Indian Economy
Relative Economic Performance of Indian States Report
- 20 Sep 2024
- 10 min read
For Prelims: Gross Domestic Product (GDP), Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM).
For Mains: Growth Drivers of the Manufacturing and Services Sectors in India, Related Challenges, Government Initiatives and Reforms for Growth of the Industrial Sector in India.
Why in News?
The Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM) recently released a report titled ‘Relative Economic Performance of Indian States: 1960-61 to 2023-24’.
- The report highlighted a significant disparity in the economic performance of Indian states from 1960-61 to 2023-24.
What are the Key Findings of the EAC-PM Report?
- Economic Performance:
- Southern States' Growth: Southern states (Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala, Tamil Nadu) have emerged as major contributors to India's GDP, accounting for 30% by March 2024.
- Their growth accelerated post-liberalization, with significant advancements in sectors like technology and industry.
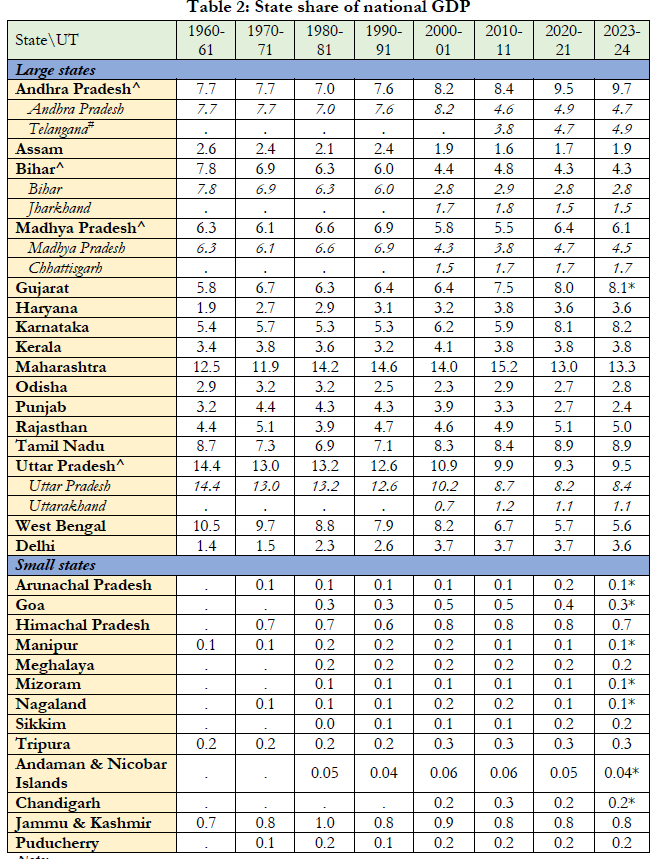
- West Bengal's Economic Decline: West Bengal's GDP contribution has decreased from 10.5% in 1960-61 to 5.6% in 2024.
- West Bengal's per capita income fell from 127.5% of the national average in the 1960s to 83.7% in 2024, now behind Rajasthan and Odisha.
- West Bengal's decline is due to policy stagnation, industrial decline, political instability, and the migration of skilled talent, all of which have hindered growth and discouraged investment.
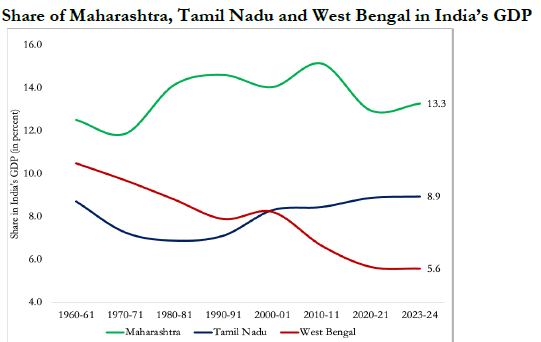
- Maharashtra remains the largest GDP contributor at 13.3%, but its share has declined from over 15%.
- Southern States' Growth: Southern states (Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Kerala, Tamil Nadu) have emerged as major contributors to India's GDP, accounting for 30% by March 2024.
