RBI to Review Framework on Liquidity Coverage Ratio | 09 Apr 2024
Why in News?
The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) is likely to review the framework on Liquidity Coverage Ratio for better management of liquidity risk by banks.
- Recent incidents in certain jurisdictions, like Silicon Valley and Signature Bank in the US, have shown the potential for quick fund withdrawals through digital banking channels during stressful times.
- The RBI Governor highlighted the need to reevaluate the LCR framework in response to these emerging risks.
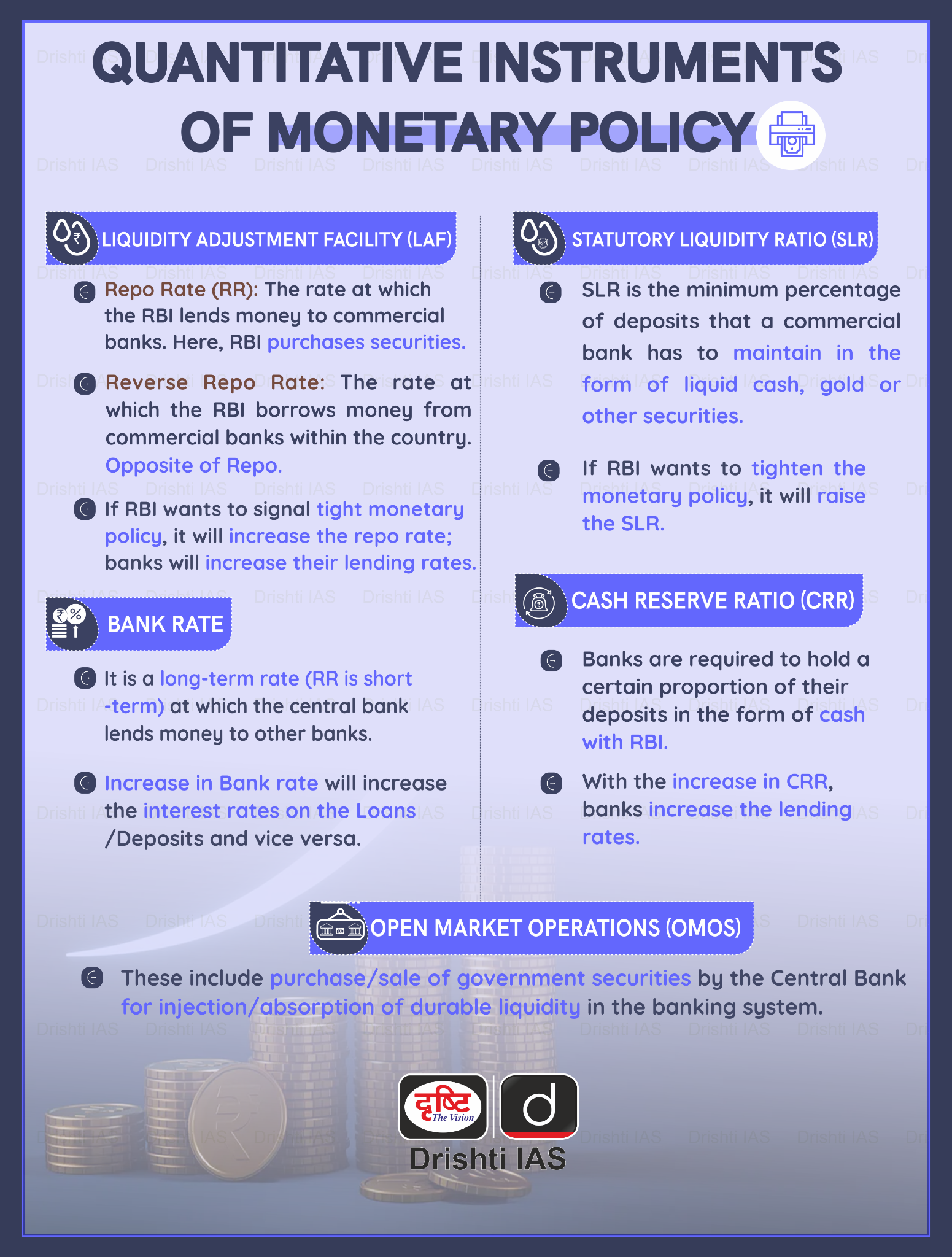
What is the Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR)?
- The LCR was introduced as part of the Basel III reforms following the 2008 global financial crisis.
- The LCR is a ratio that measures the proportion of high-quality liquid assets (HQLA) that financial institutions hold.
- Banks covered under the LCR framework must maintain a stock of HQLA to cover 30 days' net outflow under stressed conditions, with a minimum LCR of 100% since 1st January 2019.
- HQLA are liquid assets that can be sold immediately or converted to cash at little or no loss of value. HQLA can also be used as collateral for borrowing purposes.
- HQLAs include cash, short-term bonds, and other cash equivalents, as well as excess Statutory Liquidity Ratio (SLR), Marginal Standing Facility (MSF) assets and the Facility to Avail Liquidity for Liquidity Coverage Ratio (FALLCR) (set at 15% of the bank's deposits since 1st April 2020).
- The LCR is a preventive measure that can be beneficial for a bank during a financial crisis.
- Limitation: The LCR may lead to banks holding more cash and issuing fewer loans, potentially slowing economic growth.
- Status of LCR: Scheduled Commercial Banks currently maintain an LCR of 131.4%, significantly above the minimum requirement of 100%.
|
LCR = High-Quality Liquid Asset Amount (HQLA) / Total Net Cash Flow Amount |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)? (2017)
- It decides the RBI’s benchmark interest rates.
- It is a 12-member body including the Governor of RBI and is reconstituted every year.
- It functions under the chairmanship of the Union Finance Minister.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Ans: (a)
Q. If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following would it not do? (2020)
- Cut and optimize the Statutory Liquidity Ratio
- Increase the Marginal Standing Facility Rate
- Cut the Bank Rate and Repo Rate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)