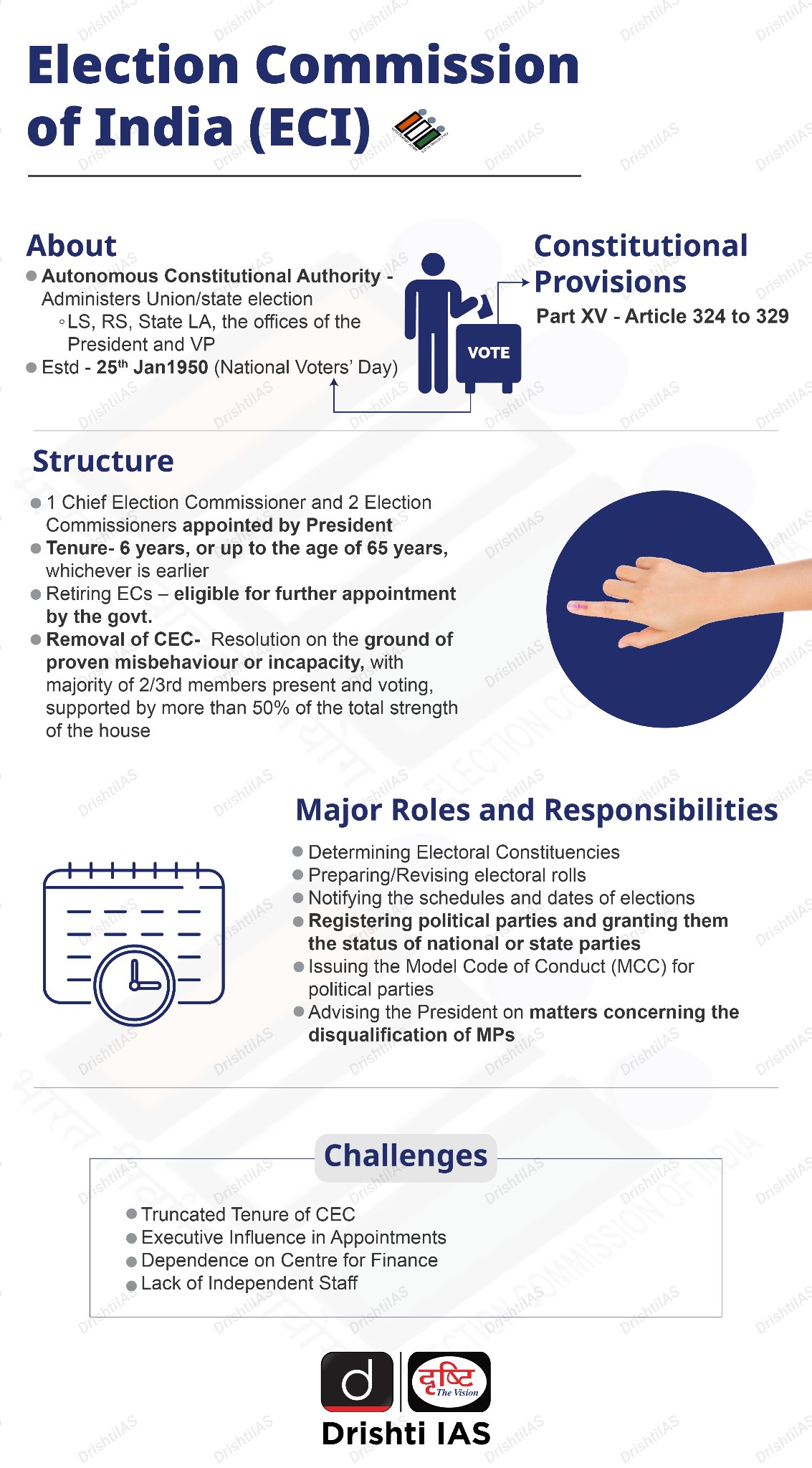
Indian Polity
Reforms to Municipal Elections
- 18 Apr 2024
- 6 min read
For Prelims: State Election Commission, Constitutional Bodies, Municipal Elections
For Mains: Challenges and Awaited Reforms related to Municipal Elections.
Why in News?
