Reforming Khap Panchayat | 16 Nov 2024
For Prelims: Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR), Caste-Based Councils, Conflict Resolution, Gender Inequality, Constitutional Rights, Legal Services Authorities Act (1987), Mediation Bill (2021), ADR system, Mediation, Human Rights, Unemployment, Education, Rural Development.
For Mains: Significance of Alternative Dispute Resolution in Dispute Resolution.
Why in News?
Khap Panchayats are sometimes seen in the news for multiple reasons, with some leaders advocating for progressive reforms to address key social and economic issues, including unemployment, education, and rural development.
- Efforts are also being made to modernise and regulate Khap Panchayats, integrating them into formal Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) systems for better governance and accountability.
What is Khap Panchayat?
- About: Khap Panchayats are traditional community-based councils primarily in North India, especially in Haryana and Uttar Pradesh, that function as informal judicial bodies.
- Originating centuries ago, they were formed among kinship groups (Khaps) to address social and governance issues within their communities.
- Historical Role: The system played a significant role in maintaining social order in rural societies, acting as a forum for conflict resolution within caste hierarchies, and operating parallel to formal legal systems while prioritising customary norms.
- Issues with Khap Panchayats:
- Patriarchal Practices: They are often associated with gender inequality, enforcing rigid social norms that restrict women's autonomy.
- Honor Killings: Infamous for opposing inter-caste and same-gotra marriages, sometimes sanctioning extreme measures like honour killings.
- Legality Concerns: Their decisions frequently violate constitutional rights, clashing with the principles of personal liberty, equality, and dignity.
- Caste and Social Inequities: Their focus on maintaining caste hierarchies reinforces discrimination and exclusion.
- Gender Dynamics and Evolving Roles of Khap Panchayats:
- Support for Women Athletes: Khaps have felicitated successful women sportspersons, contributing to a growing culture of sports among women.
- Gender Justice: Supported the 2023 wrestlers’ protest against sexual harassment, marking a shift towards gender-related activism.
- For instance, Meham Chaubisi, one of Haryana’s most influential Khaps, is playing a growing role in promoting justice, social change, and addressing women’s issues.
Supreme Court Ruling Related to Khap Panchayat
- The Shakti Vahini v. Union of India case, 2018, was a landmark judgment by the Supreme Court of India that addressed the issue of honour killings and inter-caste marriages.
- The Court ruled that honor killings are a violation of fundamental rights and emphasized the need for strict action against such crimes.
- It directed the State Governments to take proactive measures to prevent honor killings, including setting up special cells and providing protection to couples facing threats from their families.
What is Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) Mechanism?
- About:
- ADR is a non-adversarial method of dispute resolution that encourages cooperative efforts to reach mutually beneficial outcomes.
- It helps reduce court burdens and provides a satisfying experience for involved parties.
- ADR enables creative bargaining, fulfilling underlying interests and expanding solutions.
- Need for ADR:
- India's judicial system faces immense stress due to increasing case pendency and delays, highlighting the need for ADR methods.
- ADR ensures confidentiality, is cost-effective, and offers flexibility, often leading to creative solutions and improved relationships.
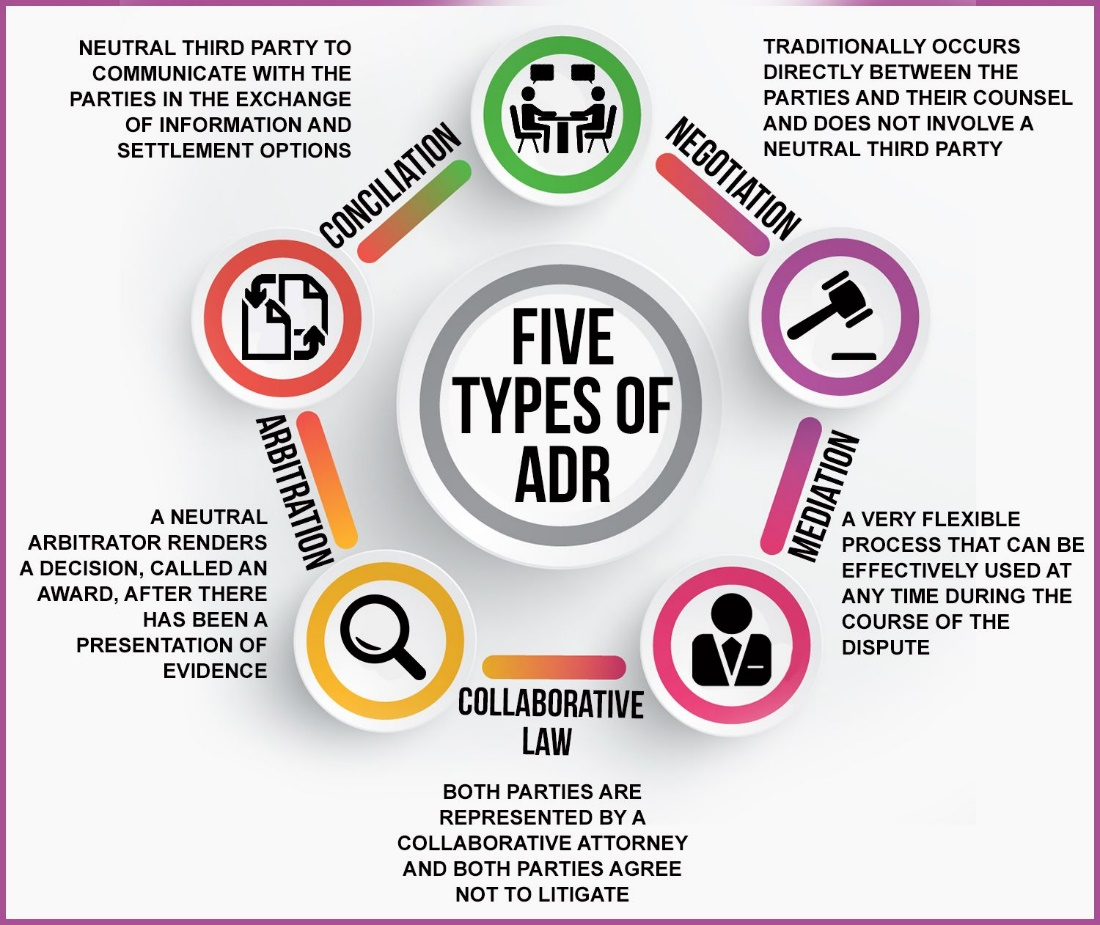
- Types of ADR Mechanisms:
- Arbitration: Disputes are resolved by an arbitral tribunal whose decision is binding and offers limited judicial intervention.
