Social Justice
Recognising the Heterogeneity of Northeast India
- 03 Oct 2023
- 6 min read
For Prelims: North East India, Indo-Chinese Mongoloid racial grouping, Indigenous Communities, Social Cohesion.
For Mains: Recognising the Heterogeneity of Northeast India.
Why in News?
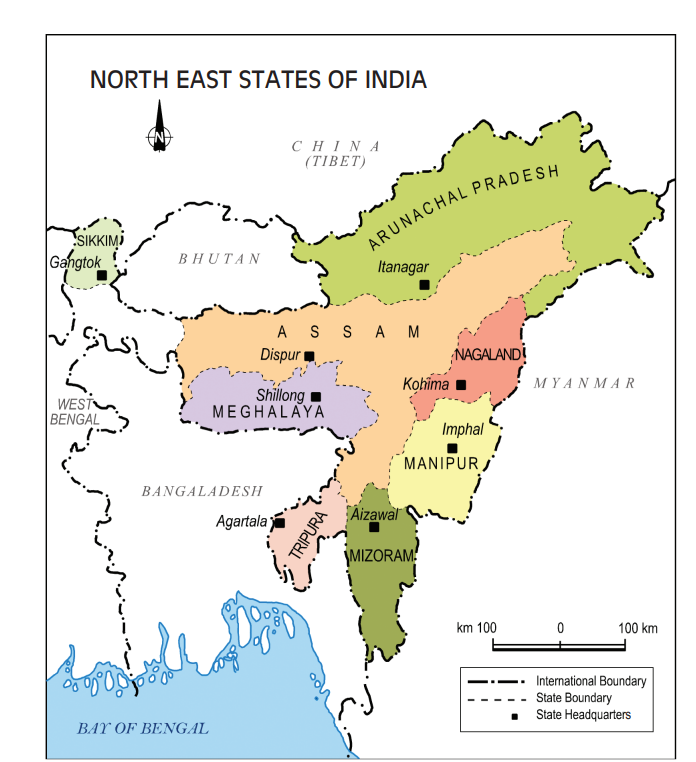
The Northeast region is home to numerous ethnic communities who have migrated from “all points of the compass, making it important to reject a singular Northeast identity and emphasizing its rich linguistic, cultural, and ethnic diversity.
What is the Ethnic Composition of the North-East?
- Ethnic Composition:
- The region is home to numerous ethnic communities, predominantly belonging to the Indo-Chinese Mongoloid racial grouping.
- Northeast India is known for its diverse population, which is made up of over 200 different ethnic groups, each with its own distinct culture and traditions.
- Some of the major ethnic groups in the region include the Assamese, Bodos, Nagas, Mizos, Khasis, Garos, and Arunachalis.
| State | Ethnic Groups |
| Arunachal Pradesh | Adis, Nyishi, Apatani, Tagin, Mismi, Khampti, Wancho, Tangsha, Monpa, etc. |
| Assam | Barmans, Bodos (Bodokacharis), Deori, Hojai, Sonowal Kacharis, Miri (Mising), Dimasa, Hajong, etc. |
| Meghalaya | The Khasis, the Garos, Jaintias, etc . |
| Manipur | Meities, Nagas, Kukis and Chins, Meitei Pangals (Meitei –Muslims) etc. |
| Mizoram | Lushei, Ralte, Hmar, Paite, Pawis (formerly known as Lais), etc. |
| Nagaland | Angami, Ao, Chang, Chiru, Phom, Rengma, Sangtam, Sema, Zeliang, etc. |
| Tripura | Tripuri, Reang, Chakma, Halam, Garo, Lusei, Darlong, etc. |
| Sikkim | Nepalis, Bhutias, Lepchas, etc. |
- The region is also home to several indigenous communities that have managed to preserve their way of life, despite the rapid modernization taking place in other parts of India.
- These communities include the Apatanis of Arunachal Pradesh, who practice a unique form of agriculture that involves cultivating rice on terraced fields, and the Khasi people of Meghalaya, who have a matrilineal society where women inherit property and have a central role in decision-making.
- Need for Rejecting Homogeneity of the Region:
- The tendency to homogenize the Northeast into a single category is a fallacy that overlooks the intricate fabric of its society.
- Such a view not only oversimplifies the reality but also perpetuates misunderstanding and misrepresentation.
- Each state within the Northeast holds a distinct cultural heritage, language, and historical narrative.
- By rejecting a monolithic identity of the region one can delve into the unique characteristics of each state and community, appreciating the richness that this diversity brings.
Why is it Important to Recognise Heterogeneity of the North-East?
- Preserving Cultural Heritage:
- The diverse cultural tapestry of the Northeast is a testament to the historical roots and practices of its various communities.
- From the vibrant festivals of Assam to the ancient traditions of Sikkim, each culture offers a unique perspective on life, values, and beliefs. Preserving and celebrating this heterogeneity ensures the safeguarding of these cultural legacies for future generations.
- Linguistic Identity:
- Northeast region is home to a plethora of languages, each representing the nuanced worldview of its speakers.
- By recognizing this linguistic heterogeneity, the distinctiveness of these languages and the communities that speak them can be honored.
- Social Cohesion:
- Acknowledging the diversity within the Northeast promotes social cohesion and inclusivity.
- It encourages a sense of unity amid differences, enabling a more harmonious coexistence. By understanding and appreciating the distinct backgrounds and experiences of various communities, social integration is enhanced, contributing to a stronger, united nation.
- Tailored Policies for Development:
- A one-size-fits-all approach is ineffective and unfair, hampering the region's progress.
- Tailored policies that consider the unique socio-economic, cultural, and historical contexts can foster sustainable development and growth.
Note: Descriptive Nicknames for Northeast States
- Arunachal Pradesh: Dawn-lit Mountains
- Assam: Gateway to North East
- Manipur: Jewel of India
- Meghalaya: Abode of Clouds
- Mizoram: Land of Blue Mountains
- Nagaland: Land of Festivals
- Sikkim: Himalayan Paradise
- Tripura: Land of Diversity
Conclusion
- To truly understand and appreciate this remarkable diversity, it is imperative to reject a singular Northeast identity and embrace the heterogeneity that defines the region.
- Only by doing so can we craft inclusive policies, celebrate unique cultural legacies, and foster social unity, paving the way for a more harmonious and prosperous society.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2013)
| Tribe | State | |
| 1. | Limboo (Limbu) | Sikkim |
| 2. | Karbi | Himachal Pradesh |
| 3. | Dongaria Kondh | Odisha |
| 4. | Bonda | Tamil Nadu |
Which of the above pairs are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)