The recent Supreme Court judgment on the Chandigarh mayoral election resurfaces the issues associated with the electoral processes of local urban bodies.
- Unlike, Lok sabha and state assemblies elections in India, municipal elections still face the challenges of timely elections and smooth transitions of power.
Legal Provisions for Local Bodies’ Elections:
- Constitutional Provisions:
- The superintendence, direction and control of the preparation of the electoral rolls for, and the conduct of, all elections to the panchayats and municipalities shall be vested in the State Election Commission (SEC).
- The 74th Constitutional Amendment bars the interference by courts in the electoral matters of municipalities.
- Article 243U through the 74th Constitution Amendment Act mandates a five-year tenure for urban local governments.
- Legal Provisions:
- The Supreme Court, in Suresh Mahajan v. State of Madhya Pradesh Case, 2022, stressed the inviolability of this constitutional mandate.
What is the Status of Municipal Elections in India?
- Annual Survey of India’s City-Systems 2023 by Janaagraha’s (non-profit institution):
- Over 1,400 municipalities in India did not have elected councils in place as of September 2021.
- This indicates a significant and widespread issue across the country.
- The Comptroller and Auditor-General of India (CAG)'s audit revealed that, between 2015 and 2021, over 1,500 municipalities didn't have elected councils.
- Major cities like Chennai, Delhi, Mumbai, and Bengaluru faced delays ranging from months to years in holding elections.
What are the Challenges Associated with Local Bodies' Elections?
- Discretionary Powers in Scheduling Elections:
- Due to the ambiguous constitutional safeguards, government officials like SECs currently possess discretionary powers when it comes to scheduling elections.
- This flexibility can sometimes lead to inconsistent or delayed election timelines, which may undermine the democratic process's transparency and fairness.
- Undue Influence by State Governments:
- There is a concern about the potential undue influence exerted by State governments to delay elections for political or strategic reasons.
- Such interference can compromise the integrity of the electoral process and erode public trust in democratic institutions.
- Reliance on Manual Ballot Paper-Based Processes:
- The continued reliance on manual ballot paper-based processes introduces vulnerabilities, such as errors in counting, the potential for tampering, and delays in declaring election results.
- This traditional approach may not be as efficient or secure as modern Electronic Voting Machine (EVM) and Voter Verifiable Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT), which could enhance the transparency and credibility of electoral outcomes.
- Delayed Formation of Councils:
- Even after elections, municipal councils in urban local governments were not promptly constituted.
- For example: In Karnataka, a delay of 12-24 months was observed post-elections.
- Even after elections, municipal councils in urban local governments were not promptly constituted.
What are the Possible Solutions Regarding Local Bodies’ Elections?
- Empowering SECs: To deal with the challenges effectively, SECs need to play a more significant role in overseeing the electoral process using the powers mentioned in the Articles 243K and 243ZA of the Constitution.
- Empowerment for Ward Delimitation: Only 11 out of 35 states and union territories have empowered SECs to conduct ward delimitation.
- Ward delimitation is crucial for ensuring fair and equitable representation in municipal elections.
- SECs should be granted greater authority, including the power to conduct ward delimitation.
- Accountability Mechanisms: Holding election officials and authorities accountable for any delays or irregularities in the conduct of municipal elections. This can be done through transparent investigation processes and appropriate disciplinary action.
- Policy Reforms: Addressing the challenges highlighted, from scheduling elections to ensuring fair processes, requires comprehensive policy reforms.
- The idea of ‘ One Nation, One Election’ can be explored with major focus on the efficient and timely election of the local bodies.
Conclusion
There is a need for comprehensive reforms relating to municipal elections in India, addressing delays, enforcing constitutional mandates, empowering State Election Commissions, and modernising electoral processes to ensure transparency, fairness, and accountability.
|
Drishti Mains Question Q.Discuss the challenges and possible solutions regarding timely elections and smooth transitions of power of Local Bodies. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements: (2017)
- The Election Commission of India is a five-member body.
- The Union Ministry of Home Affairs decides the election schedule for the conduct of both general elections and bye-elections.
- Election Commission resolves the disputes relating to splits/mergers of recognised political parties.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q. Discuss the role of the Election Commission of India in the light of the evolution of the Model Code of Conduct. (2022)