Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
- 17 May 2023
- 11 min read
Dust-Raising Winds and High PM10 Levels: Impact on AQI in Delhi
Recently, Delhi witnessed a surge in Particulate Matter (PM)10 levels with strong winds raising dust and reducing visibility. According to India Meteorological Department(IMD), the dust-raising winds are a result of low rainfall, heating, and gusty winds prevailing over the past few days, with temperatures remaining above 40 degrees Celsius. IMD scientists explained that the high temperatures caused the dry soil to be suspended in the air due to strong winds. The PM10 levels were 19 times higher than the 24-hour standard, and the PM2.5 levels also saw an increase. The 24-hour average Air Quality Index (AQI) for the city was categorized as 'very poor' or 'poor' at most monitoring stations.
Inhalable particulate matter in the air can cause respiratory symptoms such as coughing, and aggravated asthma. The source of dust in summer was attributed to dry conditions and higher wind speeds. The sub-committee for invoking actions under the Graded Response Action Plan (GRAP) met but decided not to invoke any actions as the situation is likely to improve in the next few days.
Read more: Air Quality and Health in Cities
Bangladesh Withdraws "Extra Security Escort" for Diplomats
Bangladesh has decided to withdraw extra security provided to top diplomats from India, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Saudi Arabia, deeming it discriminatory and unnecessary due to the country's well-controlled law and order situation. The decision comes after heightened security measures were implemented following a militant attack in 2016. The foreign minister stated that the current law and order situation does not warrant additional security for specific envoys, suggesting that private security services can be hired if needed. Normal security measures for diplomatic missions, in line with international conventions, will continue to be upheld by the host country.
In the context of diplomatic security, the Vienna Convention on Diplomatic Relations of 1961 plays a significant role. This international treaty establishes the framework for diplomatic relations between independent countries. The convention grants diplomatic agents and missions various privileges and immunities to ensure their effective performance and protection from undue interference by the host state. Article 22 of the convention emphasizes the inviolability of the mission premises, with the receiving state having the duty to protect them against any intrusion or damage. Furthermore, Article 29 highlights the inviolability of the person of a diplomatic agent, with the receiving state being obligated to treat them with respect and prevent any attack on their person, freedom, or dignity. The convention also grants diplomatic agents immunity from criminal jurisdiction. However, it also mandates that diplomatic agents respect the laws and regulations of the receiving state and refrain from interfering in its internal affairs. These provisions ensure the security and functioning of diplomatic missions and personnel.
Read more: Vienna Convention
Indigenous Dengue Vaccine Trials in India
Serum Institute of India and Panacea Biotec, two prominent drug manufacturers, have taken a significant step towards developing India's first vaccine against dengue. They have submitted applications to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) in response to the 'Expression of Interest' for collaborative Phase-III clinical trials for indigenous manufacturers. Phase-III trials are conducted to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity of the tetravalent dengue vaccine candidate developed by Indian manufacturers.
Dengue virus disease poses a substantial health burden globally, with India reporting 2 to 2.5 lakh cases annually. The World Health Organization (WHO) has recognized dengue as one of the top ten global health threats. Presently, there is no specific treatment for dengue, underscoring the urgent need for effective vaccines.
Dengue is a mosquito-borne tropical disease caused by the dengue virus (Genus Flavivirus), transmitted by several species of female mosquito within the genus Aedes, principally Aedes aegypti. This mosquito also transmits chikungunya, yellow fever and Zika infection.
Read more: Dengue
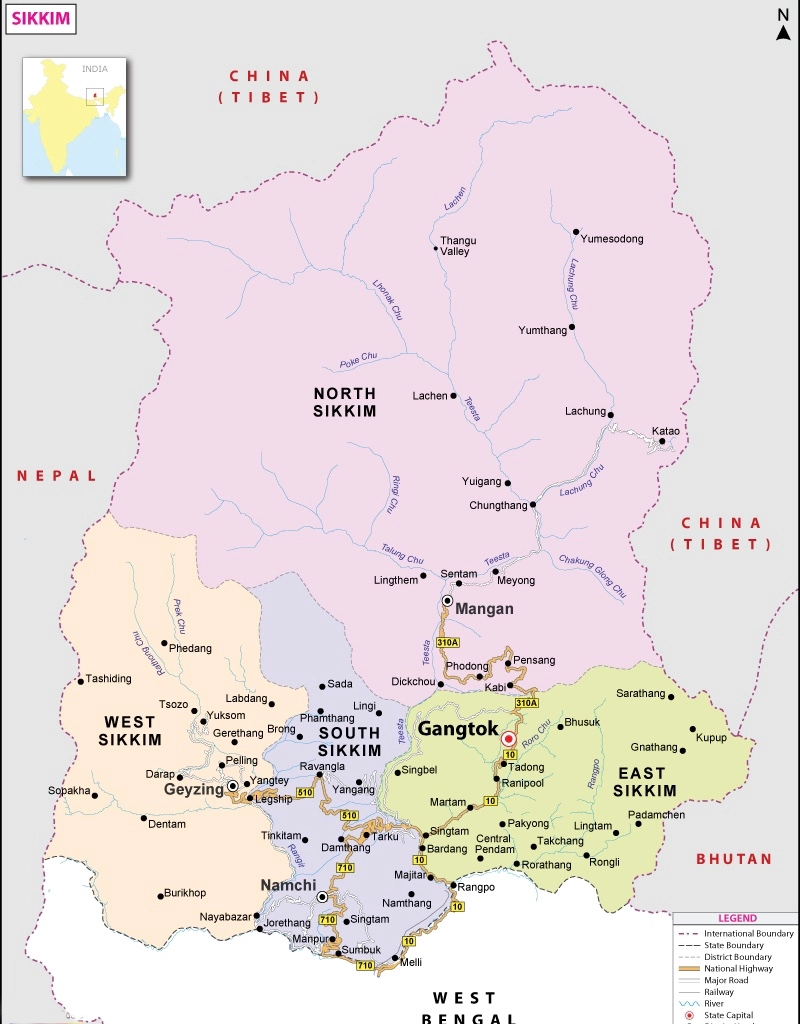
Sikkim's Statehood Day
On the occasion of Sikkim's Statehood Day, Prime Minister extended his greetings to the people of Sikkim. Celebrated annually on May 16, this day marks the acknowledgment of Sikkim's integration with India and its establishment as the 22nd state of the country in 1975.
