Russian Consignment to India via INSTC | 29 Jun 2024
For Prelims: Central Asia, Baltic, Chabahar Port, JCPOA, INSTC.
For mains: International North–South Transport Corridor, Significance, Potential and Challenges.
Why in News?
Recently, Russia has sent two trains carrying coal to India through the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) for the first time.
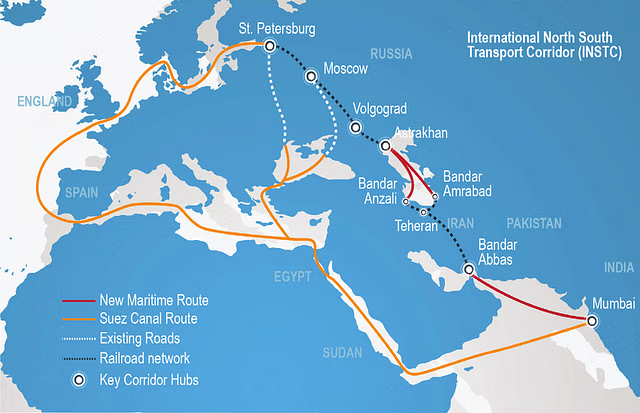
- The consignment will travel over 7,200km from St. Petersburg, Russia to Mumbai port via Bandar Abbas port of Iran.
What is the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC)?
- About:
- INSTC is a 7,200-kilometer Multimode Transit Route linking the Indian Ocean and the Persian Gulf to the Caspian Sea via Iran and onward to northern Europe via St. Petersburg in Russia.
- It connects ship, rail, and road routes for moving cargo between India, Iran, Azerbaijan, Russia, Central Asia, and Europe.
- Origin:
- It was launched on 12th September 2000 in St. Petersburg, by a trilateral agreement signed by Iran, Russia and India at the Euro-Asian Conference on Transport in 2000 for promoting transportation cooperation among the Member States.
- Ratification:
- Since then, INSTC membership has expanded to include 10 more countries (total 13)-Azerbaijan, Armenia, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, Turkey, Ukraine, Syria, Belarus, and Oman.
- Routes and Modes:
- Central Corridor: It begins from the Jawaharlal Nehru Port in Mumbai and connects to the Bandar Abbas port (Iran) on the Strait of Hormuz. It then passes through the Iranian territory via Nowshahr, Amirabad, and Bandar-e-Anzali, runs along the Caspian Sea to reach the Olya and Astrakhan Ports in Russia.
- Western Corridor: It connects the railway network of Azerbaijan to that of Iran via the cross-border nodal points of Astara (Azerbaijan) and Astara (Iran) and further to Jawaharlal Nehru port in India via sea route.
- Eastern Corridor: It connects Russia to India through the Central Asian countries of Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, and Turkmenistan.
What is the Significance of INSTC for India?
- Diversification of Trade Routes:
- INSTC allows India to bypass chokepoints like the Strait of Hormuz and the Red Sea (Suez Canal route), making its trade more secure.
- The Israel-Hamas conflict and the Houthi attacks on ships in the southern Red Sea have highlighted the significance of having alternative trade routes.
- Through this India can bypass Pakistan and unstable Afghanistan to reach Central Asia.
- Enhanced Connectivity with Central Asia:
-
It connects India to markets in Russia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe, facilitating trade, energy cooperation, defense, counterterrorism, and cultural exchanges with Central Asian Republics through initiatives like “Connect Central Asia”.
- The INSTC significantly reduces transit time by 20 days and freight costs by 30% compared to the Suez Canal route.
-
- Energy Security:
- The INSTC facilitates India's access to energy resources in Russia and Central Asia and can reduce reliance on the Middle East.
- Since the Russia-Ukraine war, imports of metallurgical coal from Russia have tripled, and are expected to grow amid declining imports from Australia.
- Strengthening Ties with Iran and Afghanistan:
-
India has invested in the Chabahar Port in Iran's Sistan-Balochistan province and signed an agreement for the INSTC, aiming to facilitate trade with Central Asian countries.
-
Chabahar Port is essential for India, Iran, and Afghanistan as it offers direct sea access and trade opportunities in the region.
-
What are the Challenges Related to Full Utilization of INSTC?
- Limited International Funding: Unlike China's Belt and Road Initiative (BRI) with its dedicated funding institutions, INSTC lacks significant financial funding from major institutions like the World Bank and Asian Development Bank.
- US Sanctions on Iran: The harsh sanctions imposed on Iran after the US's withdrawal from the JCPOA (Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action) in 2018 resulted in many global companies withdrawing from infrastructure projects in Iran.
- Security Concerns in Central Asia: The presence of terrorist organizations like the Islamic State (IS) in Central Asia poses a significant security threat along the corridor which can deter investment and smooth operation of the route.
- Differential Tariffs and Customs: Disparities in customs regulations and tariff structures across member states create complexities and delays for cargo movement.
- Uneven Infrastructure Development: The corridor utilizes various modes of transport (ship, rail, road). Uneven infrastructure development across member states, particularly underdeveloped rail networks in Iran, creates bottlenecks and hinders the seamless movement of goods.
- There is a lack of a joint work plan for developing the corridor and its business ecosystem.
Way Forward
- Proactive Approach: A proactive approach, particularly by founding members India and Russia, is crucial for the success of INSTC.
- This could involve joint marketing efforts, infrastructure development initiatives, and diplomatic efforts to address political hurdles.
- Financing Gap: Infrastructure development and corridor maintenance require substantial investment.
- Private sector participation should be encouraged by mitigating risks through improved security and political stability in the region.
- Streamlining Customs and Tariffs: Implementing a harmonized customs regime and implementing mutual recognition agreements would simplify procedures and expedite cargo movement.
Conclusion
The INSTC corridor has the potential to create a strong trade connection between India, Russia, Iran and Baltic and Scandinavian countries. It could boost economies, improve relations between involved countries, and counter China's influence in Central Asia. However, there are challenges like bureaucracy and regional conflicts that need to be addressed for INSTC to be successful.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What is the geopolitical and geoeconomic importance of the International North-South Transport Corridor (INSTC) for India? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. What is the importance of developing Chabahar Port by India? (2017)
(a) India’s trade with African countries will enormously increase.
(b) India’s relations with oil-producing Arab countries will be strengthened.
(c) India will not depend on Pakistan for access to Afghanistan and Central Asia.
(d) Pakistan will facilitate and protect the installation of a gas pipeline between Iraq and India.
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. In what ways would the ongoing U.S-Iran Nuclear Pact Controversy affect the national interest of India? How should India respond to this situation? (2018)
Q. The question of India’s Energy Security constitutes the most important part of India’s economic progress. Analyse India’s energy policy cooperation with West Asian countries. (2017)