Agriculture
Rubber Industry
- 07 Jun 2022
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Essential conditions for the growth of Rubber, Production and Distribution of Rubber, FTAs, MSME
For Mains: Distribution and Production of Rubber Industry in India and related issues
Why in News?
According to the All India Rubber Industries Association (AIRIA), the USD 2-billion non-tyre rubber sector is aiming to double its exports by 2025.
- The global market for rubber products, which is estimated at around $212 billion is expected to grow by 2025.
- The government should take steps to ensure that the terms of the Free Trade Agreements (FTAs) benefit the MSMEs to increase rubber exports.
- As MSMEs are so important to India’s economy and commerce, India’s should include FTAs provisions to address the special concerns, demands and barriers that MSMEs may face while doing business in foreign markets.
What is AIRIA (All India Rubber Industries Association)?
- The All-India Rubber Industries Association (AIRIA) is a not for profit making body serving the rubber industry and trade with the objectives of safeguarding and promoting interests of the industry.
What are Key Features of Rubber?
- About:
- Natural rubber is a polymer of isoprene, an organic compound.
- Rubber is a coherent elastic solid obtained from the latex of a number of tropical trees of which Hevea brasiliensis is the most important.
- Rubber trees have an economic life period of around 32 years in plantations.
- Sources:
- Natural rubber comes from various sources, the most common being the Pará rubber tree (Hevea brasiliensis). It grows well under cultivation and yields latex for several years.
- The vines in the genus Landolphia yield the Congo rubber. These vines cannot be grown in cultivation and this led to large-scale exploitation of the wild plants in Congo.
- Latex is also present in dandelion milk which can be used to produce rubber.
- Cultivation of Rubber Trees:
- Soil:
- The trees demand well-drained and well-weathered soils.
- Lateritic type, alluvial, sedimentary types, and non lateritic red soils are best for the growth of these trees.
- Precipitation and Temperature:
- An evenly distributed rainfall with at least 100 rainy days a year and a temperature range of about 20 to 34°C are optimum conditions for the growth of the Hevea rubber tree.
- A humidity of around 80%, 2000 hours of sunshine, and absence of strong winds are also necessary for the best results.
- Soil:
- Uses:
- Rubber is used for a variety of purposes from erasing pencil marks to manufacturing tyres, tubes and a large number of industrial products.
- Natural rubber is preferred over synthetic rubber due to its high tensile strength and vibration dampening properties, along with tear resistance.
- This makes it important for the construction and automobile industries.
- The growth of the automobile market across countries is anticipated to increase the demand for natural rubber production.
- The rise in demand for latex products, such as catheters, gloves, and belts, is also a factor that is likely to aid in the growth of the rubber market.
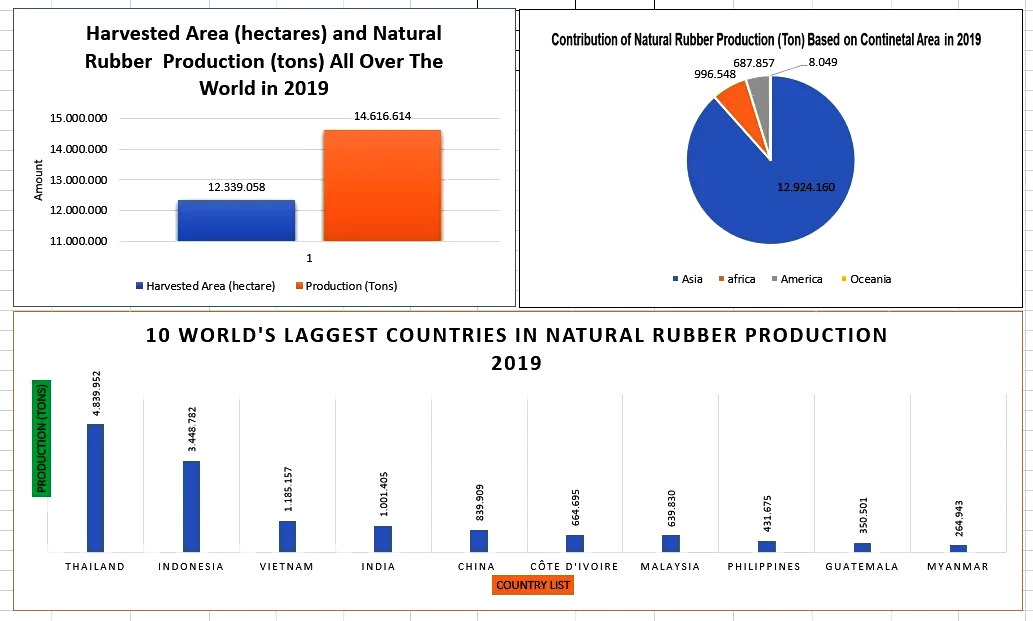
- Production and Distribution:
- According to FAOStat (Food and Agricultural Organisation Corporate Statistical Database) of 2019, Thailand is the largest Producer of Rubber in the World followed by Indonesia, Malaysia, India, China etc.
What is the Status of Rubber Production in India?
- According to FAOStat 2019, India is the fourth largest producer and consumer of Rubber in the World.
- Consumption:
- Most of the rubber consumption came from the transportation sector, followed by the footwear industry.
- Exports:
- The quantity of natural rubber which was exported from India accounted for over 12 thousand metric tons during fiscal year 2020.
- The leading countries importing natural rubber from India were Germany, Brazil, the United States and Italy.
- Export products included automotive tires and tubes, footwear, pharmaceutical goods and hoses, coats and aprons.
- Distribution:
- The first rubber plantations in India were set up in 1895 on the hill slopes of Kerala.
- However, rubber cultivation on a commercial scale was introduced in 1902.
- Kerala is the largest producer of natural rubber in India.
- Major areas: Kottayam, Kollam, Ernakulam, Kozhikode districts produce practically all the rubber of this state.
- Tamil Nadu:
- Nilgiri, Madurai, Kanniyakumari, Coimbatore and Salem are the chief rubber producing districts of Tamil Nadu.
- Karnataka:
- Chikmagalur and Kodagu are the main producing districts.
- Tripura, Assam, Andaman and Nicobar, Goa etc are some other rubber producing States.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Q. Match List-I with List-II and select the correct answer using the code given below the Lists: (2008)
| List-I (Board) | List-II (Headquarters) |
| A. Coffee Board | 1. Bengaluru |
| B. Rubber Board | 2. Guntur |
| C. Tea Board | 3. Kottayam |
| D. Tobacco Board | 4. Kolkata |
Code: A B C D
(a) 2 4 3 1
(b) 1 3 4 2
(c) 2 3 4 1
(d) 1 4 3 2
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Coffee Board: It was established through the Coffee Act VII, 1942. The Coffee Board, under the administrative control of Ministry of Commerce and Industry, is an organisation that promotes coffee production in India. It is headquartered in Bengaluru.
- Rubber Board: It was constituted under the Rubber Act, 1947 and Rubber Rules 1955. Rubber Board is a statutory body under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry for the overall development of the rubber industry in the country. Head Office of the Board is located at Kottayam in the State of Kerala.
- Tea Board: It was established by the Tea Act in 1953. The Tea Board of India is a State agency of the GoI established to promote the cultivation, processing, and domestic trade as well as export of tea from India. It is headquartered in Kolkata.
- Tobacco Board: It was constituted as a statutory body on 1st January, 1976 under Section (4) of the Tobacco Board Act, 1975. The Board is headed by a Chairman with its headquarters at Guntur, Andhra Pradesh. It is responsible for the development of the tobacco industry. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.