RBI to Review NBFCs | 22 Mar 2024
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is gearing up to conduct a comprehensive review of the categorisation of Non-Banking Finance Companies (NBFCs) in 2024.
- The review is seen as a precursor to potentially granting bank licences to select NBFCs.
- Elevating specific NBFCs could serve as a preliminary and evaluative step towards considering them for the allocation of bank licences in the future.
What are NBFCs?
- About: An NBFC is a company registered under the Companies Act, 1956 or Companies Act, 2013, involved in various financial activities like lending, investing in securities, leasing, insurance.
- They offer various banking services but do not have a banking licence.
- Key Features:
- NBFCs provide diverse financial services like personal loans, home loans, vehicle loans, gold loans, microfinance, insurance, and investment management.
- They can accept public deposits for a minimum of 12 months and a maximum of 60 months.
- However, NBFCs cannot accept demand deposits.
- They do not form part of the payment and settlement system and cannot issue cheques drawn on itself.
- Classification:
- On the Basis of Deposits:
- Deposit-taking non-banking finance companies
- Non-Deposit taking Non-Banking Financial Institutions
- On the Nature of their Major Activity:
- Investment and Credit Company
- Consumer Durable Loan Finance
- Core Investment
- Company (CIC)
- Infrastructure Finance Company (IFC)/Infrastructure Debt Fund (IDF)
- Asset Reconstruction Companies (ARC)
- Factoring Companies
- Gold Loan Companies
- Fintech cos: P2P Lenders
- On the Basis of Deposits:
- Licencing: The company must be registered under the Companies Act, 2013, either as a public or private company.
- The company should have a minimum net owned fund of at least Rs. 10 crores to be eligible for NBFC registration.
- At least one-third of the directors of the company must possess relevant work experience in the finance sector.
- The company should have a good track record with CIBIL (Credit Information Bureau India Limited) regarding its credit history and financial credibility.
- The company must comply with all the regulations, norms, and guidelines prescribed under Capital Compliances and the Foreign Exchange Management Act (FEMA) laws.
- Regulation: The RBI has been given the powers under the RBI Act 1934 to register, lay down policy, issue directions, inspect, regulate, supervise and exercise surveillance over NBFCs that meet the 50-50 criteria of principal business.
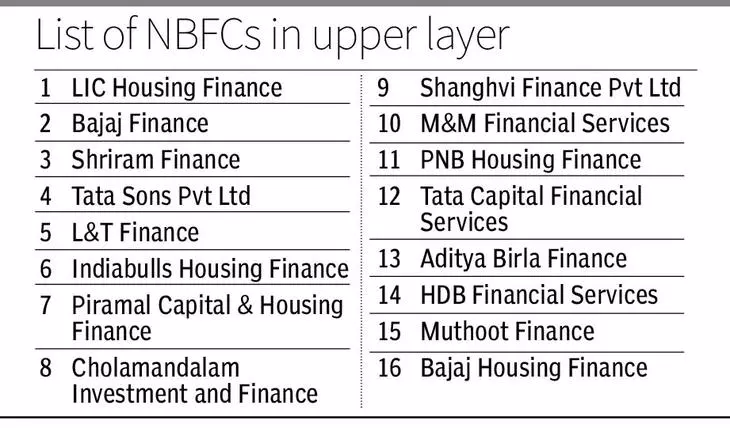
- The Reserve Bank introduced the Scale Based Regulation (SBR) in October, 2021, categorising NBFCs into Base Layer (NBFC-BL), Middle Layer (NBFC-ML), Upper Layer (NBFC-UL), and Top Layer (NBFC-TL).
- This framework outlines the methodology for identifying NBFCs in the Upper Layer based on their asset size and scoring criteria.
What is the 50-50 Criteria of Principal Business?
- RBI considers a company's principal business to be financial in nature if more than 50% of its total assets and gross income come from financial activities.
- This definition ensures that only companies primarily involved in financial operations are registered as NBFCs and fall under RBI's regulatory oversight.
- Companies primarily engaged in non-financial activities, even if they conduct some financial business on the side, are not regulated by RBI.
- This assessment is commonly referred to as the "50-50 criteria" for determining a company's involvement in financial business.
Note
Demand deposits refer to funds deposited in banks or financial institutions that can be withdrawn by the account holder on demand without any prior notice.
- They are highly liquid and accessible for day-to-day transactions, making them a preferred choice for individuals and businesses needing frequent access to their funds.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to the Non-banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) in India, consider the following statements: (2010)
- They cannot engage in the acquisition of securities issued by the government.
- They cannot accept demand deposits like Savings Account.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)