Governance
Road Accidents in India-2022
- 02 Nov 2023
- 8 min read
For Prelims: Motor Vehicles Amendment Act, 2019, Road Accidents in India-2022, Ministry of Road Transport and Highways, United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP), National Highways and Expressways.
For Mains: Road Accidents in India-2022, Government policies and interventions for development in various sectors and issues arising out of their design and implementation.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has published a Report titled- ‘Road Accidents in India-2022', shedding light on the concerning trends in road accidents and fatalities.
- The report is based on the data/information received from police departments of States/UTs on calendar year basis in standardized formats as provided by the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP) under the Asia Pacific Road Accident Data (APRAD) base project.
- APRAD is a software tool developed specifically for the UNESCAP and its member countries to help member countries in the Asia-Pacific region develop, update, maintain, and manage road accident databases.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Number of Road Accidents:
- In 2022, a total of 4,61,312 road accidents occurred in India, leading to 1,68,491 fatalities and 4,43,366 people injured.
- These figures represent an 11.9% year-on-year increase in accidents, a 9.4% rise in fatalities, and a substantial 15.3% surge in the number of people injured compared to the previous year.
- In 2022, a total of 4,61,312 road accidents occurred in India, leading to 1,68,491 fatalities and 4,43,366 people injured.
- Road Accident Distribution:
- 32.9% of accidents took place on National Highways and Expressways, 23.1% on State Highways, and the remaining 43.9% on other roads.
- 36.2% of fatalities occurred on National Highways, 24.3% on State Highways, and 39.4% on other roads.
- Demographic Impact:
- Young adults in the age group of 18 - 45 years accounted for 66.5% of the victims in 2022.
- Additionally, people in the working age group of 18 – 60 years constituted 83.4% of the total road accident fatalities.
- Rural vs. Urban Accidents:
- About 68% of road accident deaths occurred in rural areas, with urban areas contributing 32% to the total accident deaths in the country.
- Vehicle Categories:
- Two-wheelers, for the second consecutive year, accounted for the highest share in both total accidents and fatalities in 2022.
- Light vehicles, including cars, jeeps, and taxis, ranked a distant second.
- Road-User Categories:
- Among road-user categories, two-wheeler riders had the highest share in total fatalities, representing 44.5% of persons killed in road accidents in 2022.
- Pedestrian road-users were the second-largest group, with 19.5% of fatalities.
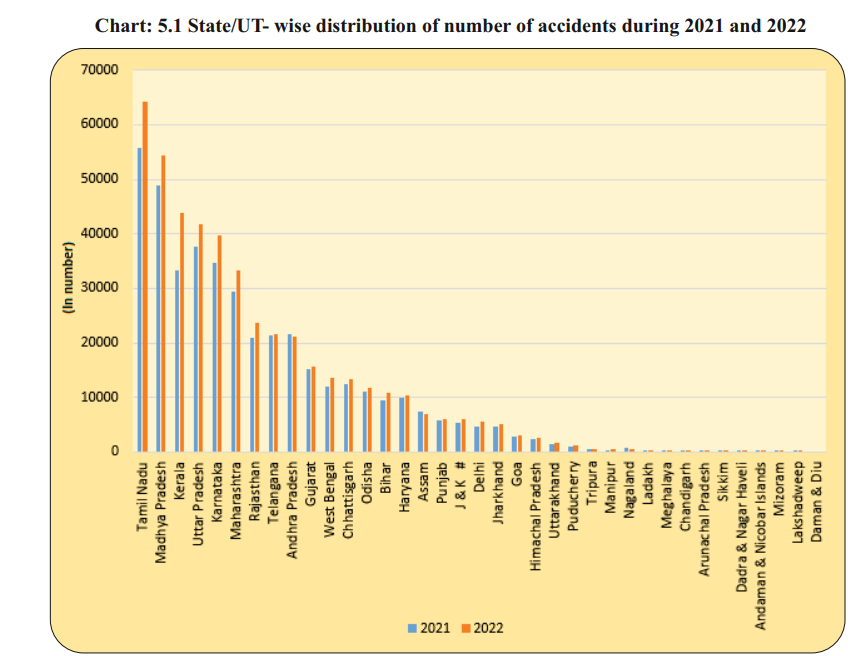
- State-Specific Data:
- Tamil Nadu recorded the highest number of road accidents in 2022, with 13.9% of the total accidents, followed by Madhya Pradesh with 11.8%.
