Regulating Nitrate absorption in Plants | 05 Jul 2022
Why in News?
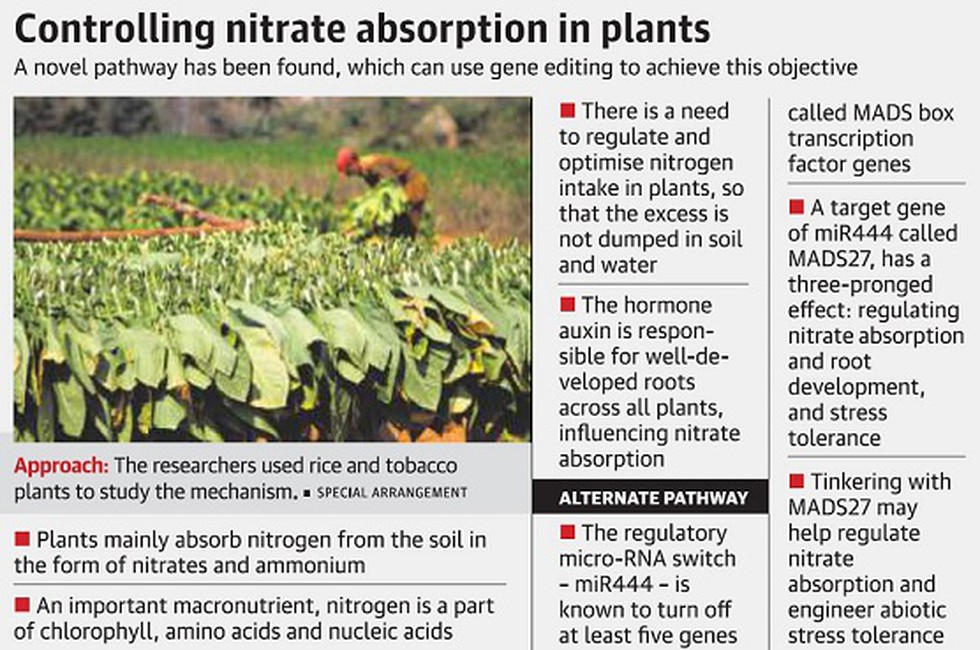
Researchers from the National Centre of Biological Sciences, Tata Institute of Fundamental Research, Bengaluru (NCBS-TIFR) discovered a new pathway that regulates nitrate absorption in plants.
What is the New Method?
- The researchers investigated a miR444 target gene called MADS27, a transcription factor that has previously received little attention.
- Transcription factors are proteins involved in the process of converting, or transcribing, DNA into RNA. Transcription factors include a wide number of proteins, excluding RNA polymerase, that initiate and regulate the transcription of genes.
- The micro-RNA, miR444, activates the Gene MADS27, which regulates nitrate absorption, root development, and stress tolerance, and thus provides a way to control these plant properties.
- The gene MADS27 appears to be an excellent candidate for modification in order to improve nitrogen use efficiency, which helps the plant absorb more nitrates, and to engineer abiotic stress tolerance.
- This mechanism was studied in both rice (monocot) and tobacco (dicot) plants by the researchers. The study was published in the Journal of Experimental Botany.
What is the Importance of Nitrogen?
- Nitrogen is one of the most important macronutrients needed for development of a plant.
- However, excessive use of nitrates in fertilisers, for example, can result in nitrate dumping in the soil, resulting in nitrate accumulation in water and soil. This accumulation contributes to soil and water pollution, as well as increased contribution to greenhouse gas emissions.
- It is a part of chlorophyll, amino acids and nucleic acids, among others.
- It is mostly sourced from the soil where it is mainly absorbed in the form of nitrates and ammonium by the roots.
- Nitrates also influence genome-wide gene expression, which in turn influences the root system, the biological clock of plants, leaf growth, and so on.
UPSC Civil Services examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following adds/add nitrogen to the soil? (2013)
- Excretion of urea by animals
- Burning of coal by man
- Death of vegetation
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
- Mammals, including humans, are the primary producers of urea. Because they secrete urea as the primary nitrogenous waste product, they are called ureotelic animals. These wastes add nitrogen to the soil. Hence, 1 is correct.
- Coal combustion produces Oxides of Carbon (COx), Oxides of Sulphur (SOx), Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) and a variety of byproducts, including fly-ash, flue gas and scrubber sludge. However, it does not directly add nitrogen to the soil. Hence, 2 is not correct.
- When plants and animals die, the Nitrogen compounds in the organic matter re-enter the soil where they are broken down by microorganisms, known as decomposers. This decomposition produces Ammonia, which goes through the nitrification process, i.e., nitrifying bacteria in the soil convert Ammonia into Nitrite (NO2 ) and then into Nitrate (NO3 ). Hence, 3 is correct. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.