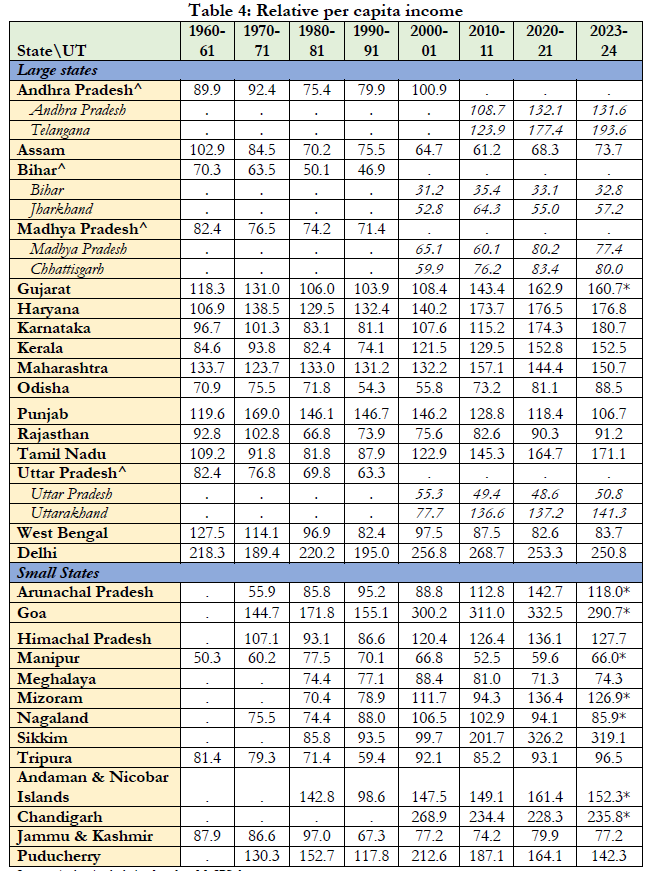
- Per Capita Income Data:
- Delhi, Telangana, Karnataka, and Haryana had the highest relative per capita income in 2023-24.
- Delhi's per capital income is at 250.8% of the national average.
- Gujarat (160.7% of the national average) and Maharashtra (150.7% of the national average) have maintained above-average incomes since the 1960s.
- Odisha per capita income improved significantly, rising from 55.8% in 2000-01 to 88.5% in 2023-24.
- Punjab vs. Haryana: Punjab has seen stagnation in economic growth since 1991, with per capita income falling to 106% of the national average.
- In contrast, Haryana has experienced substantial growth, with per capita income rising to 176.8%.
- Among Smaller States: Sikkim's per capita income rose from 93% of the national average in 1990-91 to 319% in 2023-24, while Goa's increased from 144% in 1970-71 to 290%. Both are now India's richest states by per capita income.
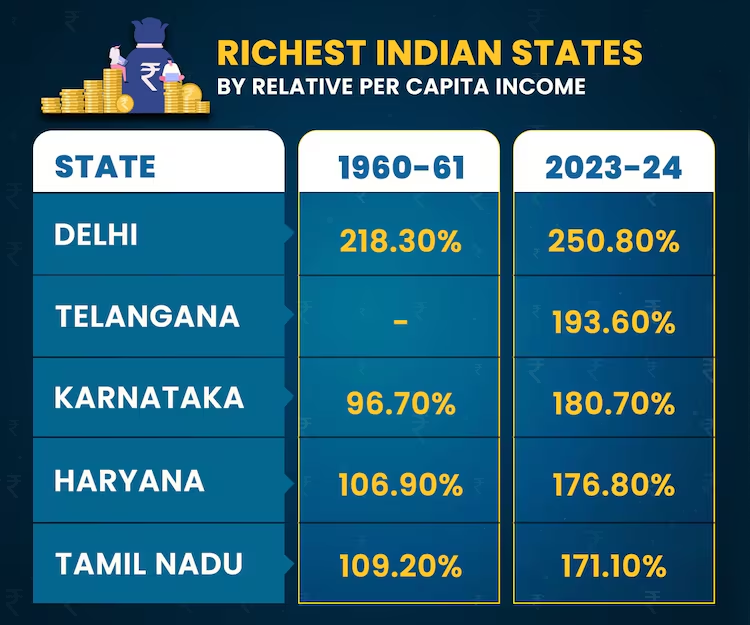
- Delhi, Telangana, Karnataka, and Haryana had the highest relative per capita income in 2023-24.
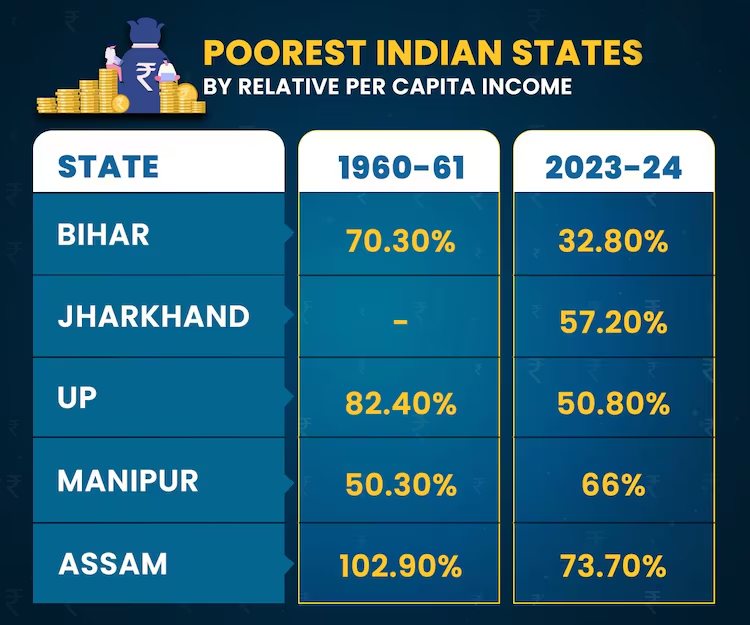
- Challenges for Poorest States: States like Uttar Pradesh and Bihar struggle to keep pace, with Uttar Pradesh contributing only 9.5% of GDP and Bihar just 4.3%.
