Rethinking India's Anaemia Policy | 05 Jun 2023
For Prelims: National Family Health Survey (NFHS),WHO,Anaemia Mukt Bharat,Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan (PMSMA)
For Mains: Issues Related to Women, Health and Government Policies & Interventions
Why in News?
India is reconsidering its anaemia policy and shifting the estimation of anaemia prevalence from the National Family Health Survey (NFHS) to the Diet and Biomarkers Survey (DABS-I).
- The decision comes after concerns were raised regarding the accuracy of haemoglobin level estimation in NFHS, considering the growing burden of anaemia in the country.
What are the Key Points Related to Anaemia?
- Anaemic Condition:
- It is a condition in which the number of red blood cells or their oxygen-carrying capacity is insufficient to meet physiologic needs, which vary by age, sex, altitude, smoking, and pregnancy status.
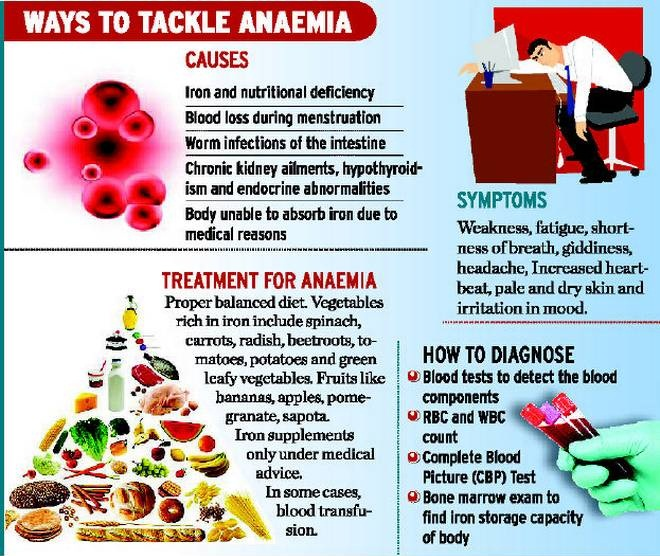
- Causes:
- Iron deficiency is the most common cause of anaemia, although other conditions, such as folate, vitamin B12 and vitamin A deficiencies, chronic inflammation, parasitic infections, and inherited disorders can all cause anaemia.
- In its severe form, it is associated with fatigue, weakness, dizziness and drowsiness. Pregnant women and children are particularly vulnerable.
- Iron deficiency is the most common cause of anaemia, although other conditions, such as folate, vitamin B12 and vitamin A deficiencies, chronic inflammation, parasitic infections, and inherited disorders can all cause anaemia.
- Anaemia Burden in India:
- NFHS-5 (2019-21) revealed a significant increase in the anaemia burden in India, with 57% of women (15-49 age group) and 67% of children (6-59 months) being anaemic.
- Reasons for the Change:
- Researchers have cautioned against over-diagnosis of anaemia in India, as the WHO cut-offs for haemoglobin may not be suitable.
- Because the cut-off point for haemoglobin depends on the age, gender, physiological status, altitude and other factors.
- Differences in blood sampling methods between NFHS and the recommended venous blood sampling were identified, potentially leading to falsely lower values.
- Researchers have cautioned against over-diagnosis of anaemia in India, as the WHO cut-offs for haemoglobin may not be suitable.
- Diet and Biomarkers Survey (DABS-I):
- DABS-I is a comprehensive national-level dietary survey aimed at determining food and nutrient adequacy across different age groups and regions.
- The survey collects individual dietary intake data and provides nutrient composition information on cooked and uncooked foods.
- DABS-I is expected to offer better estimates of anaemia prevalence and aid in developing targeted interventions.
- Importance of Anaemia Data:
- Anaemia data serves as a crucial indicator of public health, particularly for vulnerable populations such as pregnant women and children under five.
- Prevalence studies on anaemia help monitor reproductive health progress and understand the impact on work capacity and national development.
What are Government Initiatives?
- Anaemia Mukt Bharat(AMB): It was launched in 2018 as part of the Intensified National Iron Plus Initiative (NIPI) Program for accelerating the annual rate of decline of anaemia from one to three percentage points.
- The target groups for AMB are Children 6-59 months, 5-9 years, Adolescent Girls & Boys of 10-19 years, Women of Reproductive Age (15-49 years), Pregnant Women and Lactating Mothers.
- Weekly Iron and Folic Acid Supplementation (WIFS):
- This Programme is being implemented to meet the challenge of high prevalence and incidence of anaemia amongst adolescent girls and boys.
- The intervention under WIFS includes supervised weekly ingestion of Iron Folic Acid (IFA) tablet.
- Operationalization of Blood Bank:
- In District Hospitals and Blood Storage Unit in subdistrict facilities such as Sub-Divisional Hospital/ Community Health Centers is being taken to tackle complications due to severe anaemia.
- Pradhan Mantri Surakshit Matritva Abhiyan (PMSMA):
- It has been launched to focus on conducting special ANC check up on 9th of every month with the help of medical officers/ OBGYN to detect and treat cases of anaemia.
- Other steps Taken:
- To control worm infestation biannual deworming with Albendazole is provided.
- Health management information system & Mother Child tracking system is being implemented for reporting and tracking the cases of anaemic and severely anaemic pregnant women.
- Universal screening of pregnant women for anaemia is a part of ante-natal care and all pregnant women are provided iron and folic acid tablets during their ante-natal visits through the existing network of sub-centres and primary health centres and other health facilities as well as through outreach activities at Village Health & Nutrition Days (VHNDs).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements in the context of interventions being undertaken under Anaemia Mukt Bharat: (2023)
- It provides prophylactic calcium supplementation for pre-school children, adolescents and pregnant women.
- It runs a campaign for delayed cord clamping at the time of childbirth.
- It provides for periodic deworming to children and adolescents.
- It addresses non-nutritional causes of anaemia in endemic pockets with special focus on malaria, hemoglobinopathies and fluorosis.
How many of the statements given above are correct?
a) Only one
b) Only two
c) Only three
d) All four Interventions of Anaemia Mukt Bharat:
Ans: c
Exp:
- Not Prophylactic calcium supplementation but Prophylactic Iron and Folic Acid Supplementation is provided to children,adolescents and women of reproductive age and pregnant women irrespective of anemia. Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Appropriate Infant and Young Child Feeding (IYCF) withemphasis on adequate and age-appropriate complementary foods for children 6 months and above.
- Increase intake of iron-rich, protein-rich and vitamin C-rich foods through dietary diversification/quantity/frequency and food fortification
- Promoting practice of delayed cord clamping (by atleast 3 minutes or until cord pulsations cease) in all health facility deliveries followed by early initiation of breastfeeding within 1 hour of birth. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- Bi-annual mass deworming for children in the age groups between 1-19 years is carried out every year under the National Deworming Day (NDD) programme. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- The Anemia Mukt Bharat also integrates deworming of women of reproductive age and for pregnant women as part of the NDD strategy.
- Addressing non-nutritional causes of anemia in endemic pockets, with special focus on malaria, haemoglobinopathies and fluorosis.
- Hence, statement 4 is correct
Mains
Q: Public health system has limitations in providing universal health coverage. Do you think that private sector could help in bridging the gap? What other viable alternatives would you suggest? (2015)