Regional Dialogue of Secretaries of Security Councils on Afghanistan | 23 Feb 2024
For Prelims: Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR), Humanitarian Air Corridor, Regional Security Dialogue on Afghanistan, National Security Advisers, UNSCR 2593, Strategic Partnership Agreement
For Mains: India-Afghanistan relation and its significance on regional security, peace and prosperity.
Why in News?
Recently, the 6th Regional Dialogue of Secretaries of Security Councils/National Security Advisers (NSA) on Afghanistan was held in Bishkek, Kyrgyzstan.
- India reiterated its collective approach to combating terrorism as stated in the United Nations Security Council Resolution (UNSCR 2593).
What is the Regional Security Dialogue on Afghanistan?
- The Regional Security Dialogue on Afghanistan is a series of high-level meetings involving National Security Advisers (NSA) or senior security officials from countries in the region, including Afghanistan, Pakistan, Iran, China, Russia, India, and other Central Asian states.
- These dialogues are platforms for discussing and coordinating regional approaches to address security challenges and promote stability in Afghanistan and the broader region.
- Regional Security Dialogue on Afghanistan follows the objective of UNSCR 2593.
- The resolution, passed by the 15-member organ (UNSC), calls for the prevention of Afghan territory from being used to pose threats or launch attacks against any nation.
- The adoption of the resolution is a strong signal from the Security Council and the international community on its expectations in respect of Afghanistan.
- It underscores the critical necessity of combating terrorism within Afghanistan.
What are India’s Efforts for the People of Afghanistan?
- The Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR) has taken significant strides in promoting education, granting admission to over 3,000 students, including 600 Afghan girls, since August 2021.
- In a bid to provide essential support, a Humanitarian Air Corridor has been established between Delhi and Kabul.
- This corridor facilitates critical travel and aid delivery, demonstrating India's proactive response to humanitarian needs.
- India has supplied several shipments of humanitarian assistance consisting of 50,000 MTs of wheat, 250 tons of medical aid and 28 tons of earthquake relief aid.
- India has partnered with the United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime (UNODC) in Afghanistan to provide assistance for the welfare of the Afghan drug user population, especially women.
- Under this partnership, India has, since 2022, supplied 11,000 units of hygiene kits, baby food, blankets, clothing, medical aid and other miscellaneous items to UNODC, Kabul.
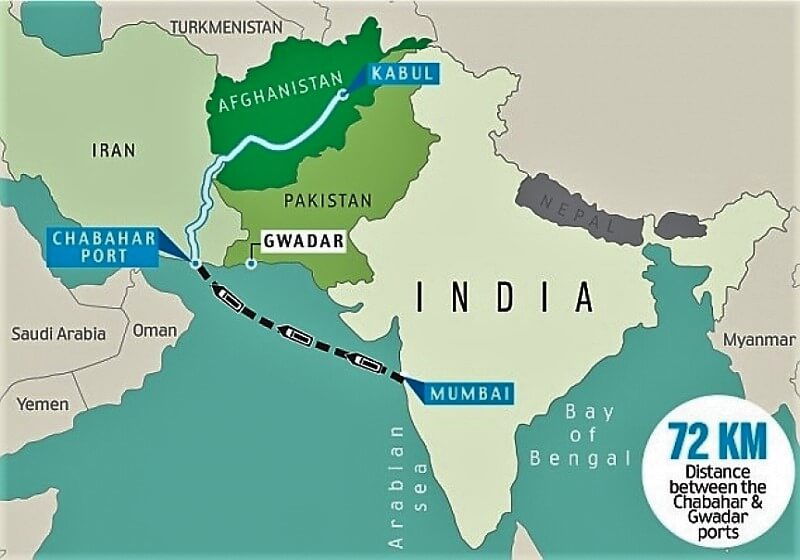
- Trade and commerce between India and Afghanistan is ongoing, including through the Chabahar port.
What are the Key Issues Affecting India-Afghanistan Relations?
- Impact on Regional Stability: The drug trade originating from Afghanistan (golden crescent) has been a major contributor to instability and violence in the region, posing challenges for both Afghanistan and neighbouring countries like India.
- Indian Interests and Influence: India's strategic interests and influence in the region faced a setback following the Taliban's capture of Kabul in 1996.
