Rapid Fire Current Affairs | 01 Apr 2023
OBCs & The Current Conflict
A nationwide campaign is taking place against an MP due to his remarks against the Other Backward Classes (OBCs) following which he has also been convicted of defamation and was disqualified from Parliament.
The Kalelkar Commission (1953), was the first to identify backward classes other than the SCs and STs at the national level. Based on the recommendation of the Second Backward Classes Commission (Mandal Commission), the Government of India in August 1990 had notified 27% reservation for Socially and Educationally Backward Classes (SEBCs) (or OBCs) in vacancies for civil posts and services that are to be filled on direct recruitment.
After this was challenged, the Supreme Court in November, 1992 (Indira Sawhney case) upheld 27% reservation for OBCs, subject to exclusion of the creamy layer.
The Justice Rohini committee was constituted in 2017 to submit its report on Sub-categorisation of Other Backward Classes (OBCs). The committee is yet to submit its report.
Read More: Defamation Law and Disqualification of MPs, Indira Sawhney Judgment (1992)
Rhino Poaching Cases in Assam
After zero cases of rhinoceros poaching were recorded in Assam in 2022, the first such case was reported recently. In 2021, the Assam Government constituted an Anti-Poaching Task Force.
There are five species of rhino – white and black rhinos in Africa, and the greater one-horned, Javan, and Sumatran rhino species in Asia.
Only the Great One-Horned Rhino is found in India. Also known as the Indian rhino, it is the largest of the rhino species. It is identified by a single black horn and a grey-brown hide with skin folds. The species is restricted to small habitats in Indo-Nepal terai and northern West Bengal and Assam. The Great One-Horned Rhino is listed as Vulnerable in IUCN Red List, mentioned in Appendix I in CITES and in Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972.
Read More: Rhinos and Protect Areas in Assam, Infographic on Rhino
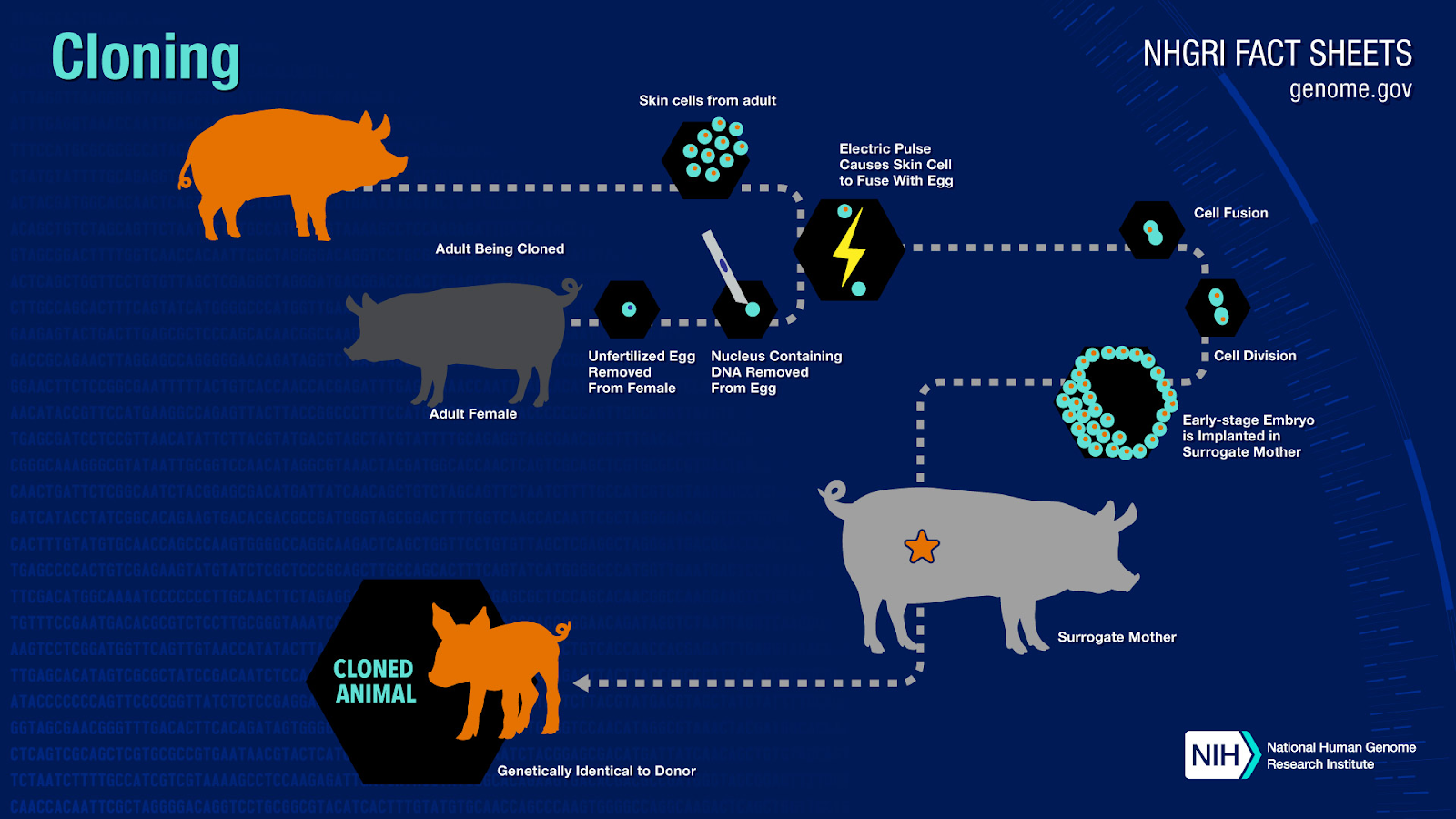
India's First Cloned Female Calf
Due to the government push for increasing milk production, the National Dairy Research Institute (NDRI), Karnal, Haryana has produced the India's first cloned female calf of the desi breed Gir.
Under a project by NDRI, the state will work on cloning of indigenous cow breeds such as Gir and Sahiwal. Indigenous cattle breeds such as Gir, Sahiwal, Tharparkar, and Red-Sindhi, play a pivotal role in milk production and the growth of the Indian dairy industry.
Gir cattle are also very popular and have been exported to Brazil, the United States, Mexico, and Venezuela for the development of zebu cows.
The term cloning describes a number of different processes that can be used to produce genetically identical copies of a biological entity. The copied material, which has the same genetic makeup as the original, is referred to as a clone.
Read More: India’s Dairy & Livestock Sector
AFINDEX-2023
The 2nd edition of the joint military exercise “the Africa-India Field Training Exercise (AFINDEX-2023)” concluded recently in Maharashtra. The strategically significant India-Africa Army Chiefs Conclave was also hosted in Pune.
The exercise was held from 16 to 29 Mar 2023. A total of 25 nations of the African continent with 124 participants and Indian troops from the Sikh, Maratha and Mahar Regiments participated in the multinational exercise.
The multinational military drill was aimed at promoting the idea of Africa-India Militaries for Regional Unity (AMRUT) and focused on incorporating the current dynamics of UN Peacekeeping Forces (UNPKF) through practical and comprehensive discussions and tactical exercises.
Read More: India-Africa Relations