Indian Economy
Schemes in Budget 2024 for Rural and Tribal Development
- 30 Jul 2024
- 13 min read
For Prelims: Union Budget, Parliament, Pradhan Mantri Gram SadakYojana (PMGSY), Interim Budget, Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY), Jal Jeevan Mission, Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM JANMAN)
For Mains: Significance of Parliament and Government Policies & Interventions for Indian Economy.
Why in News?
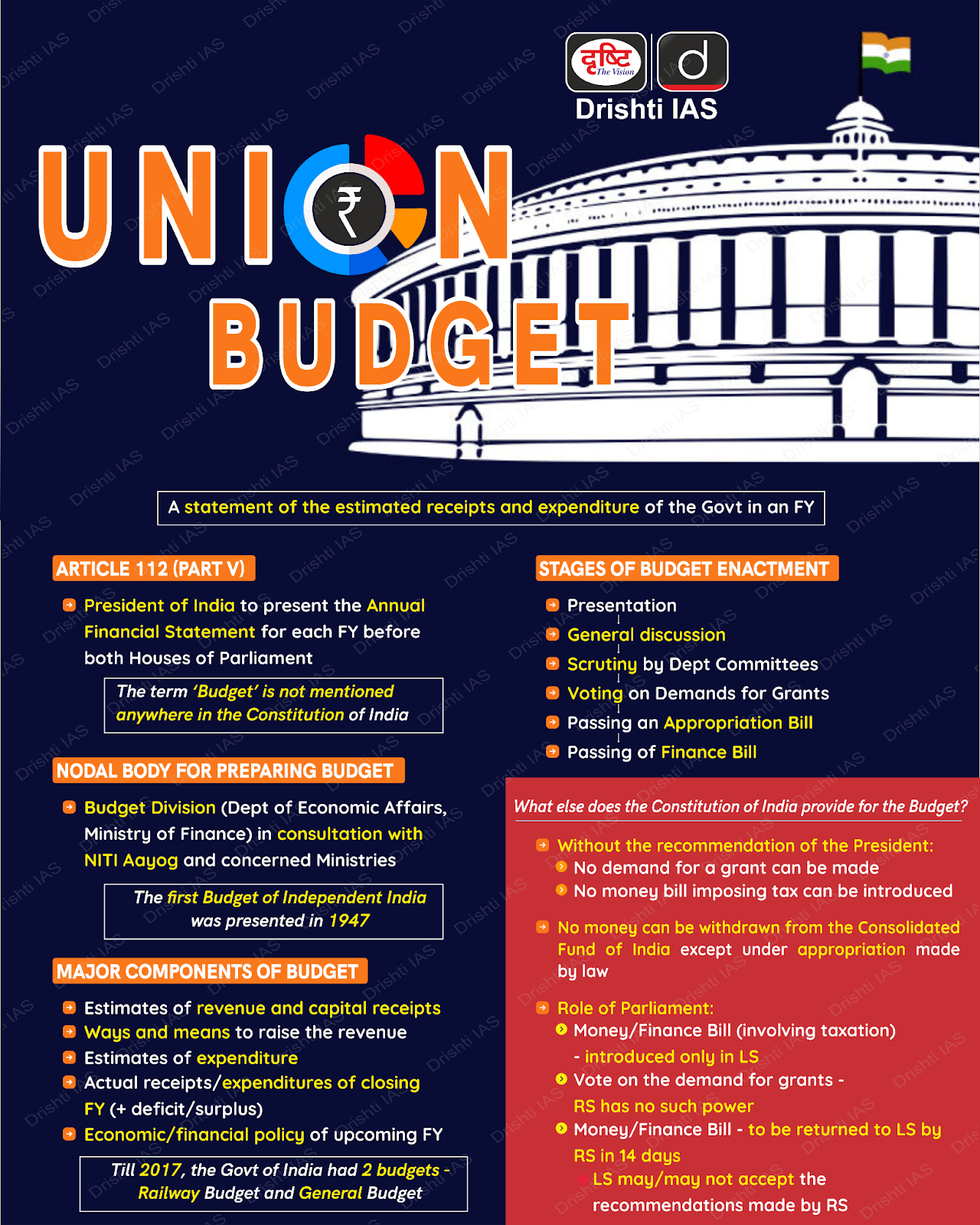
Recently, the Union Budget 2024-25 was presented in the Parliament. It was the first general budget of the 18th Lok Sabha.