The formation of the state of Sikkim came about through the 36th Amendment of the Indian Constitution. Sikkim has a rich history that dates back to the 17th century when the Namgyal dynasty founded the Kingdom of Sikkim. It is a former British protectorate, maintained its administrative independence under the Chogyal rulers. After India's independence, Sikkim continued as a protectorate with India overseeing its external relations, defense, and communications. However, in 1973, the people's agitation led to changes in governance. The Chogyal became a titular figure, and Sikkim was designated an "associated state." In 1975, Sikkim was granted statehood, integrating it into India and abolishing the monarchy on May 16.
Sikkim is bordered by the Tibet Autonomous Region of China to the north and northeast, by Bhutan to the southeast, by the Indian state of West Bengal to the south, and by Nepal to the west.
Mount Kanchenjunga, India’s highest peak and the world’s third highest mountain lies in Sikkim.The Kanchenjunga National Park (KNP) (established in 1977), near the peak is among the largest of India’s high-elevation conservation areas. KNP was designated a World Heritage Site in 2016 under the ‘mixed’ category (sites containing elements of both natural and cultural significance). Sikkim is drained by the Teesta river and its tributaries such as the Rangit, Lhonak, Talung and Lachung. Teesta river water conflict is one of the most contentious issues between India and Bangladesh.Teesta river is a tributary of Brahmaputra River.
Read more: Sikkim's Statehood Day
National Federation Cup Senior Athletics Championships 2023
The 26th Edition of National Federation Cup Senior Athletics Championships is going at Birsa Munda Stadium, Ranchi (Jharkhand) from 15 May 2023. The Competition is organized in Men and Women section. It is a domestic tournament of the Indian athletics season. It is organised by the Athletics Federation of India (AFI). Some of the Events are Jumps; throws- shot put, discus throw, javelin throw; Sprinting Events etc.
The AFI is the apex body for running and managing athletics in India and affiliated to the International Amateur Athletic Federation (IAAF), Amateur Athletic Association (AAA) and Indian Olympic Association. The AFI has as many as 32 affiliated state units and institutional units. The AFI came into existence in 1946 and the federation organises the National Championships, trains the Indian Athletics National Campers and selects the Indian Athletics Teams for various international competitions, including the Olympics, Asian Games, World Championships, Asian Championships and other international meets.
ICC Implements Changes to Playing Conditions
The International Cricket Council (ICC) has made some changes to the playing conditions of cricket matches. One of the major changes is that the 'soft signal' by on-field officials has been scrapped. According to ICC rules, a soft signal is the visual communication by the bowler's end umpire to the third umpire of his/her initial on-field decision prior to initiating an Umpire Review. This signal was used to determine whether catches taken inches off the ground were valid or not. It was often criticized by experts for creating more confusion, and the TV umpire found it difficult to make decisions based on this signal.
Another significant change is that helmets are now mandatory for high-risk positions, including batters facing fast bowlers, wicketkeepers standing up to the stumps, and fielders standing close to the batter in front of the wicket. Additionally, there has been a minor addition to the free hit rule, which states that any runs scored off a free hit when the ball hits the stumps will be counted as runs scored. These changes will come into effect on June 1st, 2023, with the Lord's Test between England and Ireland being the first match to follow the new rules. The ICC made these changes after the Cricket Executive Committee approved the recommendations from the men's and women's cricket committees.
ICC is the global governing body for cricket. Representing 104 members, the ICC governs and administers the game and works with its members to grow the sport. It has its headquarters in Dubai, UAE.