Economy
Renewables 2023 Report of IEA
- 06 Feb 2024
- 8 min read
For Prelims: International Energy Agency, Renewable energy, Solar Energy, Net Zero Emissions by 2050, Panchamrit Goals, Nationally Determined Contribution, Pradhan Mantri- Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan,, Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for High-Efficiency Solar PV Modules, Offshore Wind Energy Policy, Global Biofuel Alliance, International Solar Alliance
For Mains: Major Takeaways of Renewables 2023 Report, India’s Renewable Energy Targets and Related Government Interventions.
Why in News?
The International Energy Agency (IEA)'s recent Renewables 2023 report paints a complex picture of the renewable energy sector, highlighting both progress and challenges.
What are the Major Highlights of the Renewables 2023 Report?
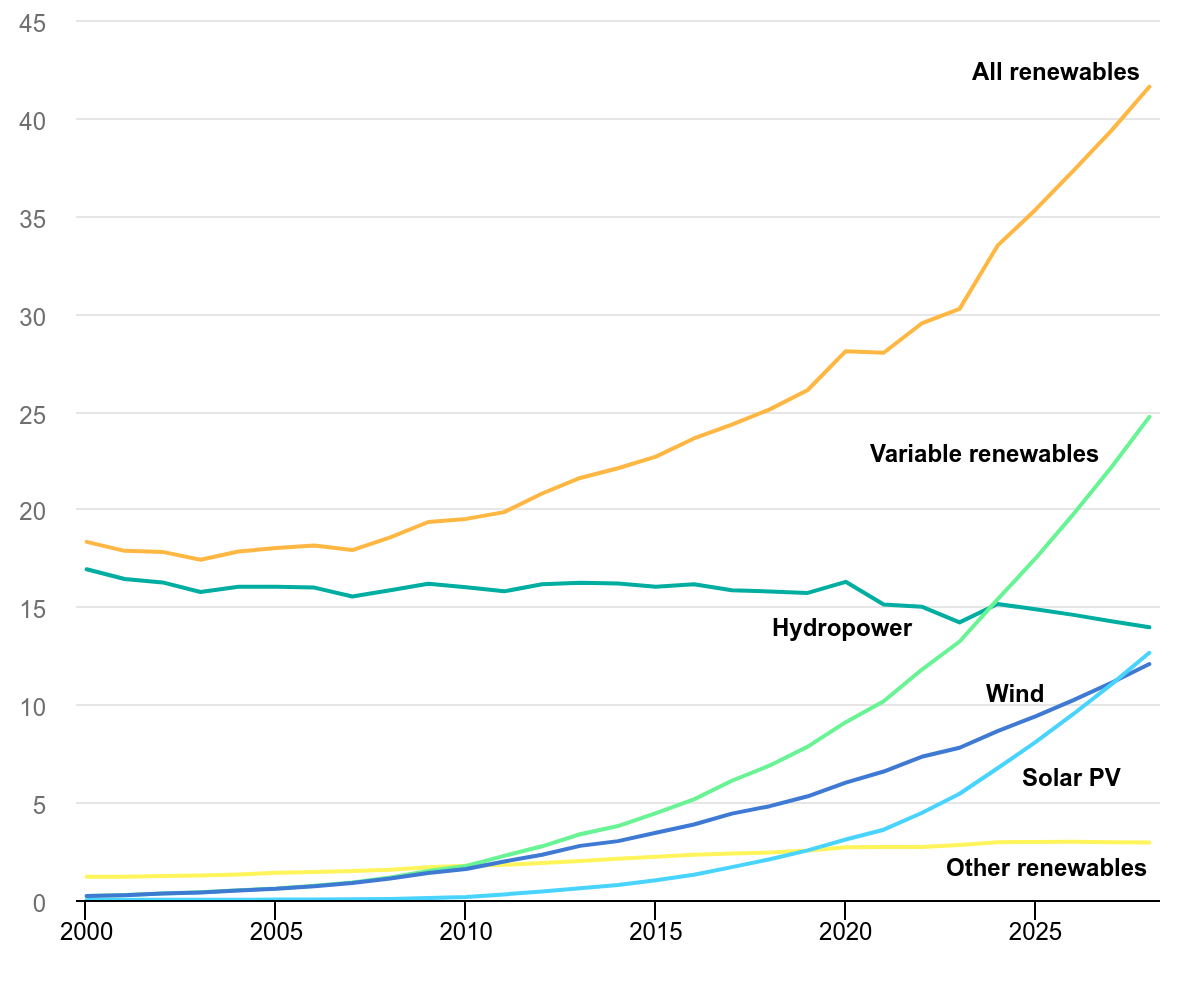
- Record Growth and China’s Dominance: Global annual renewable capacity additions surged by nearly 50% to almost 510 gigawatts (GW) in 2023, marking the fastest growth rate in two decades.
- China played a pivotal role, commissioning as much solar photovoltaics (PV) in 2023 as the entire world did in 2022, while wind additions grew by 66% year-on-year.
- Global Power Mix Transformation: Renewables are projected to surpass coal as the largest source of electricity generation by 2025, with wind and solar PV becoming dominant sources by 2028.