- Conciliation: A third party helps the disputing parties reach a mutually satisfactory settlement, with the option to accept or reject recommendations.
- Mediation: A mediator helps the parties communicate and settle disputes amicably, leaving control with the parties.
- Negotiation: A non-binding method where parties negotiate directly to resolve disputes without third-party involvement.
- Status of ADR in India:
- Statutory Backing: Legal Services Authorities Act (1987) and Arbitration and Conciliation Act (1996) promote out-of-court settlements.
- Plea-Bargaining: Introduced in the Code of Criminal Procedure (Amendment) Act, 2005 (now Bharatiya Nagarik Suraksha Sanhita) for pre-trial negotiations.
- Lok Adalats: Informal people's courts that resolve disputes without legal technicalities.
- Recent Developments: The Arbitration and Conciliation (Amendment) Bill (2021) addresses misuse, and the Mediation Bill (2021) recommends changes.
What Can Be Done to Make Khap Panchayat a Part of Formal ADR?
- Promote Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR): Integrating Khap Panchayats into the formal ADR system by legalising their mediatory roles within a framework aligned with constitutional principles.
- Offer training to Khap leaders on mediation and arbitration techniques to enhance their capability for impartial dispute resolution.
- Legal Regulation: Formulate laws to define the scope and limitations of Khap Panchayat activities, ensuring decisions align with Indian laws and human rights.
- Set up oversight mechanisms to monitor their actions, preventing unconstitutional practices like honour killings or forced marriage annulments.
- Shift Focus to Development: Some Khap leaders advocate for progressive stances, addressing social and economic challenges like unemployment, education, and rural development.
- Efforts are underway to modernise or regulate Khap Panchayats, including integrating them into formal dispute resolution systems.
- Awareness and Accountability: Create public awareness campaigns to educate communities on the importance of constitutional rights and the legal system.
- Hold Khap Panchayats accountable for actions that undermine justice or equality.
- Collaboration with Formal Institutions: Facilitate partnerships between Khap Panchayats and local governance bodies to create inclusive decision-making structures.
- Involve judiciary representatives to ensure their decisions are legally sound.
Conclusion
Khap Panchayats, while deeply rooted in tradition, must evolve to function as effective tools of Alternative Dispute Resolution. By aligning their practices with constitutional values, fostering community development, and embracing reforms, they can retain cultural significance while contributing positively to rural governance. Transitioning Khaps into ADR bodies will require legal regulation, community awareness, and strong oversight to ensure justice, equity, and harmony in society.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What are the advantages of Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR). How can integrating Khap Panchayats into the ADR system help alleviate the burden on India’s judicial system? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Prelims:
Q. With reference to National Legal Services Authority, consider the following statements: (2013)
- Its objective is to provide free and competent legal services to the weaker sections of the society on the basis of equal opportunity.
- It issues guidelines for the State Legal Services Authorities to implement the legal programmes and schemes throughout the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)
Mains:
Q. Khap Panchayats have been in the news for functioning as extra-constitutional authorities, often delivering pronouncements amounting to human rights violations. Discuss critically the actions taken by the legislative, executive and judiciary to set things right in this regard. (2015)