Shrimp Farming in India | 15 May 2024
Why in News?
Recently, India refuted the allegations made by a US based Human Rights Group of abusive conditions at shrimp farms in India. India stated that entire India’s shrimp exports are certified by the Marine Products Export Development Authority(MPEDA) and there is no scope for such concerns.
What is the State of Shrimp Farming in India?
- About: A shrimp is a crustacean (a form of shellfish) characterised by a semi transparent body flattened from side to side and a flexible abdomen terminating in a fanlike tail.
- Their close relatives include crabs, crayfish, and lobsters. They occur in all oceans, in shallow and deep water, and in freshwater lakes and streams.
- Shrimp Farming: Shrimp Farming is about raising shrimp in controlled environments such as ponds, tanks, or raceways for human consumption.
- They prefer warm water, with temperatures between 25-30°C (77-86°F).
- Preferred soil textures are clay-loam or sandy-clay loam, slightly alkaline soil with pH between 6.5 and 8.5 is optimal.
- A minimum of 5% calcium carbonate in the soil is beneficial for shrimp farming.
- Status of Shrimp Farming in India:
- India as Shrimp Exporter: India is one of the world’s largest shrimp exporters.
- In 2022-23, India’s seafood exports stood at USD 8.09 billion or ₹64,000 crore and shrimps accounted for a bulk of these exports at USD 5.6 billion.
- India’s share of seafood exports in the U.S. market was 40% in 2022-23, far ahead of rivals like Thailand, China, Vietnam and Ecuador.
- Shrimp Producing States: Andhra Pradesh is the largest shrimp producer state in India which accounts for 70% of India’s shrimp output.
- West Bengal and Gujarat are other major players in shrimp farming, with Sundarbans in West Bengal and Kutch in Gujarat being a key producer.
- Regulation:
- All shrimp units are registered with MPEDA (Marine Products Export Development Authority) and FSSAI (Food Safety and Standards Authority of India).
- They follow a HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Point) based food safety management system as per the US Code of Federal Regulations.
- Usage of pharmacologically active substances in aquaculture has been banned since 2002.
- Also, National regulations and monitoring measures like the National Residue Control Plan, ELISA screening labs, in-house labs, and pre-export checks are in place.
- India as Shrimp Exporter: India is one of the world’s largest shrimp exporters.
What is the Marine Products Export Development Authority?
- About: It is a nodal agency for the holistic development of the seafood industry in India and the realisation of its export potential.
- It was established in 1972 under Marine Products Export Development Authority Act (MPEDA), 1972.
- It functions under the Union Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- Objectives: It envisages the development of seafood production, processing, marketing, and exports in India.
- The Government of India recommends new standards for fishing vessels, storage premises, processing plants, and conveyances based on the recommendations of MPEDA.
- Functioning: The MPEDA enrols exporters, lays down quality standards, liaisons with importers to boost exports and conducts capacity-building programmes like training, awareness campaigns for relevant stakeholders to increase production and productivity.
- Headquarters: in Kochi, Kerala.
What are the Government Initiatives Related to Seafood Exports?
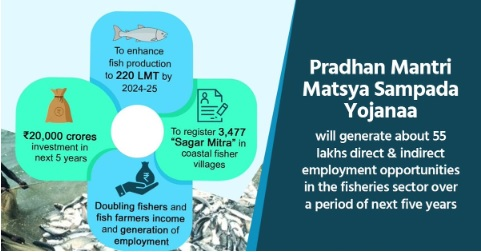
- Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY): It was launched in 2020 for providing support in quality shrimp production, species diversification, promotion of export-oriented species, branding, standards and certification, training and capacity building, creation of post harvest infrastructure through this flagship scheme.
- Fisheries and Aquaculture Infrastructure Development Fund: Launched in 2018, FIDF provides loans to address infrastructure and modernization needs in both marine and inland fisheries.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC) Fisheries scheme: It provides adequate and timely credit support to fisheries farmers for their working capital requirements.
- New cardholders can obtain credit up to Rs. 2 lakhs with interest subvention.
- Existing KCC holders can access an increased credit limit of Rs. 3 lakhs.
- The lending rate for KCC loans is 7%, including 2% interest subvention per annum by the Government of India.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Under the Kisan Credit Card scheme, short-term credit support is given to farmers for which of the following purposes? (2020)
- Working capital for maintenance of farm assets
- Purchase of combine harvesters, tractors and mini trucks
- Consumption requirements of farm households
- Post-harvest expenses
- Construction of family house and setting up of village cold storage facility
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. Defining the blue revolution, explain the problems and strategies for pisciculture development in India. (2018)