- Despite some improvements in states like Odisha, Bihar remains significantly behind in economic growth.
- Need for Policy Investigation: The report highlights the need for deeper investigation into the policies and factors influencing state-level economic growth, particularly to address the widening regional disparities in India.
What are the Reasons for Steady Growth in West and South States?
- Robust Industrial Base: Gujarat and Maharashtra have a strong, diverse manufacturing base in sectors like textiles, chemicals, and engineering.
- Their investment-friendly policies have created a business-friendly environment, attracting significant domestic and foreign investments.
- Thriving Service Sector: Southern states like Karnataka and Tamil Nadu have experienced rapid urbanisation and improved infrastructure, boosting their IT and services sectors.
- A strong focus on education and skill development has created a skilled workforce, enhancing productivity and economic growth.
- Agricultural Advancements: Maharashtra and Kerala have adopted sustainable agricultural practices such as organic farming, crop diversification, water-efficient irrigation techniques, agroforestry and diversified outputs, boosting productivity and food security.
- Government support in irrigation, market access, and technology has further enhanced agricultural performance and economic growth.
- Strong Regional Connectivity: The Western and Southern regions have strong transport and logistics networks, with Gujarat's ports and Tamil Nadu's roadways enhancing trade.
- Proximity to major markets boosts local demand, driving economic growth in these states.
Economic Advisory Council to the Prime Minister (EAC-PM)
- It is an non-constitutional, non-statutory, independent body constituted to give advice on economic and related issues to the Government of India, specifically to the Prime Minister.
- The council serves to highlight key economic issues to the government of India from a neutral viewpoint.
- It advises the Prime Minister on economic issues like Inflation, Microfinance, and Industrial output.
- NITI Aayog serves as the Nodal Agency for the EAC-PM for administrative, logistic, planning and budgeting.
- Periodic Reports: Annual Economic Outlook, Review of the Economy.
What Measures Can be Taken to Enhance the Economic Performance of the States?
- Decentralised Planning and Governance: Empower local governments to formulate and implement development plans tailored to regional needs, involving local communities in decision-making processes to ensure inclusivity.
- Infrastructure Development: Prioritise investments in roads, railways, ports, and digital connectivity through Public-Private Partnerships (PPP) to enhance trade and mobility, ensuring timely execution and resource mobilisation.
- Sectoral Focus and Diversification: Enhance agricultural productivity through technology adoption and better irrigation while promoting agro-based industries.
- Encourage sector-specific policies that boost manufacturing (e.g., textiles, electronics) and services (e.g., IT, tourism) based on regional advantages.
- Skill Development and Human Capital: Implement vocational training programs aligned with industry needs to enhance employability while improving education quality by focusing on critical thinking and access to higher education.
- Innovation and Entrepreneurship: Foster a culture of innovation by supporting startups through incubators and funding, and encourage collaboration between academia, industry, and government for research initiatives that lead to technological advancements.
- Digital Transformation: Implement digital solutions for governance to ensure transparency and efficiency in public service delivery, while promoting digital literacy programs to equip citizens with necessary skills.
- Collaborative Governance: Foster collaboration between states to share best practices and resources, ensuring effective coordination between central and state governments to align policies and resources for development.
Conclusion
The steady growth in the Western and Southern states is a result of strategic planning, strong industrial and service sectors, effective government policies, and a focus on sustainable practices. As these states continue to innovate and adapt to changing economic dynamics, they play a crucial role in driving India towards its goal of becoming a USD 7 trillion economy by 2030. Addressing regional disparities and fostering inclusive growth will be essential to sustain this momentum and ensure balanced development across the country.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Discuss the key factors influencing the economic performance of states in India. Evaluate the role of policy interventions and suggest measures to enhance sustainable economic growth at the state level. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Atal Innovation Mission is set up under the (2019)
(a) Department of Science and Technology
(b) Ministry of Labour and Employment
(c) NITI Aayog
(d) Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship
Ans: (c)
Q. The Government of India has established NITI Aayog to replace the (2015)
(a) Human Rights Commission
(b) Finance Commission
(c) Law Commission
(d) Planning Commission
Ans: (d)
Q. Sustainable development is described as the development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. In this perspective, inherently the concept of sustainable development is intertwined with which of the following concepts? (2010)
(a) Social justice and empowerment
(b) Inclusive Growth
(c) Globalization
(d) Carrying capacity
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. How are the principles followed by the NITI Aayog different from those followed by erstwhile Planning Commission in India? (2018)
Q. Access to affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy is the sine qua non to achieve Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).” Comment on the progress made in India in this regard. (2018)