- In this budget, the government has announced several measures for rural development (PMGSY) and tribal welfare like PM Janjatiya Vikas Mission (PMJVM).
What is Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) ?
- About: Launched on 25th December 2000, to provide all-weather road connectivity to unconnected habitations.
- Eligibility: Unconnected habitations with a population of 500+ in plain areas and 250+ in North-Eastern, Himalayan, Desert, and Tribal Areas (as per the 2001 census).
- Unconnected Habitation is a habitation located at least 500 metres (1.5 km in hills) from an all-weather road.
- Core Network: The essential network of roads required to provide basic access to social and economic services through at least one all-weather road.
- Funding Pattern: The Union Government covers 90% of project costs in North-Eastern and Himalayan States, and 60% in other states, with allocations based on sanctioned project values.
- Construction Standards: Rural roads are constructed according to the Indian Roads Congress (IRC) guidelines, which have been the apex body of highway engineers since 1934.
- Eligibility: Unconnected habitations with a population of 500+ in plain areas and 250+ in North-Eastern, Himalayan, Desert, and Tribal Areas (as per the 2001 census).
- PMGSY - Phase I:
- It was launched in 2000 as a 100% centrally sponsored scheme.
- Under the scheme, 1,35,436 habitations were targeted for providing road connectivity and 3.68 lakh km for the upgradation of existing rural roads to ensure full farm-to-market connectivity.
- PMGSY - Phase II:
- It was launched in 2013 for the upgradation of 50,000 km of the existing rural road network to improve its overall efficiency.
- While the ongoing PMGSY - I continued, under PMGSY phase II, the roads already built for village connectivity were to be upgraded to enhance rural infrastructure.
- The cost was shared between the centre and the states/UTs.
- Road Connectivity Project for Left Wing Extremism Affected Areas (RCPL WEA), was launched in 2016 for the construction of rural roads in LWE areas.
- PMGSY - Phase III:
- It was approved by the Cabinet in July 2019.
- It gives priorities to facilities like:
- Gramin Agricultural Markets (GrAMs): The retail agricultural markets close to the farm gate, that promote and service a more efficient transaction of the farmers’ produce.
- Higher Secondary Schools and
- Hospitals.
- Under this, it is proposed to consolidate 1,25,000 km of road length in the States. The duration of the scheme is 2019-20 to 2024-25.
- Progress of the Scheme: It has already completed over 7 lakh km of roads out of a sanctioned 8.25 lakh km with an investment of Rs. 2,70,000 crore. Additionally, a total of 1,61,561 unconnected habitations have been provided all-weather road connectivity under PMGSY.
- PMGSY - Phase IV:
- Phase IV of Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) has been announced in the Union Budget 2024-25 to connect 25,000 villages with all-weather roads.
- An amount of Rs 19,000 crore has been allocated for this for the FY 2024-25 (FY-25).
Indian Roads Congress (IRC)
- It was established in 1934 with the aim of advancing road infrastructure in India by uniting professionals and stakeholders in road development.
- Its key functions include setting standards, conducting research, and hosting knowledge-sharing events.
- Its membership spans government, private industry, and academia.
- It influences national road policies, supports bodies like the National Highway Authority of India (NHAI), and advocates for sustainable and environmentally friendly practices in road construction and maintenance.
What are the Key Highlights of the Union Budget 2024 Regarding Tribal Development?
- Launch of Pradhan Mantri Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan (PM JUGA):
- The launch of the PM JUGA Scheme marks a major effort to improve the living standards of tribal families in 63,000 villages.
- The scheme will emphasise "saturation coverage" in tribal-majority villages and aspirational districts. It is anticipated to benefit around 5 crore tribal individuals by improving their access to essential services and socio-economic opportunities.
- Budget Allocation for Different Schemes Related to Tribals:
- Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS) aimed at providing quality education to ST students have been allocated Rs 6,399 crore, an increase of Rs 456 crore from FY 2023-24.
- EMRS is a scheme for model residential schools for STs across India, started in 1997-98 under the Ministry of Tribal Affairs.
- The aim is to build schools on par with Jawahar Navodaya Vidyalayas and Kendriya Vidyalayas, with a focus on preserving local art, culture, sports, and skill development.
- Post-Matric Scholarship for ST Students allocation has increased from Rs 1,970.77 crore to Rs 2,432.68 crore.
- The Prime Minister's Janjati Vikas Mission (PMJVM) has faced a budget reduction of Rs 136.17 crore this year.
- PMJVM aims to strengthen tribal entrepreneurship, facilitate livelihood opportunities, and promote efficient, equitable, self-managed, and optimal use of natural resources, Agri/Non-Timber Forest Products (NTFPs)/ Non-farm enterprises.
- The PM DAKSH scheme allocation has been raised from Rs 92.47 crore to Rs 130 crore.
- It is a central sector scheme by the Department of Social Justice and Empowerment aimed at providing skills training to individuals from SC and ST.
- The National Overseas Scholarship Scheme for Scheduled Castes allocation has been increased to Rs 95 crore from Rs 50 crore, enhancing financial support for higher education in foreign universities.
- The NAMASTE scheme received an increased allocation of Rs 116.94 crore in FY24, up from Rs 97.41 crore in FY23.
- NAMASTE stands for National Action for Mechanised Sanitation Ecosystem.
- Launched in 2022, the NAMASTE Scheme is a Central Sector initiative replacing the Self-Employment Scheme for the Rehabilitation of Manual Scavengers (SRMS) from 2007. It will be implemented across over 4,800 Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) until 2025-26.
- It has been launched to ensure the safety and dignity of sanitation workers in urban areas by eradicating manual scavenging through mechanised sewer cleaning in India as well as providing sustainable livelihood to these workers.
- Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM JANMAN), launched in Union Budget 2023, has been continued with the allocation of Rs 25 crores in Union Budget 2024.
- It aims to provide essential amenities such as secure housing, clean drinking water, sanitation, improved access to education, health, and nutrition, as well as enhanced road and telecom connectivity, and sustainable livelihood opportunities to PVTGs households and habitats.
- Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS) aimed at providing quality education to ST students have been allocated Rs 6,399 crore, an increase of Rs 456 crore from FY 2023-24.
What were the Other Schemes and their Allocations Announced in the Union Budget 2024-25?
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana (PMAY):
- Objective of PMAY-G: To provide affordable housing to the underprivileged, with a total target of 2.95 crore rural houses since its launch in 2016. As of July 2024, nearly 2.94 crore houses have been sanctioned.
- Unit Cost Increase: The government has decided to increase the unit cost under PMAY-G from Rs 1.2 lakh to Rs 2 lakh in plain areas, and from Rs 1.3 lakh to Rs 2.20 lakh in Integrated Action Plan (IAP) districts, hilly regions, and difficult areas from 2024-25 onward.
- IAP is a government initiative in India aimed at promoting development in certain underserved areas.
- Target and Allocation: 3 crore additional houses under PMAY in rural and urban areas.
- Of these, 2 crore homes will be constructed in villages under PMAY-Gramin (PMAY-G) with an allocation of Rs 54,500 crore.
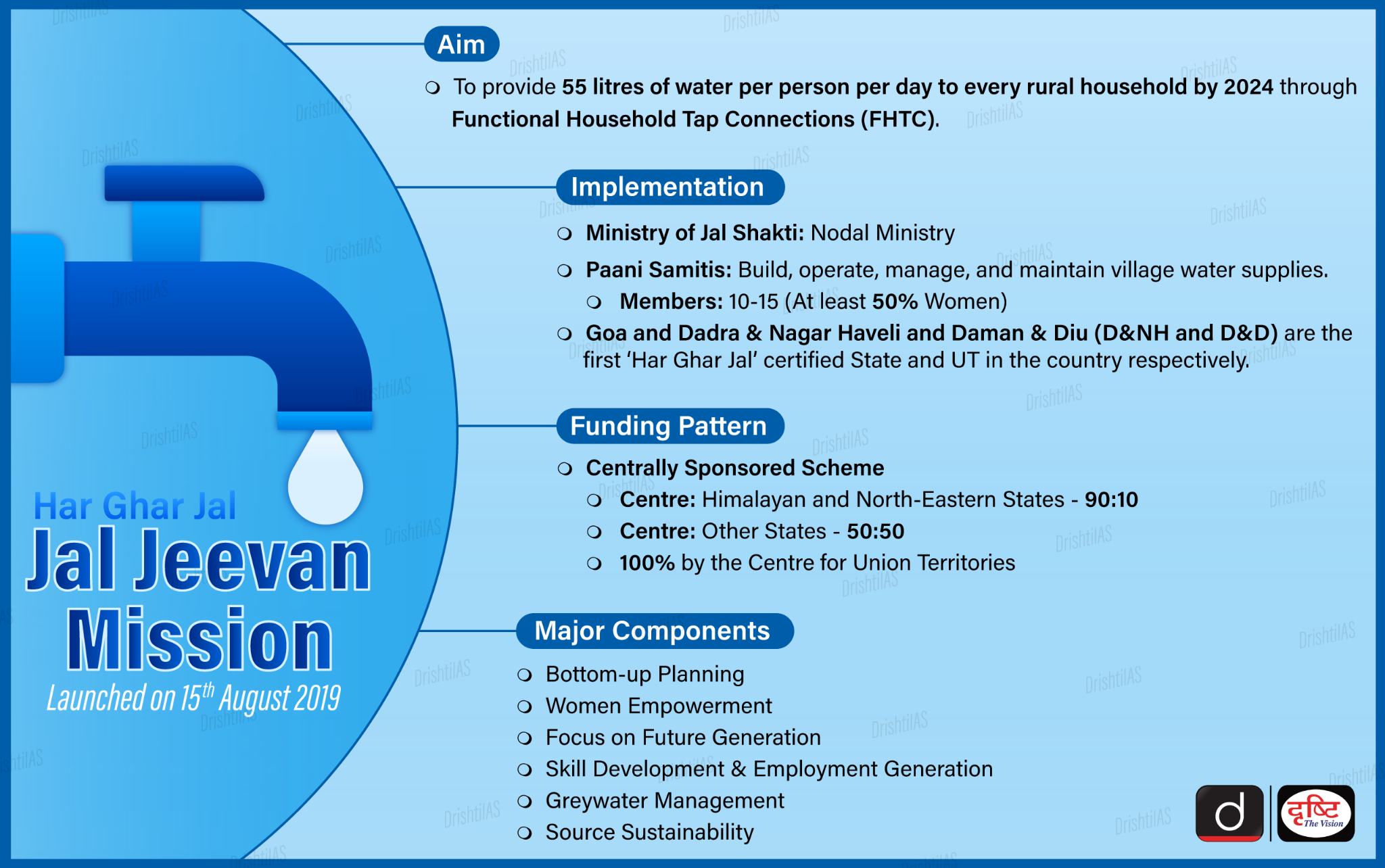
- Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) (Rural): Allocation: Rs 69,926.65 crore.
- Objective: To provide a safe and adequate drinking water supply to all rural households, enhancing public health and sanitation.
- About JJM: Launched in 2019, it envisages a supply of 55 litres of water per person per day to every rural household through Functional Household Tap Connections (FHTC) by 2024.
- Achievement: It has provided tap water connections to 15 crore rural households nationwide. It has rapidly increased rural tap connection coverage from 3 crore to 15 crore between 2019 and 2024. 8 states and 3 Union Territories have achieved 100% coverage, with others like Bihar, Uttarakhand, Ladakh, and Nagaland making substantial progress.
- Rural Land Reforms:
-
Objective: These reforms aim to facilitate credit flow and improve land management, thereby enhancing agricultural productivity.
-
Reforms:
- Assignment of Unique Land Parcel Identification Numbers (Bhu-Aadhaar).
- Digitization of cadastral maps.
- Survey of map subdivisions based on current ownership.
- Establishment of a land registry.
- Linking land records to a farmers' registry.
-
What is the Jal Jeevan Mission (Urban)?
- In the Budget 2021-22, Jal Jeevan Mission (Urban) was announced under the MInistry of Housing of Urban Affairs to provide universal coverage of water supply to all households in urban areas through functional taps in all statutory towns in accordance with Sustainable Development Goal- 6.
- It complements the Jal Jeevan Mission (Rural).
- Objectives of Jal Jeevan Mission (Urban):
- Securing tap and sewer connections.
- Rejuvenation of water bodies.
- Creating a circular water economy.
|
Drishti Mains Question What are the Initiatives taken by the Union Government for Tribal and Rural Development? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Along with the Budget, the Finance Minister also places other documents before the Parliament which include ‘The Macro Economic Framework Statement’. The aforesaid document is presented because this is mandated by (2020)
(a) Long standing parliamentary convention
(b) Article 112 and Article 110(1) of the Constitution of India
(c) Article 113 of the Constitution of India
(d) Provisions of the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q. Distinguish between Capital Budget and Revenue Budget. Explain the components of both these Budgets. (2021)