- Economic and Infrastructure Hurdles: The fall of Afghanistan in the hands of the Taliban (2021) presented formidable obstacles to India's endeavours to construct infrastructure like the Salma Dam and Parliament Building and to make investments in the country. These efforts have been impeded by security concerns, corruption, and various other challenges.
- Attack on Indian Nationals: The bombing of a Sikh gurdwara in Kabul claimed by ISIS-K, has raised concerns for India.
- Shift in Security Dynamics: Until August 2021, India relied on a friendly government in Kabul and the security presence of the United States in Afghanistan for its security.
- The US withdrawal from Afghanistan necessitated a careful reassessment of the security landscape by India.
How is India’s Relations with Afghanistan?
- History:
- India's policy towards Afghanistan is rooted in historical and civilizational ties, dating back centuries.
- India has historically enjoyed relatively good ties with Afghanistan, which go back to the Treaty of Friendship, 1950.
- As a contiguous neighbour, India has both legitimate economic and security interests in Afghanistan.
- India's policy towards Afghanistan is rooted in historical and civilizational ties, dating back centuries.
- Economic Relations:
- Through nearly 500 projects spanning all 34 provinces, India has invested over USD 3 billion in critical areas such as power, water supply, road connectivity, healthcare, education, agriculture, and capacity building.
- The Indian Army's Border Roads Organisation constructed a major road in 2009 in the remote Afghan province of Nimroz, connecting Delaram to Zaranj.
- This has proved a viable alternative route for the duty-free movement of goods through the Chabahar port in Iran to Afghanistan.
- Tariff concessions under South Asian Free Trade Agreement (SAFTA) continue to be provided to Afghan traders.
- Salma Dam, Afghan-India Friendship Dam (AIFD) is a hydroelectric and irrigation dam project located on the Hari River in Herat Province of western Afghanistan.
- In 2006, India made a commitment to funding the project for its completion.
- Political Relations:
- India-Afghanistan relations have been strengthened by the Strategic Partnership Agreement, which was signed between the two countries in October 2011.
- The Strategic Partnership Agreement (SPA) between the two sides, provides for assistance to help rebuild Afghanistan's infrastructure and institutions, education and technical assistance.
- India has been a strong supporter of Afghan democracy and has consistently advocated for a stable, peaceful, and prosperous Afghanistan.
- Humanitarian Assistance:
- To combat the global pandemic of COVID-19 and related issues of food security, India is committed to delivering 75,000 MT of Wheat to Afghanistan in 2020.
- India has also undertaken the supply of the tablets of Hydroxy-chloroquine, Paracetamol and pairs of surgical gloves to the Government of Afghanistan in 2020.
- Provision of food assistance of 11 lakh tonnes of wheat, both as grains and biscuits, was distributed to approximately 1.5 million school children.
- To promote food security, particularly for children during times of drought, India distributed 2000 tonnes of pulses to Afghanistan in 2018.
- A Medical Diagnostic Centre in Kabul was set up in 2015. The Centre provides the latest diagnostic facilities to children of Afghanistan thereby generating goodwill for India.
- To combat the global pandemic of COVID-19 and related issues of food security, India is committed to delivering 75,000 MT of Wheat to Afghanistan in 2020.
What is the Indian Council for Cultural Relations?
- The Indian Council for Cultural Relations (ICCR), is an autonomous organization of the Government of India, involved in India's external cultural relations (cultural diplomacy), through cultural exchange with other countries and their peoples.
- It was founded in 1950 by Maulana Abul Kalam Azad, independent India’s first Education Minister.
- ICCR has been assigned the responsibility of facilitating the celebration of the International Day of Yoga by Indian Missions/Posts abroad since 2015.
Conclusion
- India's deep-rooted historical, economic, and political ties with Afghanistan underscore its commitment to the nation's stability and prosperity.
- Through strategic partnerships, significant investments, and humanitarian assistance, India continues to play a pivotal role in supporting Afghanistan's development journey.
- By fostering goodwill and providing essential services, India strengthens its bonds with Afghanistan, contributing to regional peace and security.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following countries: (2022)
- Azerbaijan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Tajikistan
- Turkmenistan
- Uzbekistan
Which of the above have borders with Afghanistan?
(a) 1, 2 and 5 only
(b) 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. The proposed withdrawal of the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) from Afghanistan in 2014 is fraught with major security implications for the countries of the region. Examine in light of the fact that India is faced with a plethora of challenges and needs to safeguard its own strategic interests. (2013)