- Accelerated Growth in Key Regions:
- US, EU, India, Brazil: Supportive policies and improving economic attractiveness are driving accelerated growth in solar PV and onshore wind installations in these regions.
- Middle East and North Africa: Policy incentives are spurring renewable capacity growth.
- While sub-Saharan Africa is lagging despite its resource potential.
- Growth Forecast for India: India is forecast to add 205 GW over 2023-2028, doubling 2022’s cumulative installed capacity, making it the world’s third-largest market for renewables.
- Solar PV Market Dynamics: Solar PV module prices dropped by nearly 50% in 2023 due to increased manufacturing capacity.
- Solar PV and onshore wind are cheaper than both new and existing fossil fuel plants, driving their rapid adoption globally.
- Biofuel Expansion and EV Adoption: Emerging economies, led by Brazil, are driving biofuel expansion.
- Biofuels and renewable electricity in EVs are forecasted to offset significant oil demand by 2028, emphasizing their complementary role.
- Major Challenges Highlighted in the Report:
- Financial Constraints: Emerging and developing economies face inadequate financing for renewable projects.
- Rising interest rates are increasing financing costs, posing challenges to renewable energy developers.
- Grid Bottlenecks: Rapid deployment of variable renewables poses integration challenges, leading to increased curtailment in many countries due to inadequate grid expansion.
- Wind Industry Challenge: The wind industry faces challenges from supply chain disruptions, especially in offshore wind.
- Financial Constraints: Emerging and developing economies face inadequate financing for renewable projects.
- Major Recommendations: IEA urged governments to triple global renewable power capacity by 2030, aligning with the Net Zero Emissions by 2050 (NZE) Scenario.
- To meet the 2030 targets, addressing policy uncertainties, investing in grid infrastructure, easing administrative barriers, and enhancing financing in emerging economies is crucial.
What are India’s Renewable Energy Targets and Related Government Interventions?
- India's Renewable Energy Targets:
- Panchamrit Goals:
- Reaching a non-fossil fuel energy capacity of 500 GW by 2030.
- Fulfilling at least half of its energy requirements via renewable energy by 2030
- Reducing CO2 emissions by 1 billion tons by 2030; reducing carbon intensity below 45 percent by 2030.
- Net-Zero emission target by 2070.
- In August 2022, India updated its Nationally Determined Contribution (NDC) according to which the target to reduce emissions intensity of its GDP has been enhanced to 45% by 2030 from 2005 level.
- Panchamrit Goals:
- Related Government Initiatives:
- Pradhan Mantri- Kisan Urja Suraksha evam Utthaan Mahabhiyan (PM- KUSUM)
- National Solar Mission
- Production Linked Incentive (PLI) Scheme for High-Efficiency Solar PV Modules
- Offshore Wind Energy Policy
- Global Biofuel Alliance
- International Solar Alliance
- Suryamitra Skill Development Programme: It aims for skill development among the youth, considering the opportunities for employment in the growing Solar Energy Power Project’s installations.
What is IEA?
- Establishment and Evolution: IEA was established in 1974 to ensure oil supply security in response to the 1973-1974 oil crisis.
- Initially focusing on oil supply security and policy cooperation, its mandate expanded over time to encompass a broader range of energy issues.
- Currently, the IEA has four main areas of focus: energy security, economic development, environmental awareness and engagement worldwide.
- In 2022, IEA member governments agreed to expand the Agency's mandate to guide countries towards building net-zero emission energy systems and include critical minerals and metals for clean energy technologies.
- Membership: IEA is made up of 31 member countries.
- In addition, the IEA also includes thirteen association countries (including India).
- Five countries are seeking accession to full membership, Chile, Colombia, Israel, Latvia and Costa Rica.
- A candidate country for the IEA must be a member country of the OECD.
- Major Reports:
- World Energy Outlook Report
- India Energy Outlook Report
- World Energy Investment Report
- The Annual Energy Efficiency Market Report
Read More: IEA Report Electricity 2024
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q1. Consider the following statements:
- “The Climate Group” is an international non-profit organization that drives climate action by building large networks and runs them.
- The International Energy Agency in partnership with the Climate Group launched a global initiative “EP100”.
- EP100 brings together leading companies committed to driving innovation in energy efficiency and increasing competitiveness while delivering on emission reduction goals.
- Some Indian companies are members of EP100.
- The International Energy Agency is the Secretariat to the ‘Under2 Coalition’.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2, 4 and 5
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Q.2 The term ‘Intended Nationally Determined Contributions’ is sometimes seen in the news in the context of (2016)
(a) pledges made by the European countries to rehabilitate refugees from the war-affected Middle East
(b) plan of action outlined by the countries of the world to combat climate change
(c) capital contributed by the member countries in the establishment of the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank
(d) plan of action outlined by the countries of the world regarding Sustainable Development Goals
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. Describe the benefits of deriving electric energy from sunlight in contrast to conventional energy generation. What are the initiatives offered by our government for this purpose? (2020)
Q. “Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)”.Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (2018)