Important Facts For Prelims
Revised Currency Swap Framework for SAARC
- 01 Jul 2024
- 4 min read
Why in News?
Recently, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI), has decided to put in place a revised framework for currency swap arrangements for SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation) countries for the period 2024 to 2027.
What is a Currency Swap Agreement?
- About:
- A currency swap agreement between two countries is a contract to exchange currencies with predetermined terms and conditions for liquidity support.
- Central banks and Governments engage in currency swaps with foreign counterparts to meet short-term foreign exchange liquidity requirements or to ensure adequate foreign currency to avoid the Balance of Payments (BOP) crisis till longer arrangements can be made.
- These swap operations carry no exchange rate or other market risks as transaction terms are set in advance.
- RBI’s Framework for Swap Facilities for SAARC:
- The SAARC currency swap facility first came into operation on 15th November 2012, to provide a backstop line of funding for short-term foreign exchange liquidity requirements or balance of payment crises of the SAARC countries till longer-term arrangements are made.
- The RBI can offer a swap arrangement within the overall corpus of USD 2 billion.
- The swap can be made in US dollars, euro or Indian rupees. The framework provides certain concessions for swap in the Indian rupee.
- The facility will be available to all SAARC member countries, subject to their signing the bilateral swap agreements.
- Changes in New Framework:
-
Under the framework for 2024-27, a separate INR (Indian Rupee) swap window has been introduced with various concessions for swap support in Indian Rupee.
-
The total corpus of the rupee support is Rs. 250 billion.
-
-
The RBI will continue to offer swap arrangements in USD and Euro under a separate US Dollar/ Euro swap window with an overall corpus of USD 2 billion.
-
-
Other Bilateral Currency Swap Agreements:
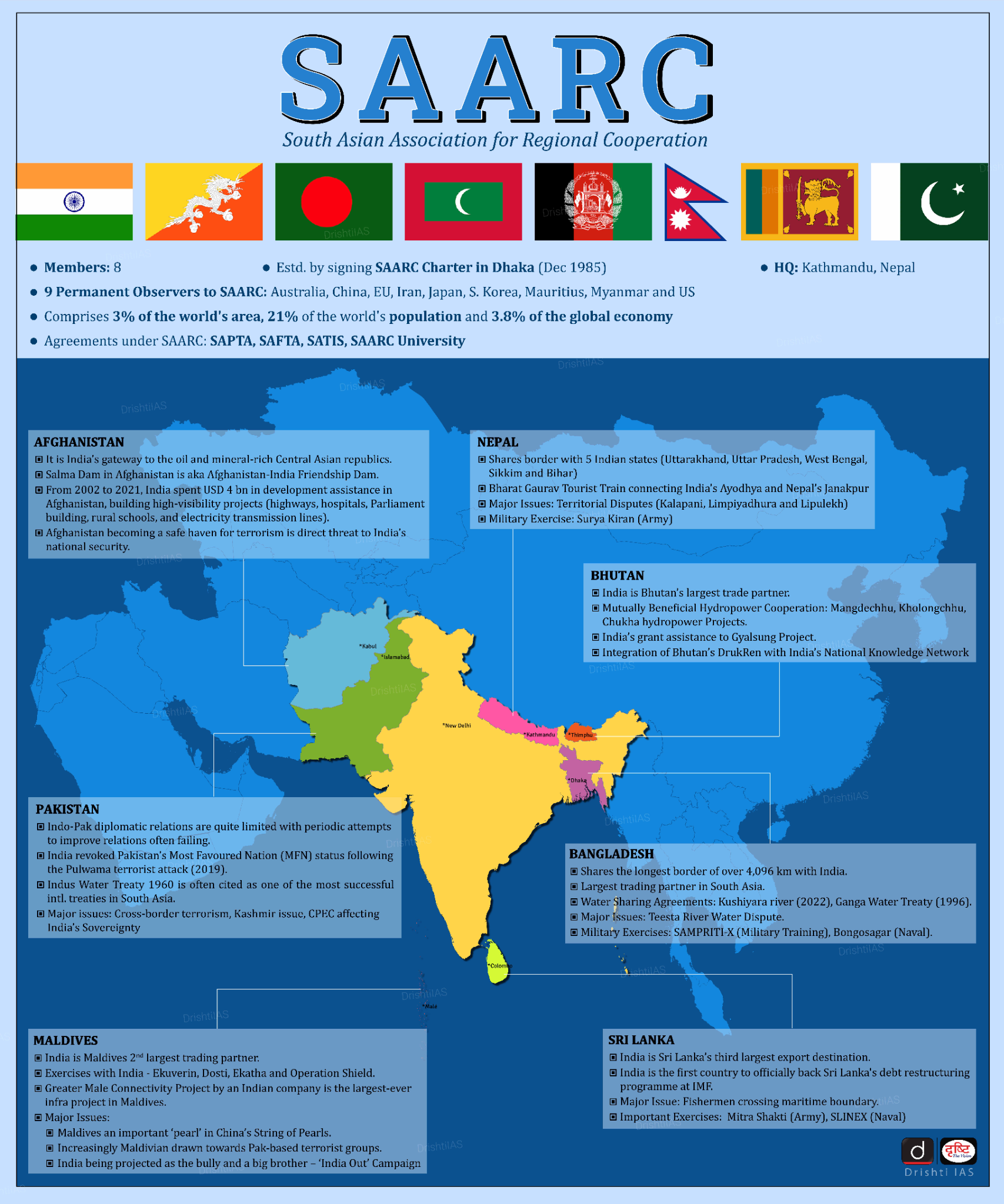
South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC)
- Establishment: SAARC was established with the signing of the SAARC Charter in Dhaka (Bangladesh) on 8th December 1985.
- Member States: Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan and Sri Lanka.
- Secretariat: Kathmandu (Nepal)
- Objective: To promote the welfare of the people of South Asia, to improve their quality of life, and accelerate economic growth, among other things
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. In the context of India, which of the following factors is/are contributor/contributors to reducing the risk of a currency crisis? (2019)
- The foreign currency earnings of India’s IT sector
- Increasing the government expenditure
- Remittances from Indians abroad
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. “Increasing cross-border terrorist attacks in India and growing interference in the internal affairs of several member-states by Pakistan are not conducive for the future of SAARC (South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation).” Explain with suitable examples. (2016)