Salt Pans Land | 23 Sep 2024
Why in News?
Recently, the Centre approved the transfer of 256 acres of salt pan land in Mumbai to the Dharavi Redevelopment Project Pvt Ltd (DRPPL) for building rental housing for slum dwellers.
- Environmentalists raised ecological concerns about construction on salt pan lands.
What are Salt Pan Lands?
- About:
- Salt pans are low-lying tracts of land where seawater periodically flows in, leaving behind deposits of salt and minerals.
- This natural process plays a critical role in maintaining the balance of coastal ecosystems.
- Protection Status:
- Under the CRZ Notification of 2011, these ecologically sensitive areas are classified under CRZ-1B and restrict economic activities except salt extraction and natural gas exploration.
- Salt Pans in India:
- In Mumbai, a total of 5,378 acres have been designated as salt pan lands.
- On a national scale, around 60,000 acres of salt pan lands are identified, distributed across states like Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Odisha, Gujarat, and Karnataka.
- Andhra Pradesh has the largest expanse (20,716 acres), followed by Tamil Nadu (17,095 acres) and Maharashtra (12,662 acres).
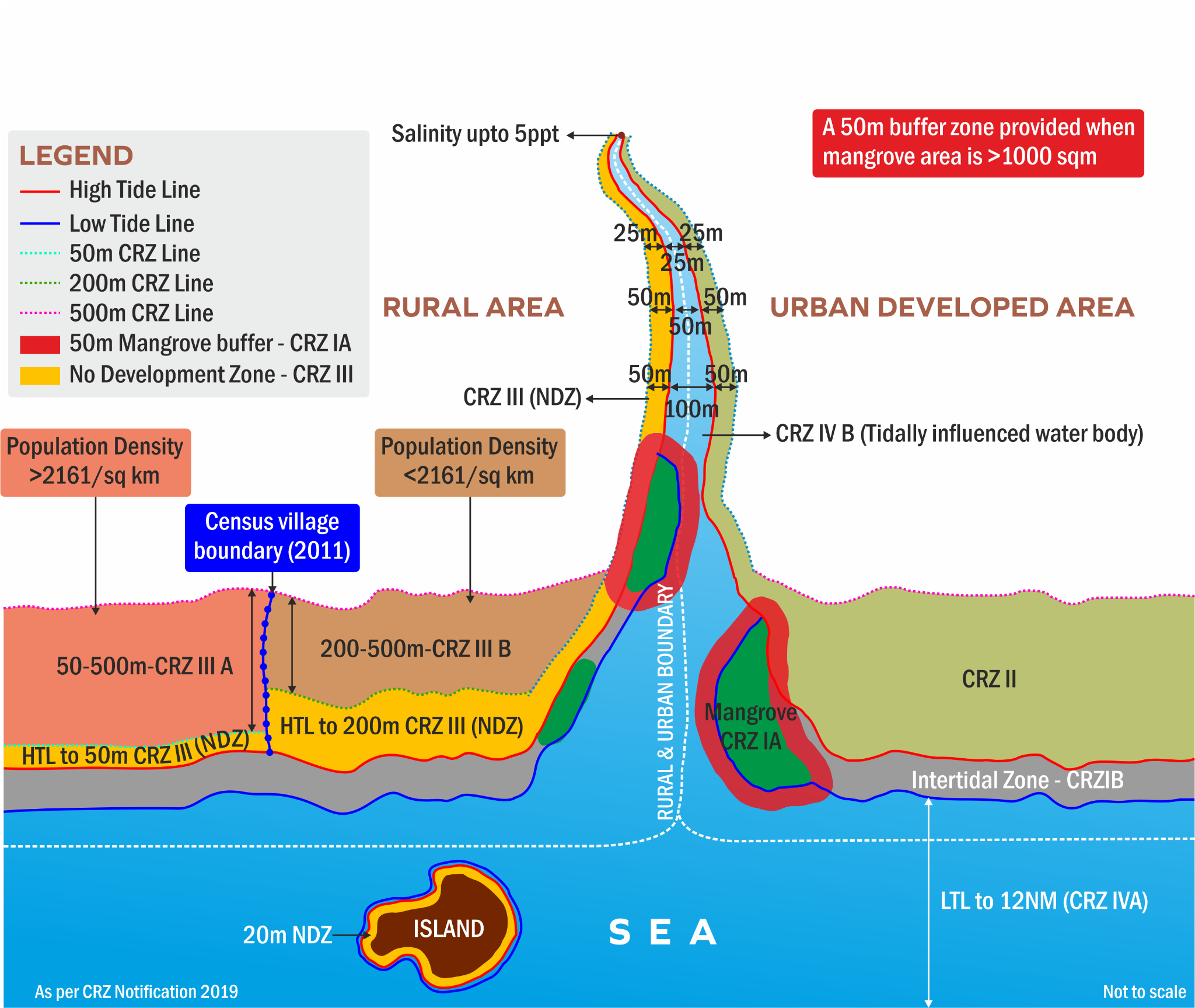
Coastal Regulation Zone (CRZ)
- The CRZ was first notified in 1991 by the Ministry of Environment and Forests (MoEF) under the Environment Protection Act of 1986. The CRZ is categorized into five zones: CRZ-I, CRZ-II, CRZ-III, CRZ-IV, and CRZ-V.
- CRZ-I are ecologically sensitive areas like mangroves, coral reefs, biosphere reserves etc.
- CRZ-II includes built-up areas – villages and towns that are already well established.
- CRZ-III are areas that are undisturbed and do not fall under either in Category I or II.
- CRZ-IV is the aquatic area from low tide line up to territorial limits.
- CRZ is an area near the coastline that's governed by rules to protect the environment and promote sustainable development. The CRZ includes:
- It is the land between the high tide line (HTL) and the low tide line (LTL).
- A 100-metre stretch along the banks of rivers, estuaries, backwaters, and creeks that are affected by tides.
- The river banks on either side of estuaries.
What is the Significance of Salt Pans?
- Environmental: Alongside the coastal mangroves, salt pans form a vital ecological barrier that mitigates flooding risks.
- Economic: Salt pans provide employment for a large number of workers, especially in rural and coastal areas. Labourers engage in activities like harvesting, processing, and transporting salt.
- Raw Material: Salt produced in salt pans is essential for various industries, including chemical production (e.g., chlorine, caustic soda), agriculture (as animal feed), and water treatment.
- Tourism Attraction: Some salt pans, especially those with scenic landscapes, have become tourist destinations, adding economic value through ecotourism and cultural tourism.
What are Welfare Schemes the Government Initiated for Salt Workers?
- Scheme for Grant of Rewards to the Children of Salt Labourers: It provides financial rewards to students for their educational development.
- Namak Mazdoor Awas Yojana (NMAY): It provides for the construction of houses for salt workers. It promotes cooperative societies in the salt industry.
- Salt Commissioner's Organization (SCO): It monitors the development of the salt industry, including planning, facilitating technology upgradation, and conducting training programs for salt workers.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Among the following, who are the Agaria Community?(2009)
(a) A traditional toddy tappers community of Andhra Pradesh
(b) A traditional fishing community of Maharashtra
(c) A traditional silk-weaving community of Karnataka
(d) A traditional salt pan workers community of Gujarat
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. The effective management of land and water resources will drastically reduce the human miseries. Explain. (2016)