- Uttar Pradesh had the highest number of fatalities due to road accidents (13.4%), followed by Tamil Nadu (10.6%). Understanding state-specific trends is essential for targeted interventions.
- International Comparison:
- India has the highest number of total persons killed due to road accidents, followed by China and the United States.
- Venezuela has the highest rate of persons killed per 1,00,000 population.
What is the Status of the Indian Road Network?
- India's road density at 1,926.02 per 1,000 sq.km of area in 2018-19 was higher than that of many developed countries though surfaced/paved road constituting 64.7 % of the total road length is comparatively lower than that of developed countries.
- National Highways constituted 2.09% of the total road length of the country in 2019.
- The balance road networks comprise of State Highways (2.9%), District Roads (9.6%), Rural Roads (7.1%), Urban Roads (8.5%) and Project Roads (5.4%).
What are the Road Accident Mitigation Measures Taken by the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways?
- Education Measures:
- To create effective public awareness about road safety, the Ministry undertakes various publicity measures and awareness campaigns through social media, electronic media and print media.
- Further, Ministry implements a scheme to provide financial assistance to various agencies for administering Road Safety Advocacy.
- Engineering Measures:
- Road safety has been made an integral part of road design at planning stage. Road Safety Audit (RSA) of all highway projects has been made mandatory at all stages.
- The Ministry has notified the mandatory provision of an airbag for the passenger seated on the front seat of a vehicle, next to the driver.
- Enforcement Measures:
- The Motor Vehicles (Amendment) Act, 2019.
- Electronic Monitoring and Enforcement of Road Safety rules (specify the detailed provisions for placement of electronic enforcement devices (speed camera, body wearable camera, dashboard camera, etc)).
What are the Initiatives Related to Road Safety?
- Global:
- Brasilia Declaration on Road Safety (2015):
- The declaration was signed at the second Global High-Level Conference on Road Safety held in Brazil. India is a signatory to the Declaration.
- The countries plan to achieve Sustainable Development Goal 3.6 i.e., to halve the number of global deaths and injuries from road traffic accidents by 2030.
- Decade of Action for Road Safety 2021-2030:
- The UN General Assembly adopted resolution "Improving global road safety " with the ambitious target of preventing at least 50% of road traffic deaths and injuries by 2030.
- The Global Plan aligns with the Stockholm Declaration, by emphasizing the importance of a holistic approach to road safety.
- The International Road Assessment Programme (iRAP) :
- It is a registered charity dedicated to saving lives through safer roads.
- Brasilia Declaration on Road Safety (2015):
- India:
- Motor Vehicles Amendment Act, 2019:
- The Act hikes the penalties for traffic violations, defective vehicles, juvenile driving, etc.
- It provides for a Motor Vehicle Accident Fund, which would provide compulsory insurance cover to all road users in India for certain types of accidents.
- It also provides for a National Road Safety Board, to be created by the Central Government.
- The Carriage by Road Act, 2007:
- The Act provides for the regulation of common carriers, limiting their liability and declaration of the value of goods delivered to them to determine their liability for loss of, or damage to, such goods occasioned by the negligence or criminal acts of themselves, their servants or agents and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- The Control of National Highways (Land and Traffic) Act, 2000:
- The Act provides for the control of land within the National Highways, right of way and traffic moving on the National Highways and also for removal of unauthorized occupation thereon.
- National Highways Authority of India Act, 1998:
- The Act provides for the constitution of an authority for the development, maintenance and management of NHs and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- Motor Vehicles Amendment Act, 2019: