a record high of almost Rs 1.27 trillion in FY24, up 16.7% over the previous year's figure of about Rs 1.09 trillion.
- It shows India’s defence ecosystem has covered over 40% of the ambitious annual defence production target of Rs 3 trillion by FY29.
- Expansion of Arms Production: Apart from the 16 DPSUs, India's defence-industrial base has also expanded to over 430 licenced companies and 16,000 micro, small and medium enterprises.
- The private sector accounts for 21% of this expansion in arms production capacity.
- Export Destinations: Currently, India exports to over 100 nations, with the top three destinations for defence exports in 2023-24 being the USA, France, and Armenia.
What are India’s Initiatives to Boost Defence Indigenisation and Exports?
- Liberalized FDI Policy: FDI limit in the defence sector was raised in 2020 to 74% through the automatic route for companies seeking new defence industrial licenses and up to 100% through the government route for those likely to result in access to modern technology.
- Priority for Domestic Procurement: Emphasis is placed on procuring capital items from domestic sources under the Defence Acquisition Procedure (DAP)-2020.
- Positive Indigenization Lists: Five Positive Indigenization Lists with 509 items and five lists of 5,012 items from Defence Public Sector Undertakings (DPSUs) were issued, with import bans after specified timelines.
- Additionally, launch of the Self-Reliant Initiatives through Joint Action (SRIJAN) portal to facilitate indigenization by Indian industry, including MSMEs.
- iDEX Scheme: The Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX) scheme was launched to involve startups and Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSMEs) in defence innovation.
- Public Procurement Preference: Implementation of the Public Procurement (Preference to Make in India) Order 2017 to support domestic manufacturers.
- Defence Industrial Corridors: Establishment of two Defence Industrial Corridors, one each in Uttar Pradesh and Tamil Nadu, to promote defence manufacturing.
- Defence Research & Development (R&D) has been opened up for industry and startups to foster innovation and collaboration.
Conclusion
India's defence sector has made significant strides in indigenization, with key initiatives driving growth in production and exports. The rise in arms revenues globally, coupled with India's growing share in the global defence market, reflects the success of strategic policies aimed at enhancing self-reliance and international partnerships.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Enumerate various government initiatives for promoting indigenous defense production. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following is the best description of ‘INS Astradharini’, that was in the news recently? (2016)
(a) Amphibious warfare ship
(b) Nuclear-powered submarine
(c) Torpedo launch and recovery vessel
(d) Nuclear-powered aircraft carrier
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. What is the significance of Indo-US defense deals over Indo-Russian defense deals? Discuss with reference to stability in the Indo-Pacific region. (2020)
Q. Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in the defense sector is now set to be liberalized: What influence is this expected to have on Indian defense and economy in the short and long run? (2014)