Indian Economy
Remittance Inflow
- 20 Jun 2023
- 6 min read
For Prelims: World Bank, Remittances, Foreign exchange, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development, Gulf Cooperation Council, National Payments Corporation of India, E-commerce
For Mains: Remittance Trends Across the Globe, Factors Affecting Remittance Flows to India.
Why in News?
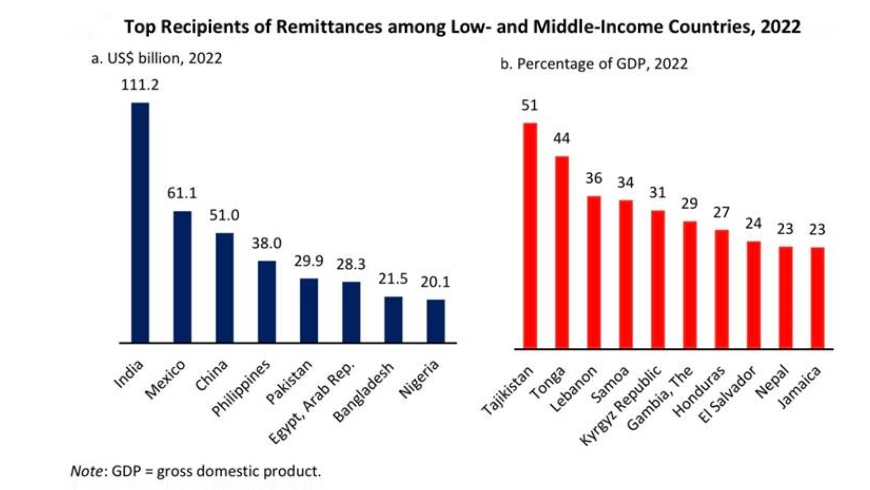
According to the World Bank’s latest Migration and Development Brief, India, which saw a record-high of USD 111 billion in remittances in 2022, is expected to experience minimal growth of just 0.2% in remittance inflows in 2023.
- The main reasons for this are the slower growth in OECD economies, especially in the high-tech sector, and the lower demand for migrants in the GCC countries.
- Overall, remittance growth is projected to be slower globally, with Latin America and the Caribbean showing the highest growth while South Asia lags behind.
What are Remittances?
- Remittances are money transfers that migrants send to their families and friends in their home countries.
- They are an important source of income and foreign exchange for many developing countries, especially those in South Asia.
- Remittances can help reduce poverty, improve living standards, support education and health care, and stimulate economic activity.
What are the Remittance Trends Across the Globe?
- The top five recipient countries for remittances in 2022 were India, Mexico, China, the Philippines, and Pakistan.
- Remittance flows to low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) are projected to moderate to 1.4% in 2023, with total inflows estimated at USD 656 billion.
- East Asia and the Pacific region may witness a decline in remittance growth due to tight monetary stances, limited fiscal buffers, and global uncertainty surrounding geopolitical events.
- Remittances to Europe and Central Asia are anticipated to grow by 1%, influenced by a high base effect, weakened flows to Ukraine and Russia, and a depreciating Russian ruble.
- Remittances in the Middle East and North Africa may recover with declining oil prices, particularly for countries like Egypt.
- Remittance growth rates for East Asia and Pacific, as well as Sub-Saharan Africa, are projected to be around 1% in 2023.
- Remittance inflows played a vital role in funding current account and fiscal shortfalls in countries like Tajikistan, Tonga, Lebanon, Samoa, and the Kyrgyz Republic.
What are the Factors Affecting Remittance Flows to India?
- Top Sources of Remittances for India
- Approximately 36% of India's remittances originate from high-skilled Indian migrants in three high-income destinations: the US, United Kingdom, and Singapore.
- The post-pandemic recovery led to a tight labor market in these regions, resulting in wage hikes that boosted remittances.
- Other high-income destinations for Indian migrants, such as the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, experienced favorable economic conditions, including high energy prices and curbed food price inflation, which increased remittance inflows.
- Factors Affecting Remittance Flows to India:
- Slower Growth in OECD economies: The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is a grouping of 38 high-income democratic countries. These countries are major destinations for high-skilled and high-tech Indian migrants, who account for almost 36% of India’s remittances.
- The World Bank expects that the growth of these economies will moderate from 3.1% in 2022 to 2.1% in 2023 and 2.4% in 2024.
- This could affect the demand for IT workers and lead to a diversion of formal remittances toward informal money transfer channels.
- The World Bank expects that the growth of these economies will moderate from 3.1% in 2022 to 2.1% in 2023 and 2.4% in 2024.
- Lower Demand for Migrants in GCC countries: GCC is a political and economic alliance of six Middle Eastern countries—Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, the United Arab Emirates, Qatar, Bahrain, and Oman.
- These countries are the single largest destination for less-skilled South Asian migrants, who account for about 28% of India’s remittances.
- The World Bank expects that the growth of these countries will slow from 5.3% in 2022 to 3% in 2023 and 2.9% in 2024.
- This is mainly due to the declining oil prices, which have dented their fiscal revenues and public spending.
- Slower Growth in OECD economies: The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) is a grouping of 38 high-income democratic countries. These countries are major destinations for high-skilled and high-tech Indian migrants, who account for almost 36% of India’s remittances.
What are the Ways to Enhance Remittance Inflow in India?
- Unified Payment Interface: UPI can enable real-time fund transfers, allowing remittances to be sent and received instantly. This eliminates the need for lengthy processing times associated with traditional remittance methods, providing recipients with quicker access to funds.
- In January 2023, The National Payments Corporation of India (NPCI) allowed NRIs living in 10 countries to use UPI using their international mobile numbers.
- The ten countries include Singapore, Australia, Canada, Hong Kong, Oman, Qatar, USA, Saudi Arabia, United Arab Emirates, and the United Kingdom.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)-Driven Risk Assessment: India can utilize AI algorithms to analyze transaction patterns, detect potential fraud, and assess risk factors associated with remittance transfers.
- This approach can enhance security and help prevent illegal activities, ensuring compliance with regulations.
- Integration with E-commerce Platforms: India can collaborate with e-commerce platforms to integrate remittance services directly into their platforms.
- This enables recipients to utilize remittance funds for online purchases or bill payments, enhancing financial inclusion and expanding the scope of remittance utilization.